We suspect the market is underestimating the impact that S&P Global's Jennifer Gnana, Kelly Norways, and Mohammed Al-ansare detail below,
The Red Sea Situation Is Worse Than It looks
Under-Appreciated Risks Of The Red Sea Crisis
- Aside from the increased costs to global shipping, and the risk of America getting into a shooting war in the Mideast, there are some additional, under-appreciated risks.
Is The Market Paying Attention?
Although Zero Hedge has been covering this issue prominently, mainstream financial media hasn't been.
What Happens To Egypt?
Our friend Aristophanes makes a good point in his long post on the Red Sea situation, that to the extent Iran is arming the Houthis, who are driving shipping traffic away from the Suez Canal, Iran can exert leverage on Egypt in ways that can make the Israel-Gaza war worse.
Here's the key part:
A massive share of Egypts income comes from the Suez Canal. This broke a record in 2022 at 9.4 billion USD, which is almost 30 percent of their annual revenue. If the Suez is closed, they aren't making money.
The Egyptian Government is also stressed from multiple angles.
- They have a refugee crisis on their border with Sudan, but particularly topical right now is their land border with Gaza.
- The Rafah Crossing is the only link into Gaza that is not controlled by Israel. Iran having a quarter of the Egyptian economy by the balls unless the US intervenes, means Iran has leverage over what gets into Gaza.
- If you use your imagination, this could include anything from chemical weapons in Syria, to a dirty bomb or even a nuclear weapon from Iran being not beyond the realm of the possible.
- This is a nightmare scenario for the US because such an event might force a more tangible military commitment in the region than we already have.
Can South Africa Even Handle The Increased Cape Traffic?
Ernst van Zyl, the head of public relations at Afriforum, points out that South Africa's port infrastructure has trouble handling its current shipping traffic.
While The Market Ignores This
So far, the market seems unperturbed by the worsening situation in the Red Sea. We've been taking advantage of the current calm to place a few short term technical trades on names that look poised for breakouts in the near term. We placed two yesterday, and have one teed up for later today. If you'd like a heads up when we place it, feel free to subscribe to our trading Substack/occasional email list below.
'Operation Prosperity Guardian' - Pentagon Launches Expansive Naval Coalition To Defend Red Sea Passage
Update(1150ET): A US-led naval coalition is finally coming together to protect international shipping transit in the Red Sea and vital Bab al-Mandab Strait, per a breaking development from Politico's chief Pentagon correspondent: "The Pentagon is expected to announce tomorrow the formation of Operation Prosperity Guardian, a new task force to protect shipping from Houthi attacks in the Bab Al-Mandeb Strait and Red Sea, per DOD official," writes Lara Seligman on X.
"The operation will be within the framework of the existing Combined Maritime Force 153, a partnership of 39 nations focused on counter piracy and counter terrorism in the Red Sea."
Soon after this reporting, Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin said, "I am announcing the establishment of Operation Prosperity Guardian, an important new multinational security initiative under the umbrella of the Combined Maritime Forces and the leadership of its Task Force 153, which focuses on security in the Red Sea."
Just hours ago, we reminded readers of Zoltan Poszar's prediction of central-bank-analogized 'military protection' and said it's soon to become a reality... and just like that, it has:
Protection is a conceptual counterpart to par. When you decide to take money out of a sight deposit, you expect the same amount back that you put in (par).
When you sail foreign cargo from port A to port B, you expect to unload the same amount of cargo that you onloaded.
Banks can deliver par on deposits most of the time. When not, central banks step in to help.
Commodity traders can deliver foreign cargo from port A to port B most of the time, but when not, the state intervenes again: not the monetary arm, but the military arm of the state.
What central banks are to the protection of par promises, the military branch is to the protection of shipments: foreign cargo needs to sail on sea routes and through choke points like the Strait of Hormuz, and “par” in this context means being able to sail from here to there freely, safely, and without undue delays…
It has also emerged that Australia is expected to play a major role in Red Sea operations in the context of deepening ties with the US related to the AUKUS deal.
Rabobank explains in the following...
- This request comes just days after Congress passed laws enabling the sale of Virginia class submarines to Australia under the terms of the AUKUS pact.
The agreement marks just the second time that the United States has shared nuclear secrets with another country (on purpose, at least), so it appears that there is an element of “I scratch your back, you scratch mine” going on here. This is not without its complications, as many members of Australia’s political establishment (particularly within the ruling Labor Party) still cling to dreams of ‘strategic autonomy’ of the kind that doesn’t even work for Europe.
Their fear is that AUKUS, and an Australian warship shooting down drones in the Red Sea, further locks Australia in as an organ of US foreign policy, which it probably does. But really, this is par for the course and probably just the modern incarnation of Australia’s long-running policy of having ‘great and powerful friends’.
Quite aside from the diplomatic horse-trading that accompanies it, disruption of shipping in the Red Sea is a big problem, and Europe has the most to lose. 150 years of supply chain improvement risks being unwound as major shipping companies redirect vessels around the Cape of Good Hope to avoid traversing the region to pass through the Suez Canal into the Mediterranean.
* * *
Amid further attacks and reroutings...
...we look at the true scale of the Houthi attacks on MidEast tankers.
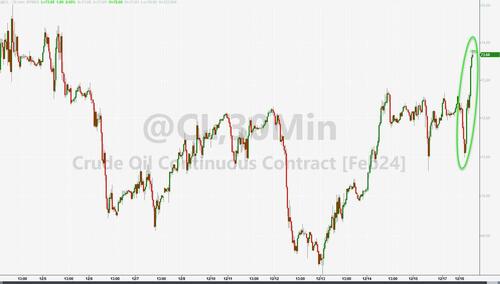
Oil prices are rising...
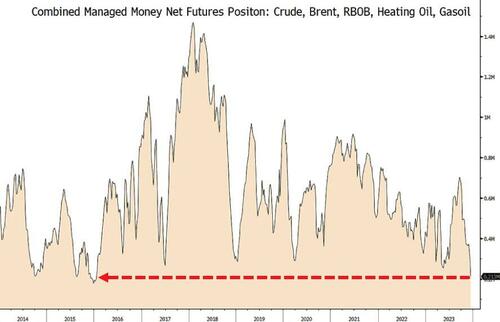
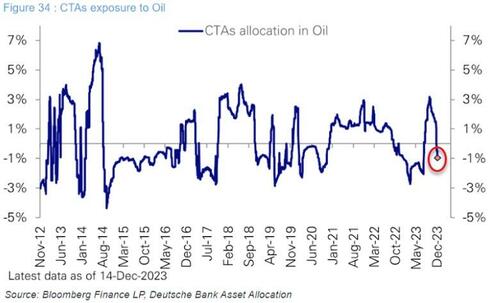
And given the extreme positioning in managed money...
And CTAs swinging short...
We suspect the market is underestimating the impact that S&P Global's Jennifer Gnana, Kelly Norways, and Mohammed Al-ansare detail below,
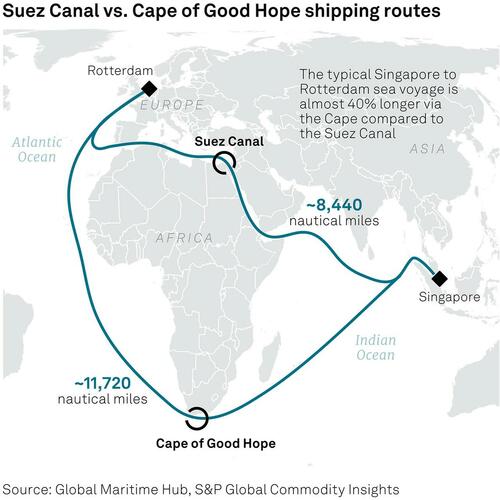
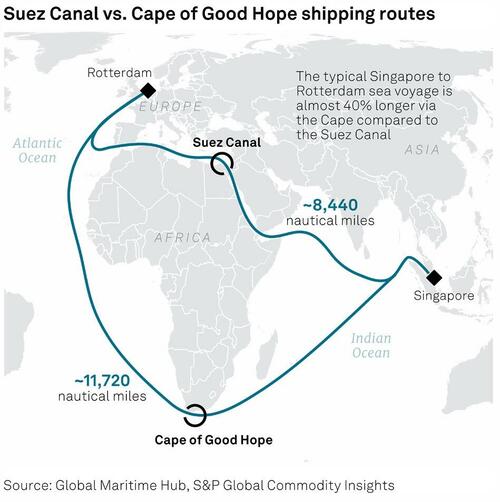
Cape transport option adds 40% to voyage distance
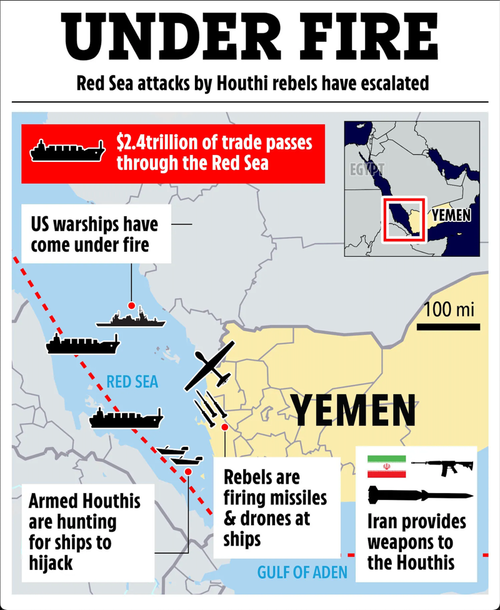
Houthis targeting tankers, container, cargo shipping
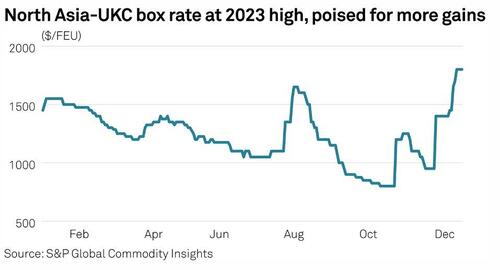
Container rates rise to 2023 high
Major shipping companies paused transiting the Middle East's critical Bab al-Mandeb chokepoint for seaborne trade Dec. 15 after repeated attacks by Yemen's Houthi militants threatened to upend global trade flows.
Danish shipping giant A.P Moller-Maersk -- which accounts for 15% of the global container freight market -- suspended voyages passing through the Bab al-Mandeb until further notice. Hapag-Lloyd -- which controls 7% of the container market -- also paused traffic through the Red Sea until at least Dec. 18 after one of its ships was attacked by Houthis.
Hapag-Lloyd's Liberia-flagged Al Jasrah containership caught fire in the Red Sea on Dec. 15 after being hit by a missile from Houthi rebels in Yemen. The attack came a day after the Houthis attacked the Maersk ship Gibraltar on Dec 14 in a near-miss by a cruise missile.
The suspensions are the latest sign major ship charterers who in recent weeks have deployed armed guards to safeguard transit through Bab al-Mandeb are beginning to reconsider using the narrow strait through which 10% of global seaborne oil flows.
The Houthis have threatened to attack any ships with Israeli ownership or bound for one of the country’s ports. As a result, all commercial ships have come under attack, from car carriers to tankers and dry bulkers, including many with no obvious connection to Israeli trade.
"The pattern I see [in the] last few days is more attacks on all these container line big boys like MSC, Maersk, NYK Line, Hapag-Lloyd. If you scare them, then you stop hundreds of their ships," Luv Menghani, a shipbroker with Dubai-based BluePeak Commodities and Shipping, said.
Maersk's instruction to its ships to avoid the Red Sea "suggests an escalation in the response to the Houthi attacks," Gregory Brew, an analyst with Eurasia Group, said.
"Yesterday's attacks suggest the Houthis are broadening their attacks are becoming more indiscriminate, rather than focusing just on ships owned by Israeli companies or bound for Israeli ports," he added.
Trade Flows
- It accounted for 8.8 million b/d of total oil flows in the first half of 2023, according to the US Energy Information Administration.
- LNG shipments through the strait were 4.1 billion cf/d during the same period, EIA data showed.
The suspension of the Red Sea route by the two shipping companies followed a notice to their fleets on Dec. 14 to use the longer Cape of Good Hope as an option, a move that adds 40% to the voyage distance.
The ongoing conflict in the Middle East had already caused some carriers in the past few weeks to avoid the Suez Canal in the interest of security, with the accumulation of attacks from Yemeni rebels leading liner companies to re-route ships via the Cape of Good Hope (CGH) to avoid hostilities impacting container ship traffic in the Red Sea.
According to live AIS data tracking from S&P Global Commodities at Sea, Eastbound vessels MSC Diana and Zenith Lumos have traveled via the Cape of Good Hope as of Dec. 12, having trans-shipped in Tangier and Algeciras respectively.
On Westbound trade, the Maersk Camden, Maersk Campton and MSC Virgo have all diverted via the CGH, despite recent historical vessel tracking showing previous movements have been through the Red Sea and the Suez Canal.
With the Maersk and Hapag-Lloyd announcement, other carriers could be primed to follow suit in making public their stance against further Red Sea shipments whilst the situation is still volatile.
"Despite the complications it would cause with our shippers in terms of delivery and transit times, what is most important is the dialogue we have with our crew in our ships," a carrier source told S&P Global Commodity Insights.
War risk
Freight forwarders are also increasing rates on shipments. For example, a container bound for the Middle East will now attract a war risk surcharge of $100/teu on dry and reefer cargo, according to a document seen by S&P Global.
Several carriers have begun to accrue war risk surcharges on passages through the Red Sea. Zim Integrated Shipping Services (Zim) -- an Israeli carrier based in Haifa -- has increased freight rates on its Asia-Mediterranean service to cover the rising costs of securing its vessels.
Container rates for key shipping lanes from North Asia westbound will likely be given increased support should more carriers follow suit. An estimated additional 10-15 days for delivery times could be seen in the market, stripping out already weak supply due to carriers pursuing aggressive blank sailing strategies in the build-up to the Lunar New Year period where demand increases.
Container rates for shipments from North Asia to the UK -- a route which uses the Red Sea and Suez Canal -- have hit record highs for 2023, according to assessments by S&P Global Platts.
The recent surge in attacks on the oil product tanker and container vessels moved the needle on oil prices. Platts-assessed Dated Brent up at $77.085/b on Dec. 15, up just under 1% on week.
Vandana Hari, founder of Singapore-based Vanda Insights said "shipping will often be the canary in the coalmine" with geopolitical tensions set to remain center-stage for 2024.
LPG flows
The threat to shipping has also impacted charterers bound on shorter routes for Yemen.
Sources told S&P Global that ship charterers contracted to deliver liquefied petroleum gas to Yemen -- which has increased shipments of the fuel -- are reluctant to set sail due to fear of attack.
For example, an LPG vessel carrying a 44,000-ton cargo bound for Yemen and chartered by a Dubai-based company recently refused to set sail amid safety concerns from the crew, said the sources.
The crew's refusal to sail to Yemen comes amid an uptick in LPG buying by the war-torn country. Yemen received 46,000 tons of LPG in December, entirely from Iran, according to S&P Global Commodities at Sea. The LPG import is nearly double the volume of the last shipment Yemen received in July, shipping data showed.
With the latest escalation, tanker rates for Yemen are also rising, a shipbroking source said.
"One vessel below 15,000-ton dead weight, old built, transporting gasoline from the UAE to Hodeidah in Yemen used to charge $12,000-$13,000 per day. Now they charge $16,000-$17,000 per day," said the source.
* * *
* * *
Protection is a conceptual counterpart to par. When you decide to take money out of a sight deposit, you expect the same amount back that you put in (par).
When you sail foreign cargo from port A to port B, you expect to unload the same amount of cargo that you onloaded.
Banks can deliver par on deposits most of the time. When not, central banks step in to help.
Commodity traders can deliver foreign cargo from port A to port B most of the time, but when not, the state intervenes again: not the monetary arm, but the military arm of the state.
What central banks are to the protection of par promises, the military branch is to the protection of shipments: foreign cargo needs to sail on sea routes and through choke points like the Strait of Hormuz, and “par” in this context means being able to sail from here to there freely, safely, and without undue delays…



No comments:
Post a Comment