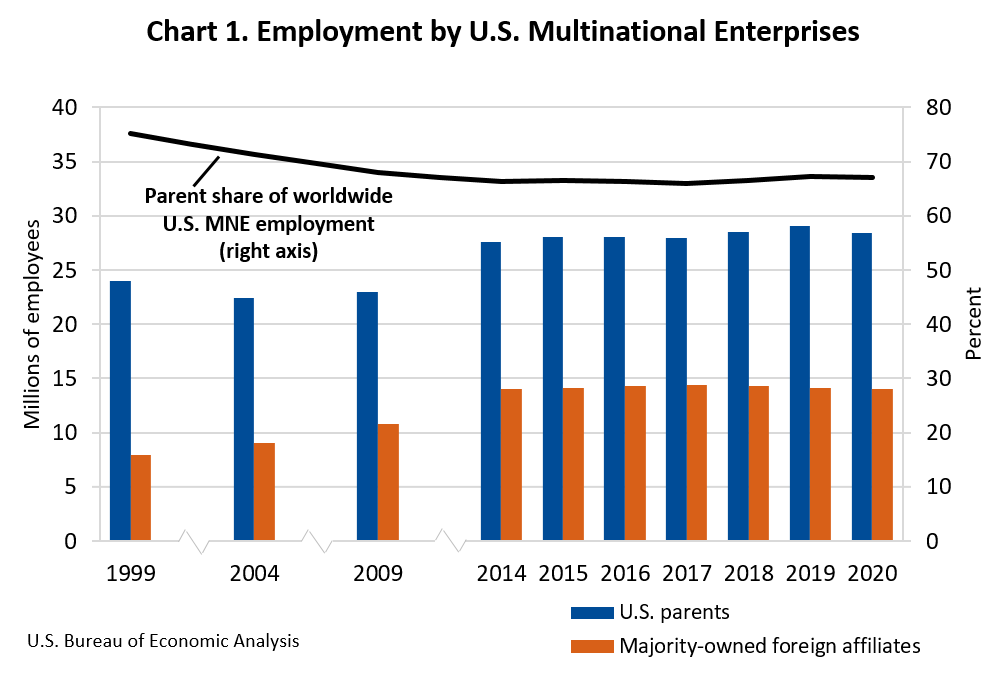
Worldwide employment by U.S. multinational enterprises (MNEs) decreased 1.8 percent to 42.4 million workers in 2020 (preliminary) from 43.2 million workers in 2019 (revised), according to statistics released today by the U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) on the operations and finances of U.S. parent companies and their foreign affiliates.
Employment in the United States by U.S. parents decreased 2.2 percent to 28.4 million workers in 2020. U.S. parents accounted for 67.0 percent of worldwide employment by U.S. MNEs, down from 67.3 percent in 2019. Employment abroad by majority-owned foreign affiliates (MOFAs) of U.S. MNEs decreased 1.0 percent to 14.0 million workers and accounted for 33.0 percent of employment by U.S. MNEs worldwide.
U.S. parents accounted for 23.1 percent of total private industry employment in the United States in 2020, up from 22.1 percent in 2019 as total private industry employment fell more than U.S. parent employment. Employment by U.S. parents was largest in manufacturing and retail trade. Employment abroad by MOFAs was largest in the United Kingdom, India, Mexico, China, and Canada.
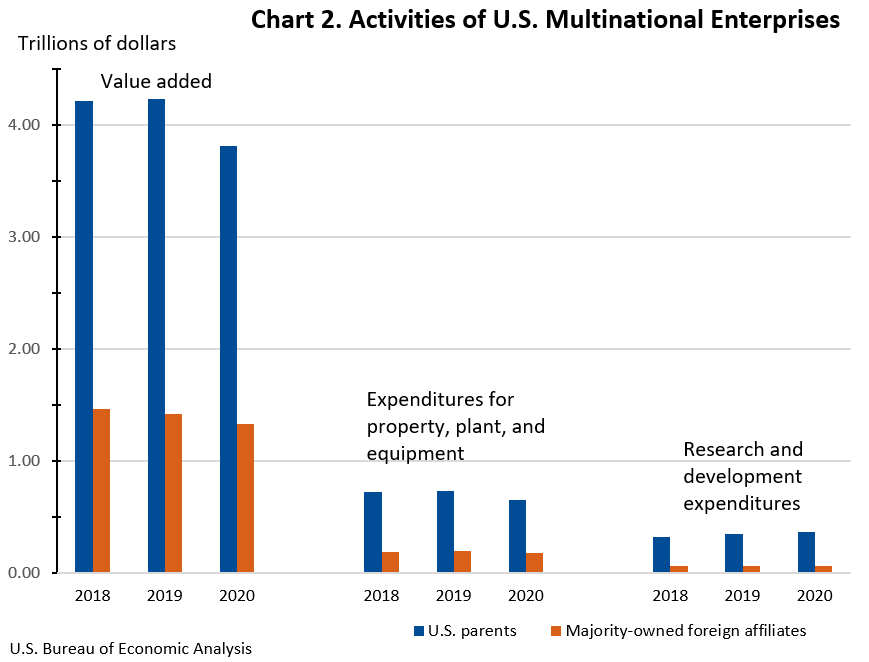
Worldwide current-dollar value added of U.S. MNEs decreased 9.0 percent to $5.1 trillion. Value added by U.S. parents, a measure of their direct contribution to U.S. gross domestic product, decreased 9.9 percent to $3.8 trillion. U.S parents accounted for 20.8 percent of total U.S. private-industry value added, down from 22.6 percent in 2019. MOFA value added decreased 6.4 percent to $1.3 trillion. Value added by MOFAs was largest in the United Kingdom, Canada, and Ireland.
Worldwide expenditures for property, plant, and equipment of U.S. MNEs decreased 9.7 percent to $833.1 billion. Expenditures by U.S. parents accounted for $651.9 billion, and MOFA expenditures accounted for $181.2 billion.
Worldwide research and development expenditures of U.S. MNEs increased 3.2 percent to $420.2 billion. U.S. parents accounted for expenditures of $361.2 billion, and MOFAs accounted for $59.1 billion.
Additional statistics on the activities of U.S. parent companies and their foreign affiliates including sales, balance sheet and income statement items, compensation of employees, trade in goods, and more are available on BEA’s website. More industry detail for U.S. parents and more industry and country detail for foreign affiliates are also available on the website.
Coronavirus (COVID–19) Impact on the 2020 Activities of U.S. Multinational Enterprises
Most of the key indicators included in the U.S MNE statistics decreased in 2020 resulting in part from the impact of COVID–19. The full economic effects of the COVID–19 pandemic cannot be quantified in the statistics because the impacts are generally embedded in source data (BEA direct investment surveys) and cannot be separately identified. The response rates for the surveys were consistent with those in periods before the pandemic. No special adjustments to BEA’s imputation and estimation procedures were necessary.
Updates to the statistics
Statistics for 2019 were revised to incorporate newly available and revised source data. Preliminary statistics for 2019 were released in November 2021 and highlighted in “Activities of U.S. Multinational Enterprises in 2019” in the December 2021 Survey.
| U.S. Parents | MOFAs | |||
| Preliminary estimate |
Revised estimate |
Preliminary estimate |
Revised estimate |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of employees (thousands) | 29,297.3 | 29,075.7 | 14,610.6 | 14,153.8 |
| Value added | 4,234.5 | 4,231.6 | 1,437.0 | 1,416.2 |
| Expenditures for property, plant, and equipment | 738.9 | 731.2 | 205.0 | 191.7 |
| Research and development expenditures | 350.2 | 349.0 | 58.2 | 58.3 |
Next release: November 17, 2023
Activities of U.S. Multinational Enterprises, 2021
.jpg)


No comments:
Post a Comment