- Breaking The New
==========================================================================
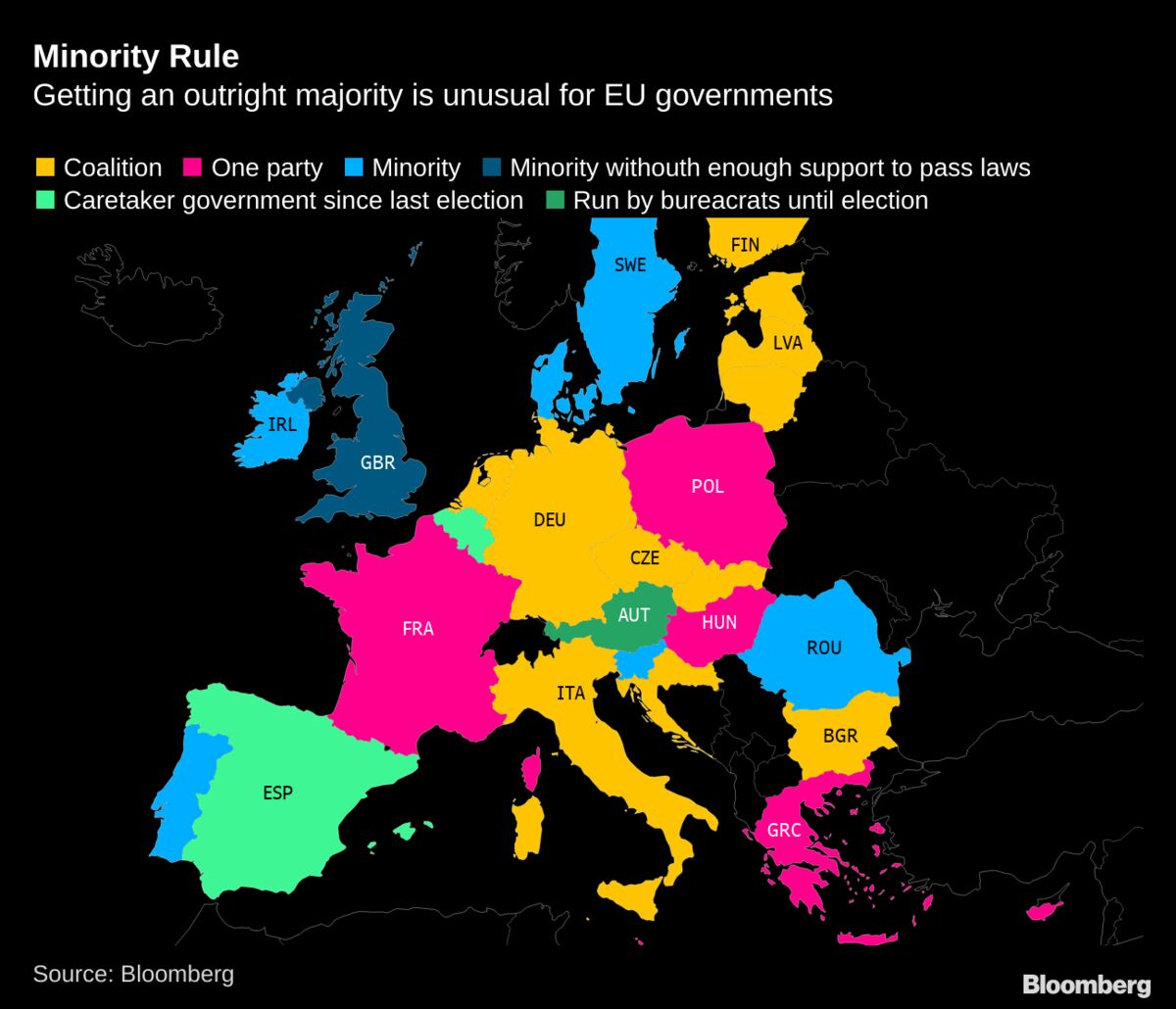
Unstable minority governments in the EU stem from
political fragmentation, where no single party wins a majority, forcing fragile deals, like recent examples in France, Netherlands, Spain, and Portugal,
leading to policy gridlock, frequent elections, and difficulty
addressing major issues like the Ukraine war, weakening EU unity and
global influence, with some external actors like the US Trump
administration criticizing them as failing to deliver stability. > While
some minority governments can be stable with formal support, others
without agreements (substantive minorities) face higher risks of
collapse, a trend amplified by rising populism and internal divisions.
Key Examples of Instability
- France: Recent snap elections resulted in a hung parliament, leading to fragile minority governments struggling to pass legislation amidst far-right gains.
- Netherlands & Spain: Both countries have experienced instability, struggling to form lasting coalitions or minority governments.
- Portugal: Faced multiple elections in a short period, highlighting deep political polarization between center-right, socialists, and the far-right.
- Bulgaria: Severe political polarization between pro-Russia and pro-West factions led to repeated elections and near-constant instability.
Causes of Instability
- Political Fragmentation: Voters are spreading votes across more parties, breaking down traditional blocks.
- Rise of Populism/Far-Right: Parties like Marine Le Pen's National Rally in France gain traction by focusing on issues like immigration, challenging mainstream parties.
- Internal Divisions: Deep ideological divides within countries (e.g., Poland's liberal government vs. conservative President) paralyze policymaking.
Consequences for the EU
- Weakened Unity: Internal crises undermine strategic cohesion and the EU's ability to act as a unified bloc.
- Policy Gridlock: Difficulty passing national legislation slows progress on EU-wide goals and impacts economic/social policy.
- Eroding Global Influence: Unstable governments reduce Europe's credibility and capacity to project power globally.
- External Criticism: Some (like the recent Trump administration) point to these governments as weak, hindering strategic goals like supporting Ukraine.
Types of Minority Governments
- Substantive Minority Governments: Rely on ad-hoc deals; less stable without formal pacts.
- Contract Minority Governments: Have written support agreements with other parties; can be as stable as majority governments.
In
essence, recent years show a trend where fragmented politics and deep
societal divides make stable, effective minority governments a
significant challenge across Europe, impacting both national governance
and the EU's overall strength
===================================================================================
=======================================================================================






No comments:
Post a Comment