- The territory’s Defense Ministry told Bloomberg the military has “multiple backups, with satellite as one of the measures,” but added it doesn’t “comment on details of war preparations.”
With any Starlink deal in limbo, officials are searching for other alternatives, including seeking a workaround to the ownership laws.
Musk Ultimatum to Taiwan Imperils Its Push to War-Proof Internet
The billionaire is pushing for 100% control of any local venture at a time when the island needs a low-Earth orbit satellite network should China invade
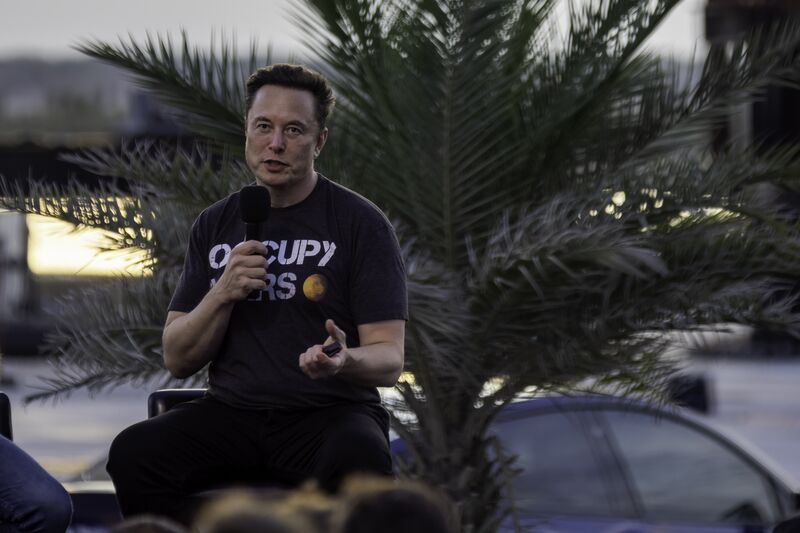
SpaceX founder Elon Musk speaks at an event in Boca Chica, Texas, in August. The company pushed Taiwan to change its local ownership laws before it would consider supplying Starlink satellites.
Photographer: Michael Gonzalez/Getty Images North AmericaAnd as tensions with Asia’s biggest economy increase, Taiwan’s government has been trying to bolster the island’s communications, traveling the globe to find a low-orbit satellite system that could back up connections in the event of a failure.
- Elon Musk and his Starlink network are one clear solution, but there are a few problems, not least of all Taiwan’s distrust of the billionaire, given his deep business ties with China and pro-Beijing comments.
- The Taiwanese and SpaceX began exploratory talks about the satellite supply chain in 2019, but in early 2022, the cordial tenor of those talks changed. Space Exploration Technologies Corp., as SpaceX is formally known, and its representatives in Taiwan began urging government officials to change a law that requires any telecommunications joint venture to have local majority ownership of at least 51%, according to two officials who took part in the meetings. That insistence made Taiwan wary, they said.
- Indeed in China, Tesla Inc.’s most important market outside of the US, the electric carmaker wholly owns its factory in Shanghai, an anomaly in a country where other foreign automakers must have local partners.
- The lobbying also came with an ultimatum: Unless Taiwan agreed to change its ownership rules, the island would get no deal at all.
- While talks have now broken down — SpaceX officials haven’t spoken to Taiwanese government officials since September — Taiwan’s vulnerability, along with Musk’s significant financial stakes in China, are still playing high on many people’s minds.
In February, the territory received a preview of what that might look like, when two subsea internet cables near the Taiwan-controlled Matsu Islands were severed by boats flying Chinese flags. About 14,000 residents spent more than 50 days suffering from painfully slow internet before Taiwan was able to repair the cables.
Taiwan would need to be ready to withstand a much more comprehensive attack on its digital lifelines in the event of a war with China, according to military historian David Silbey, director of teaching and learning at Cornell University’s program in Washington, D.C.
“You cannot fight a conventional war if you cannot communicate with your troops by satellite communications,” he said.
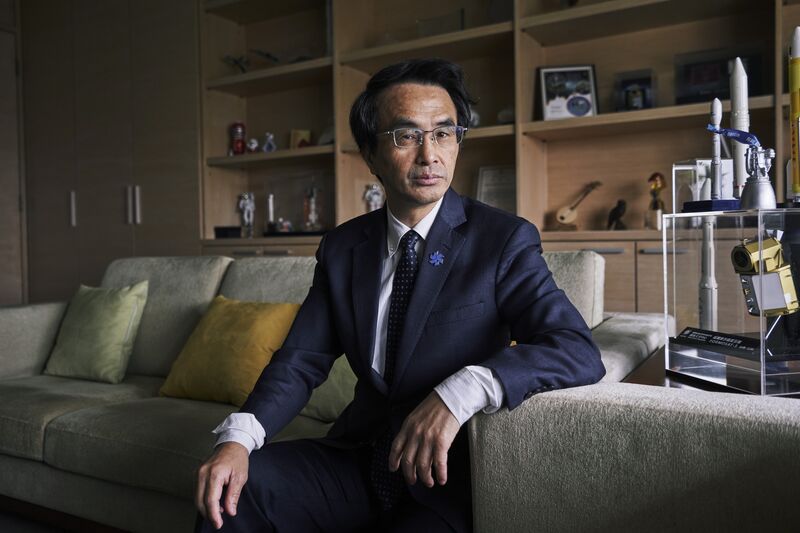
- To address that vulnerability, the Taiwan Space Agency (TASA) intends to launch its first self-made low-Earth orbit communication satellite in 2026 and at least one more by 2028, Director General Wu Jong-shinn said.
- Taiwan also will have rockets capable of carrying payloads weighing over 100 kilograms, he added in an interview.
- “Taiwan’s vision is to launch its homegrown rocket with a self-made satellite, with home-made ground equipment and satellite constellation,” he said.
- “By that, we can safeguard our own country.”
Still, even NSTC’s Wu admits that for Taiwan to build a minimum constellation of around 20 to 30 communications satellites, it would need “help from global companies or Taiwan’s private sector.”
- That sort of scale is required because while newer low-Earth orbit constellations like the ones deployed by SpaceX, which travel at an altitude of about 340 miles (550 kilometers), can provide faster internet access than satellites in higher orbits, those low-Earth orbit networks need many more satellites to ensure a constant signal as they move across the skies.
- The bigger numbers also provide safety, said Mark Matossian, founder of Efficient Frontier Space, a consulting firm in Silicon Valley.
- Targeting one satellite wouldn’t be enough because “it’s gone in a few minutes and there are more coming,” he said. While China demonstrated its anti-satellite capabilities back in 2007 by using a missile to destroy one of its own satellites, knocking out an entire low-Earth orbit constellation would be more difficult, Matossian said.
- In his comments to the Financial Times published in October, Musk said Beijing had “made clear its disapproval” of the Starlink rollout in Ukraine to help the military circumvent Russia’s severing of internet access.
- He added Beijing had sought assurances that he wouldn’t sell the service in China.
“If I’m China, I would ask Elon Musk to control all the satellite receivers in Taiwan. If I can control him, in an emergency I can turn it off,” Herming Chiueh, Taiwan’s deputy minister of digital affairs, said. “That’s my perspective, because we know China better than anyone else.”
Lincoln Hines, a China space expert and assistant professor at the US Air War College in Montgomery, Alabama, agrees Taiwan has reason to be concerned.
“Could Taiwan really count on the goodwill of Elon Musk in a crisis? That’s a position not many countries would like to be in,” he said.
- Taiwan may also be pursuing military options with the US and other allies. The territory’s Defense Ministry told Bloomberg the military has “multiple backups, with satellite as one of the measures,” but added it doesn’t “comment on details of war preparations.”
- In September, the territory’s Ministry of Digital Affairs announced a proof-of-concept program that would allow satellite providers to operate in Taiwan on an emergency basis, without having to set up a new company or be bound by local ownership requirements.
Regardless, Tang said her goal remains to set up 700 satellite receivers in and around Taiwan, using a “plurality” of satellite providers to avoid a single point of failure.
- The ministry is in discussions with Project Kuiper, Amazon.com Inc.’s satellite enterprise, and London-based OneWeb Ltd. has also signaled interest, Tang said. OneWeb plans to offer some coverage for Taiwan by the end of the year.
- Meanwhile local electronics giant Foxconn Technology Group, best known as the maker of Apple Inc. iPhones, expects to launch its first low-Earth orbit communication satellite in the fourth quarter, Chairman Young Liu said in May.
Her government in 2019 pledged to invest NT$25.1 billion ($803 million) in the sector over the next decade.
- Some 46 Taiwanese companies are already in the supply chain for Starlink and other global operators, and the territory aims to increase the output value of its space industry to NT$1 trillion by 2029, from NT$216 billion last year, according to TASA.
Taiwan’s space industry may surpass NT$1 trillion by 2029
Source: TASA
- Some companies are focused on going deeper into space. Taipei-based Lung Hwa Electronics, which has a partnership with Hughes Network Systems LLC, won approval in April to offer a satellite service in Taiwan via a geosynchronous satellite, which typically orbits about 37,000 kilometers above the equator.
“Taiwan really needs satellites due to the vulnerability of the undersea cables,” Lung Hwa Electronics CEO Sharon Wang said.
- Taiwan faces obstacles to its space-based communications backup plan, though. Approximately 120 satellites in low-Earth orbit will be needed to ensure uninterrupted coverage, TASA Director General Wu said. That’s far more than his agency anticipates launching in the coming years.
- Another bottleneck is the shortage of rockets capable of carrying the satellites into space. There are no local options, although startup Taiwan Innovative Space Inc. expects to conduct its third rocket launch attempt in the coming months.
Last November, TASA announced a March launch aboard an Arianespace SA rocket for Triton, Taiwan’s first locally built weather satellite. A failed Arianespace launch in December set back that plan, however, and TASA now hopes it can get Triton into orbit next month.
- That’s one reason Lung Hwa Electronics’ Wang believes Taiwan needs to hedge its bets instead of committing too deeply to local solutions. Her company has spent six years building its space business, requiring large amounts of technology, capital and talent.
— With assistance by Loren Grush
Continue > Bloomberg Cybersecurity






No comments:
Post a Comment