It is important to note that the exposed assets are not necessarily vulnerable or misconfigured in a way that allows attackers to interact with them.
However, Cyble’s research shows that unauthenticated visitors can glean information, including settings, that could be used to mount an attack.
Security Gaps in Green Energy Sector: Unveiling the Hidden Dangers of Public-Facing PV Measuring and Diagnostics Solutions
Over 130,000 solar energy monitoring systems exposed online
Bill Toulas
- July 6, 2023
- 05:04 AM
- 0

These systems are used for remote performance monitoring, troubleshooting, system optimization, and other functions to allow remote management of renewable energy production units.
Sensitive info exposed
Cyble’s threat analysts scanned the web for internet-exposed PV utilities and found 134,634 products from various vendors, which include Solar-Log, Danfoss Solar Web Server, SolarView Contec, SMA Sunny Webbox, SMA Cluster Controller, SMA Power Reducer Box, Kaco New Energy & Web, Fronis Datamanager, Saj Solar Inverter, and ABB Solar Inverter Web GUI.
It is important to note that the exposed assets are not necessarily vulnerable or misconfigured in a way that allows attackers to interact with them.
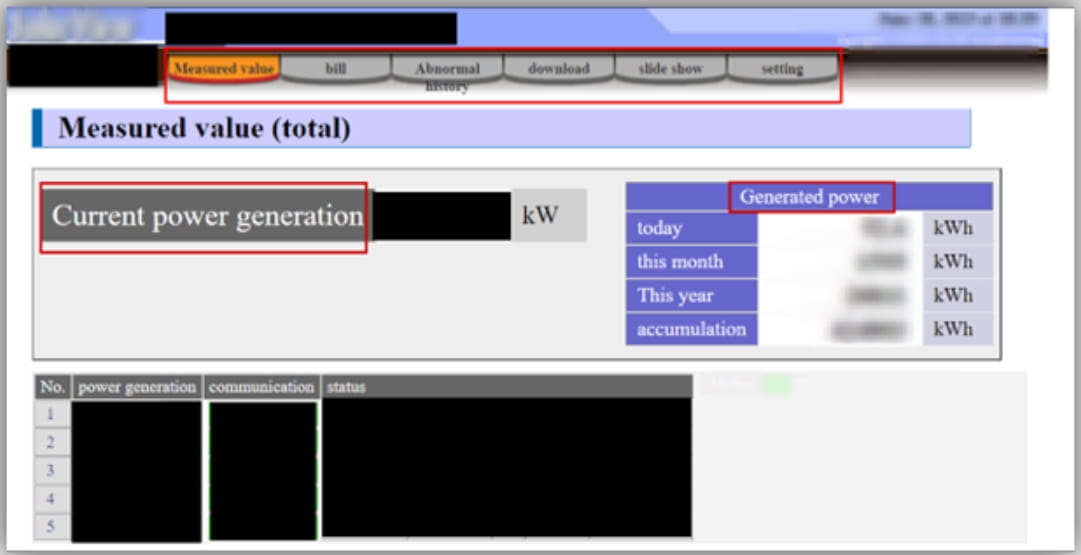
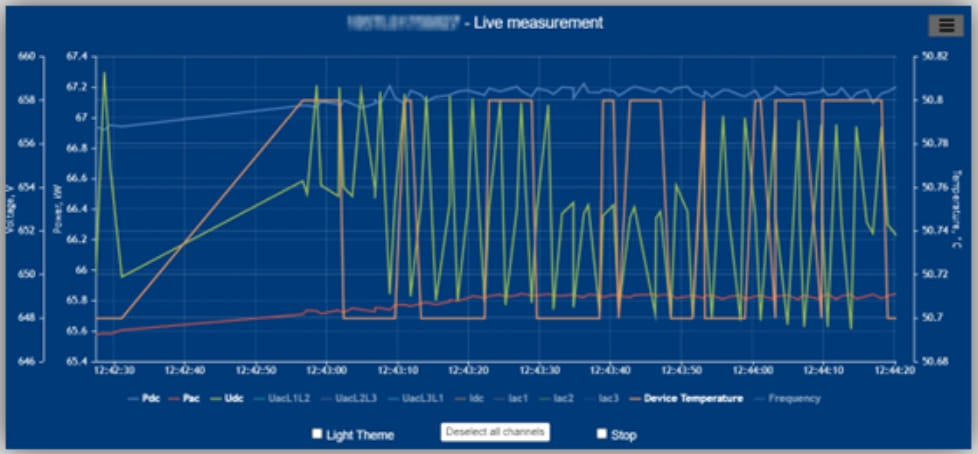
- The report also highlights that vulnerabilities have been found and reported for the products above and there is proof of concept (PoC) exploit code available for several of them, which increases the likelihood of attacks against the systems running an older firmware version.
- Even when PV control systems are adequately secured, Cyble points out the risk of information-stealing malware that can collect logins for these tools.
Active exploitation
For example, CVE-2022-29303, an unauthenticated remote command injection vulnerability impacting Contec’s SolarView system was used by a relatively new Mirai variant looking for fresh systems to grow its distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) power.
Cyble’s scans found 7,309 internet-exposed SolarView devices globally, while another report from VulnCheck today discovered 425 instances of Contec’s SolarView that use a vulnerable firmware version.
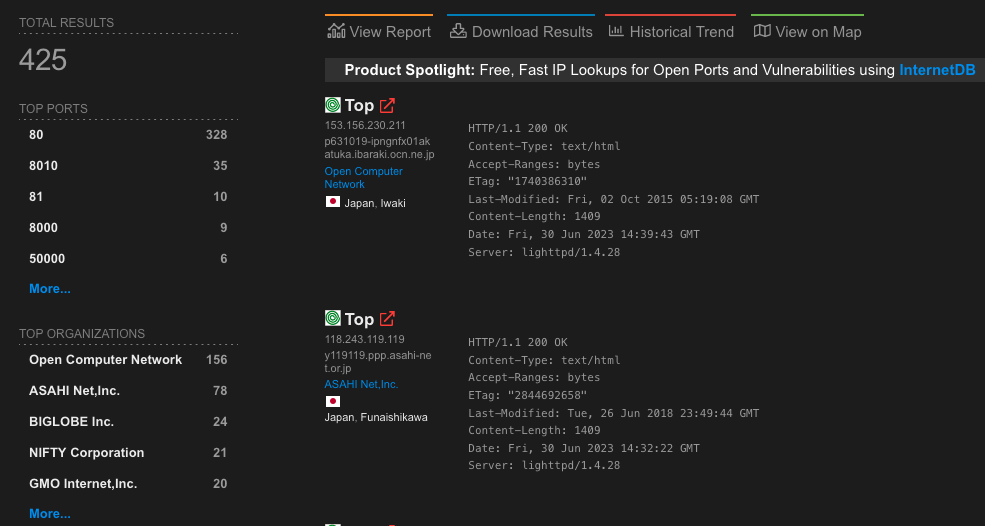
- VulnCheck’s report also highlights another recently-discovered unauthenticated remote code execution bug impacting the same product, tracked as CVE-2023-23333, for which multiple exploits exist in the public space.
Systems of this type often face a degree of neglect in terms of maintenance and upgrades, which gives attackers good chances of success when they leverage fairly recent vulnerabilities.
If PV system admins need to expose the interfaces for remote management, they should at least use strong, unique credentials, activate use multi-factor authentication where available, and keep their systems updated. Segregating the equipment to its own network also counts as a good defense."
Internet Exposure of Photovoltaic Diagnostic & Monitoring systems
Previously Cyble researcher blogs have discussed the impact and vulnerabilities in one of the Control Systems used in PV plants globally in the blog “Photovoltaic Plants PV Facing Risk of Cyberattack“.
CRIL researchers further investigated the internet exposure of these systems to understand the attack surface available for Threat Actors. They observed that there are over 130K internet-exposed PV diagnostic and monitoring solutions globally. Given below is the graph for the same.

- Not all devices need to be prone to cyber-attacks; rather, the high exposure of these devices provides a large attack surface for attackers.
Impact
- Targeting PV monitoring solutions can have severe repercussions, extending beyond the energy sector. It can lead to reduced energy production, causing an energy crisis and imbalances in supply and demand.
- Disruptions in PV monitoring can also affect the transportation sector, particularly electric vehicles, by impacting charging infrastructure and mobility services.
- Additionally, economic impacts may arise, with businesses facing downtime and financial losses.
- TAs might gain a strategic advantage in a war-like situation if they have access to thousands of PV measuring & monitoring and exploiting their underlying vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
- Researchers at Cyble observed a huge number of PV monitoring assets exposed over the internet that are located globally. In the list of solutions observed during the investigation, multiple solutions might be vulnerable and misconfigured, increasing the risk of cyber attacks.
- Hence, the operators of these solutions must ensure that the products are updated with the latest patch released by official vendors and are being monitored for intrusions.
Official vendors and State authorities provide regular updates and alerts on such devices. However, the high internet exposure of this device indicates that a large chunk of asset owners still lack visibility into PV monitoring and diagnostic solutions.



No comments:
Post a Comment