DECEMBER 1, 2023
Japanese experimental nuclear fusion reactor inaugurated
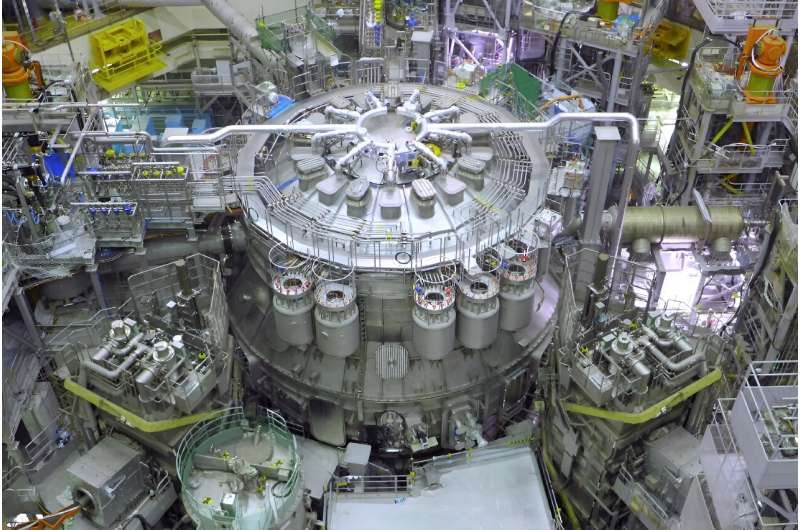
The world's biggest experimental nuclear fusion reactor in operation was inaugurated in Japan on Friday, a technology in its infancy but billed by some as the answer to humanity's future energy needs.
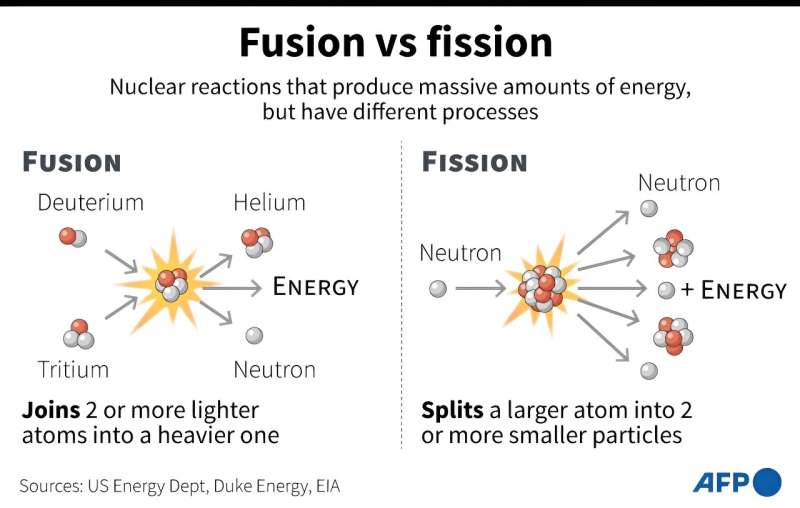
Fusion differs from fission, the technique currently used in nuclear power plants, by fusing two atomic nuclei instead of splitting one.
The goal of the JT-60SA reactor is to investigate the feasibility of fusion as a safe, large-scale and carbon-free source of net energy—with more energy generated than is put into producing it.
The six-story-high machine, in a hangar in Naka north of Tokyo, comprises a donut-shaped "tokamak" vessel set to contain swirling plasma heated up 200 million degrees Celsius (360 million degrees Fahrenheit).
It is a joint project between the European Union and Japan, and is the forerunner for its big brother in France, the under-construction International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER).
The ultimate aim of both projects is to coax hydrogen nuclei inside to fuse into one heavier element, helium, releasing energy in the form of light and heat, and mimicking the process that takes place inside the Sun.
Researchers at ITER, which is over budget, behind schedule and facing major technical problems, hope to achieve nuclear fusion technology's holy grail, net energy.
"It's the result of a collaboration between more than 500 scientists and engineers and more than 70 companies throughout Europe and Japan," Davis said at Friday's inauguration.
EU energy commissioner Kadri Simson said the JT-60SA was "the most advanced tokamak in the world", calling the start of operations "a milestone for fusion history".
"Fusion has the potential to become a key component for energy mix in the second half of this century," Simson added.
The feat of "net energy gain" was managed last December at the National Ignition Facility at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in the United States, home to the world's largest laser.
The US facility uses a different method to ITER and the JT-60SA known as inertial confinement fusion, in which high-energy lasers are directed simultaneously into a thimble-sized cylinder containing hydrogen.
The US government called the result a "landmark achievement" in the quest for a source of unlimited, clean power and an end to reliance on carbon-emitting fossil fuels that cause climate change as well as geopolitical upheaval.
Unlike fission, fusion carries no risk of catastrophic nuclear accidents—like that seen in Fukushima in Japan in 2011—and produces far less radioactive waste than current power plants, its exponents say.
NOVEMBER 30, 2023

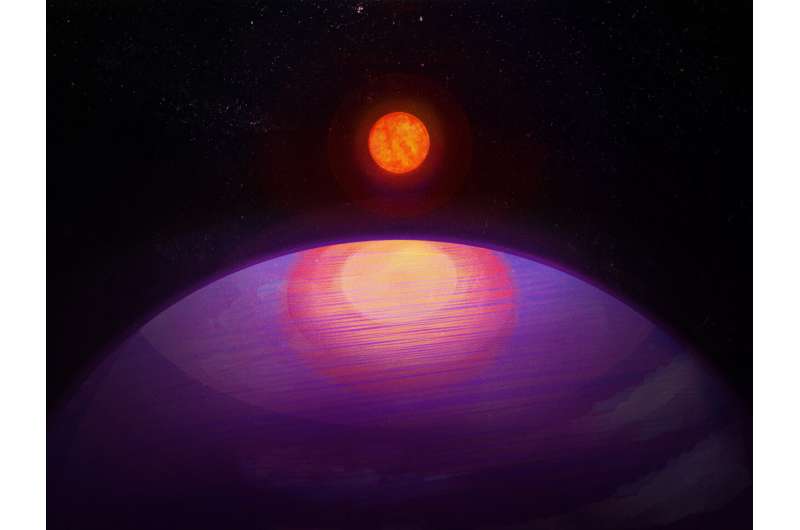
The discovery of a planet that is far too massive for its sun is calling into question what was previously understood about the formation of planets and their solar systems, according to Penn State researchers.
In a paper published in the journal Science, researchers report the discovery of a planet more than 13 times as massive as Earth orbiting the "ultracool" star LHS 3154, which itself is nine times less massive than the sun. The mass ratio of the newly found planet with its host star is more than 100 times higher than that of Earth and the sun.
The finding reveals the most massive known planet in a close orbit around an ultracool dwarf star, the least massive and coldest stars in the universe. The discovery goes against what current theories would predict for planet formation around small stars and marks the first time a planet with such high mass has been spotted orbiting such a low-mass star.
"This discovery really drives home the point of just how little we know about the universe," said Suvrath Mahadevan, the Verne M. Willaman Professor of Astronomy and Astrophysics at Penn State and co-author on the paper. "We wouldn't expect a planet this heavy around such a low-mass star to exist."
He explained that stars are formed from large clouds of gas and dust. After the star is formed, the gas and dust remain as disks of material orbiting the newborn star, which can eventually develop into planets.
"The planet-forming disk around the low-mass star LHS 3154 is not expected to have enough solid mass to make this planet," Mahadevan said. "But it's out there, so now we need to reexamine our understanding of how planets and stars form."
The researchers spotted the oversized planet, named LHS 3154b, using an astronomical spectrograph built at Penn State by a team of scientists led by Mahadevan. The instrument, called the Habitable Zone Planet Finder or HPF, was designed to detect planets orbiting the coolest stars outside our solar system with the potential for having liquid water—a key ingredient for life—on their surfaces.
While such planets are very difficult to detect around stars like our sun, the low temperature of ultracool stars means that planets capable of having liquid water on their surface are much closer to their star relative to Earth and the sun. This shorter distance between these planets and their stars, combined with the low mass of the ultracool stars, results in a detectable signal announcing the presence of the planet, Mahadevan explained.
"Think about it like the star is a campfire. The more the fire cools down, the closer you'll need to get to that fire to stay warm," Mahadevan said. "The same is true for planets. If the star is colder, then a planet will need to be closer to that star if it is going to be warm enough to contain liquid water. If a planet has a close enough orbit to its ultracool star, we can detect it by seeing a very subtle change in the color of the star's spectra or light as it is tugged on by an orbiting planet."
Located at the Hobby-Eberly Telescope at the McDonald Observatory in Texas, the HPF provides some of the highest precision measurements to date of such infrared signals from nearby stars.
"Making the discovery with HPF was extra special, as it is a new instrument that we designed, developed and built from the ground-up for the purpose of looking at the uncharted planet population around the lowest mass stars," said Guðmundur Stefánsson, NASA Sagan Fellow in Astrophysics at Princeton University and lead author on the paper, who helped develop HPF and worked on the study as a graduate student at Penn State.
"Now we are reaping the rewards, learning new and unexpected aspects of this exciting population of planets orbiting some of the most nearby stars."
The instrument has already yielded critical information in the discovery and confirmation of new planets, Stefánsson explained, but the discovery of the planet LHS 3154b exceeded all expectations.

"Based on current survey work with the HPF and other instruments, an object like the one we discovered is likely extremely rare, so detecting it has been really exciting," said Megan Delamer, astronomy graduate student at Penn State and co-author on the paper. "Our current theories of planet formation have trouble accounting for what we're seeing."
In the case of the massive planet discovered orbiting the star LHS 3154, the heavy planetary core inferred by the team's measurements would require a larger amount of solid material in the planet-forming disk than current models would predict, Delamer explained.
The finding also raises questions about prior understandings of the formation of stars, as the dust-mass and dust-to-gas ratio of the disk surrounding stars like LHS 3154—when they were young and newly formed—would need to be 10 times higher than what was observed in order to form a planet as massive as the one the team discovered.
"What we have discovered provides an extreme test case for all existing planet formation theories," Mahadevan said. "This is exactly what we built HPF to do, to discover how the most common stars in our galaxy form planets—and to find those planets."
More information: Guðmundur Stefánsson et al, A Neptune-mass exoplanet in close orbit around a very low mass star challenges formation models, Science (2023). DOI: 10.1126/science.abo0233. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abo0233
Frédéric Masset, A low-mass star with a large-mass planet, Science (2023). DOI: 10.1126/science.adl3365 , www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.adl3365
Journal information: Science
Provided by Pennsylvania State University

One of the largest magnetic storms in history quantified: Aurorae from the tropics to the polar regions
In early November of this year, aurora borealis were observed at surprisingly low latitudes, as far south as Italy and Texas. Such phenomena indicate the impacts of a solar coronal ...
ASTRONOMY
10 HOURS AGO
0
33

'Bone biographies' reveal lives of medieval England's common people—and illuminate early benefits system
A series of 'bone biographies' created by a major research project tell the stories of medieval Cambridge residents as recorded on their skeletons, illuminating everyday lives during ...
ARCHAEOLOGY
10 HOURS AGO
0
26

A mineral produced by plate tectonics has a global cooling effect, study finds
MIT geologists have found that a clay mineral on the seafloor, called smectite, has a surprisingly powerful ability to sequester carbon over millions of years.
EARTH SCIENCES
18 HOURS AGO
1
149

Study identifies the 'fingerprints' of energy models exploring emission mitigation scenarios
Over the past decades, environmental scientists and engineers have been trying to devise effective solutions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the adverse effects of climate change. This has led to the creation ...

New research explores future limits of survival and livability in extreme heat conditions
Commonly associated with longer days and slower paces, this summer's record-smashing heat in Arizona demonstrated a concerning future for the planet's warmest season. From power outages endangering entire neighborhoods and ...
ENVIRONMENT
12 HOURS AGO
0
32

Dwarf planet Eris is 'squishier' than expected
University of California, Santa Cruz Professor of Planetary Sciences Francis Nimmo recently co-authored a Science Advances paper about the internal structure of the dwarf planet Eris.
PLANETARY SCIENCES
21 HOURS AGO
8
80

Astronomers inspect supernova remnants with MeerKAT
Using the MeerKAT radio telescope, astronomers from the National Radio Astronomy Observatory (NRAO) in Charlottesville, Virginia, and elsewhere have investigated a batch of 36 high latitude supernova remnants. Results of ...

New bottlenose dolphin sense discovered: Research suggests they can feel weak electric fields
Born tail first, bottlenose dolphin calves emerge equipped with two slender rows of whiskers along their beak-like snouts—much like the touch-sensitive whiskers of seals. But the whiskers fall out soon after birth, leaving ...
PLANTS & ANIMALS
11 HOURS AGO
0
149

Long-term ADHD medication use associated with increased cardiovascular disease
Research led by the Karolinska Institutet, Sweden, has found an increased risk of cardiovascular disease associated with long-term ADHD medication use. Specific associations with different medications and dosages were connected ...

Why reading nursery rhymes and singing to babies may help them to learn language
Parents should speak to their babies using sing-song speech, like nursery rhymes, as soon as possible, say researchers. That's because babies learn languages from rhythmic information, not phonetic information, in their first ...
NEUROSCIENCE
59 MINUTES AGO
0
0
Anthrobots: Scientists build tiny biological robots from human tracheal cells
Researchers at Tufts University and Harvard University's Wyss Institute have created tiny biological robots that they call Anthrobots from human tracheal cells that can move across a surface and have been found to encourage ...
ROBOTICS
14 HOURS AGO
0
69


No comments:
Post a Comment