- China’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs spokesperson Lin Jin said Beijing would oppose all unilateral sanctions after new warnings from G7 countries on small Chinese banks about their links to Russia.
US unveils sweeping sanctions targeting Russia over Ukraine war
More than 300 new sanctions are largely aimed at deterring individuals and companies in countries including China, the United Arab Emirates and Turkey from helping Moscow circumvent Western blocks on obtaining key technology. They also threaten foreign financial institutions with sanctions if they do business with almost any sanctioned Russian entity, underscoring the U.S. view that the Kremlin has pivoted the Russian economy to a war footing.
Russia’s military is “desperate for access to the outside world,” said Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen.
The announcement came shortly before President Joe Biden arrived in Italy where he and other G7 leaders are urgently looking at aiding Ukraine, including turning frozen Russian assets into billions of dollars of support for Kyiv.
US expands sanctions against Russia
The new measures target companies in countries such as China in a bid to “discourage” trade with Moscow

According to the Treasury Department, the latest measures target individuals and companies suspected of enabling Moscow to evade the Western embargo.
“Today’s actions strike at their remaining avenues for international materials and equipment, including their reliance on critical supplies from third countries,”
“We are increasing the risk for financial institutions dealing with Russia’s war economy and eliminating paths for evasion, and diminishing Russia’s ability to benefit from access to foreign technology, equipment, software, and IT services.”
The two departments have issued a new interpretation of existing executive orders that prohibit US citizens from providing anyone in Russia with “IT consultancy and design services,” as well as “IT support services and cloud-based services for enterprise management software and design and manufacturing software.”
The Department of Treasury has also redefined Russia’s military-industrial base to include all persons sanctioned under Executive Order 14024 – including Sberbank and VTB – meaning that third-country financial institutions “risk being sanctioned for conducting or facilitating significant transactions, or providing any service” to them.
Washington has sanctioned more than 4,000 Russian individuals and companies since February 2022, aiming to harm the country’s military efforts against Kiev.
- The move by the US comes before the G7 summit in Italy, where Washington had hoped to announce progress on the confiscation of frozen Russian sovereign assets.
- However, the US and its EU allies have reportedly been unable to agree on the next step.
Moscow “will not leave the aggressive actions of the US unanswered,” Russian Foreign Ministry spokeswoman Maria Zakharova said in response to Washington’s announcement.
Russia not to leave US’ aggressive actions without response — diplomat on new sanctions
"As always in cases like this, Russia will not leave such aggressive actions without a response," the diplomat said
Previously, the US Department of State and the Department of the Treasury imposed sanctions on over 30 persons and over 200 legal entities from Russia and China. In particular, the sanctions covered Rusgazdobycha, Arctic LNG-1, Arctic LNG-3 and the Moscow Exchange.
Meanwhile, the Moscow Stock Exchange has announced that it will not conduct trading in US dollars and euros from Thursday due to the new US sanctions.
- By Reuters
U.S. Treasury Widens Sanctions To Curb Russia's War Production
The U.S. Treasury Department on June 12 announced new sanctions on over 300 entities suspected of providing Russia with products and services needed to sustain military production for its war in Ukraine.
U.S. officials expressed concern over Russia's ability to procure advanced semiconductors, optical equipment, and other goods needed to produce advanced weapons systems, despite prior sanctions.
The latest sanctions primarily target Belarusian and Chinese entities suspected of aiding Russia’s defense and energy sectors. The sanctions come on the eve of the June 13-15 G7 summit in Italy.
More News
- By Reuters
Russian Warships Enter Havana Harbor Following Military Exercises
A Russian navy frigate and a nuclear-powered submarine docked on June 12 in Havana harbor, a stopover the United States and Cuba said posed no threat but which was widely seen as a Russian show of force as tensions rise over the Ukraine war. The Admiral Gorshkov frigate and the nuclear-powered submarine Kazan were accompanied by a tugboat and fuel ship that arrived earlier in the morning. The four vessels sailed to Cuba after conducting "high-precision missile weapons" training in the Atlantic Ocean, the Russian Defense Ministry said. The ministry said the submarine and frigate carry Zircon hypersonic missiles, Kalibr cruise missiles, and Onyx anti-ship missiles.
As Russia Completes Transition to a Full War Economy, Treasury Takes Sweeping Aim at Foundational Financial Infrastructure and Access to Third Country Support
June 12, 2024Over 300 new sanctions issued across Treasury and State
Foreign financial institutions that support Russia’s war economy face greater risk of sanctions
WASHINGTON — As President Biden and Group of Seven (G7) Leaders prepare to meet this week in Italy, the U.S. Department of the Treasury is issuing sweeping new measures guided by G7 commitments to intensify the pressure on Russia for its continued cruel and unprovoked war against Ukraine. Today’s actions ratchet up the risk of secondary sanctions for foreign financial institutions that deal with Russia’s war economy; restrict the ability of Russian military-industrial base to take advantage of certain U.S. software and information technology (IT) services; and, together with the Department of State, target more than 300 individuals and entities both in Russia and outside its borders—including in Asia, the Middle East, Europe, Africa, Central Asia, and the Caribbean—whose products and services enable Russia to sustain its war effort and evade sanctions.
“Russia’s war economy is deeply isolated from the international financial system, leaving the Kremlin’s military desperate for access to the outside world,” said Secretary of the Treasury Janet L. Yellen. “Today’s actions strike at their remaining avenues for international materials and equipment, including their reliance on critical supplies from third countries. We are increasing the risk for financial institutions dealing with Russia’s war economy and eliminating paths for evasion, and diminishing Russia’s ability to benefit from access to foreign technology, equipment, software, and IT services. Every day, Russia continues to mortgage its future to sustain its unjust war of choice against Ukraine.”
Treasury is targeting the architecture of Russia’s financial system, which has been reoriented to facilitate investment into its defense industry and acquisition of goods needed to further its aggression against Ukraine. Treasury is also targeting more than a dozen transnational networks laundering gold for a designated Russian gold producer, supporting Russia’s production of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and procuring sensitive and critical items such as materials for Russia’s chemical and biological weapons program, anti-UAV equipment, machine tools, industrial machinery, and microelectronics. Today’s action also takes further steps to limit Russia’s future revenue from liquefied natural gas.
The State Department is targeting over 100 entities and individuals engaged in the development of Russia’s future energy, metals, and mining production and export capacity; sanctions evasion and circumvention; and furthering Russia’s ability to wage its war against Ukraine.
NEW SECONDARY SANCTIONS RISK
On December 22, 2023, President Biden expanded Treasury’s tools to disrupt and degrade Russia’s war machine by authorizing Treasury to impose sanctions on foreign financial institutions for aiding Russia’s military-industrial base. Today, Treasury is broadening the definition of Russia’s military-industrial base to include all persons blocked pursuant to Executive Order (E.O.) 14024. This means that foreign financial institutions risk being sanctioned for conducting or facilitating significant transactions, or providing any service, involving any person blocked pursuant to E.O. 14024, including designated Russian banks such as VTB Bank Public Joint Stock Company (VTB) and Public Joint Stock Company Sberbank of Russia (Sberbank). This expanded definition reflects Treasury’s assessment that Russia has re-oriented its economy and marshalled all parts of its government toward supporting its reprehensible war effort. Foreign financial institutions face sanctions risk for continuing to facilitate transactions involving Russia’s military-industrial base. Financial institutions should review OFAC’s updated sanctions advisory for practical guidance on how to identify sanctions risks and implement corresponding controls.
FOREIGN LOCATIONS OF DESIGNATED RUSSIAN BANKS
To help clarify the risk foreign financial institutions face by conducting or facilitating significant transactions or providing any service involving Russia’s designated banks, OFAC has updated the Specially Designated Nationals and Blocked Persons List (SDN List) information for five sanctioned Russian financial institutions, to include the addresses and aliases of their foreign locations.
Specifically, OFAC has updated the listings for Promsvyazbank Public Joint Stock Company to include its locations in Beijing, People’s Republic of China (PRC), Bishkek, Kyrgyz Republic, and New Delhi, India; for State Corporation Bank for Development and Foreign Economic Affairs Vnesheconombank to include its locations in Beijing, PRC and Mumbai, India; for Sberbank to include its locations in Beijing, PRC and New Delhi and Mumbai, India; for VTB to include its locations in New Delhi, India, and Beijing and Shanghai, PRC; and for VTB Capital Holdings Closed Joint Stock Company to include its location in Hong Kong, PRC.
SOFTWARE AND IT-RELATED SERVICES PROHIBITIONS
In coordination with the U.S. Department of Commerce and in line with G7 efforts to disrupt the Russian military-industrial base’s reliance on foreign IT systems, Treasury has taken steps to restrict the Russian military-industrial base’s access to certain software and IT-related services. To implement this policy, Treasury, in consultation with the Department of State, has issued a new determination under Executive Order (E.O.) 14071, which prohibits the supply to any person in the Russian Federation of (1) IT consultancy and design services; and (2) IT support services and cloud-based services for enterprise management software and design and manufacturing software. The determination will take effect on September 12, 2024.
The United States strongly supports the free flow of information and communications globally, and these actions are not intended to disrupt civil society and civil telecommunications. Despite the new prohibitions, OFAC continues to maintain authorizations for certain telecommunication and internet-related transactions, as well as humanitarian transactions, under General Licenses 6D and 25D, which mitigate the impacts to Russian civil society and protect public access to information communications technology.
RUSSIAN FINANCIAL INFRASTRUCTURE
The Moscow Exchange (MOEX) operates Russia’s largest public trading markets for equity, fixed income, derivative, foreign exchange, and money market products, as well as Russia’s central securities depository and the country’s largest clearing service provider. U.S.-designated Russian President Vladimir Putin has approved a series of measures to further attract capital through MOEX from both Russian and non-Russian persons from “friendly countries”—expanding opportunities for both Russians and non-Russians to profit from the Kremlin’s war machine by making investments in Russian sovereign debt, Russian corporations, and leading Russian defense entities, including U.S.-designated State Corporation Rostec, Public Joint Stock Company United Aircraft Corporation (UAC), Kamaz Publicly Traded Company (Kamaz), Irkut Corporation Joint Stock Company, Uralvagonzavod, and Joint Stock Company Russian Helicopters.
The National Clearing Center (NCC) is the central counterparty and clearing agent for, and a subsidiary of, MOEX. NCC is supervised by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation (CBR).
The Non-Bank Credit Institution Joint Stock Company National Settlement Depository (NSD) is Russia’s central securities depository and is a subsidiary of MOEX. NSD provides bank account services, registration of over-the-counter trades, and liquidity management services. The European Union (EU) previously sanctioned NSD in June 2022.
Gas Industry Insurance Company Sogaz (Sogaz) is an insurance company that provides insurance to Russian military personnel and personnel of leading defense entities, including U.S.-designated UAC, Joint Stock Company Experimental Design Bureau Novator, and Federal State Enterprise Ya M Sverdlov Plant. Sogaz has also been sanctioned by Australia, Canada, the EU, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom (UK).
Joint Stock Company Russian National Reinsurance Company (RNRC) is a Russian state-owned reinsurance provider that was created in 2016 to provide protection for sanctioned persons. RNRC has also been sanctioned by the EU and UK.
MOEX, NCC, NSD, Sogaz, and RNRC were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the financial services sector of the Russian Federation economy. Sogaz was also designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the defense and related materiel sector of the Russian Federation economy.
SANCTIONS EVASION, CIRCUMVENTION, AND BACKFILL
Russia relies on complex transnational supply chains to feed its war machine and enable production of materiel to sustain its war effort. Similar networks also attempt to evade sanctions using convoluted schemes to move money and other valuable goods and assets. Today’s action targets more than a dozen of these types of networks, designating more than 90 individuals and entities across Russia, Belarus, the British Virgin Islands, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, the Kyrgyz Republic, the PRC, Serbia, South Africa, Türkiye, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
For more information on these targets, please see Annex 1.
RUSSIA’S DOMESTIC WAR ECONOMY
Russia has transformed into a war economy in which companies across the spectrum of Russian industry contribute to Russia’s war effort. Today’s action reflects the intricate landscape of Russia’s domestic war economy by targeting more than 100 entities that operate or have operated in the defense and related materiel, manufacturing, technology, transportation, or financial services sectors of the Russian Federation economy.
For more information on these targets, please see Annex 2.
LIMITING RUSSIA’S FUTURE REVENUE FROM LIQUEFIED NATURAL GAS
Guided by commitments made by President Biden and G7 leaders to limit Russia’s future energy revenues and impede Russia’s development of future energy projects, today Treasury is targeting entities involved in three liquefied natural gas (LNG) projects that Russia hopes to bring online in the future: the Obsky LNG, Arctic LNG 1, and Arctic LNG 3 projects. Today’s action also includes designations of three entities involved in either construction of natural gas-related projects or manufacturing specialized equipment for LNG transportation, as well as the identification of seven under-construction LNG vessels.
For more information on these targets, please see Annex 3.
ANNEX 1: SANCTIONS EVASION, CIRCUMVENTION, AND BACKFILL
Aero-HIT Network
Limited Liability Company Aero-HIT (Aero-HIT) is a Khabarovsk, Russia-based company that has purchased equipment and components to produce several modifications of the Veles multi-rotor first person view strike drone. Aero-HIT-manufactured Veles drones have been used by Russian forces based in Kherson against Ukrainian targets. The Veles drones can be used as an attack drone, as optical reconnaissance devices, or as part of an electronic reconnaissance system. Russia-based Andrei Andreevich Anisimov (Anisimov) is the Director General of Aero-HIT. In his capacity as Director General, Anisimov has worked to expand production of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for use by Russian forces. PRC-based Shenzhen Huasheng Industry Co Ltd has contracted with Aero-HIT to supply UAV components for Aero-HIT. Russia-based Obshchestvo S Organichennoi Otvetstvennostyu Renovatsio-Invest (Renovatsio-Invest) procured PRC-manufactured UAVs on behalf of Aero-HIT. Renovatsio-Invest has also attempted to provide similar services of procuring PRC-manufactured UAVs to other entities in the Russian military-industrial base.
Aero-HIT, Anisimov, Shenzhen Huasheng Industry Co Ltd, and Renovatsio-Invest were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the defense and related materiel sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Russian Machine Tool Evasion Network
Russia-based Newton-ITM is a supplier and producer of metalworking equipment and high-precision parts for the aerospace industry. Russian national Dmitrii Vladimirovich Alikhanov (Alikhanov) is the director of Newton-ITM. Alikhanov has worked with European machine tool manufacturers to illicitly procure machinery for Russian end-users. Alikhanov has used Kyrgyz Republic-based Obshchestvo s Ogranichennoy Otvestvennostyu Nova Proekt (Nova Proekt) as a falsified end-user to procure machine tools for Russian end-users.A number of foreign intermediaries, including Türkiye-based Safes Lojistik Ithalat Ihracat Sanayi Ticaret Limited (Safes Lojistik), PRC-based Chongqing Fagima Electromechanical Equipment Co Ltd (Chongqing Fagima), and Hong Kong-based GBL International Logistics Co Ltd (GBL), helped to ship foreign-origin machine tools to Newton-ITM.
Newton-ITM, Alikhanov, Nova Proekt, Safes Lojistik, Chongqing Fagima, and GBL were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the manufacturing sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Russian Intelligence Procurement Network
Russia-based Silk Way Rally Association (Silk Way) holds an annual off-road rally race that the U.S.-designated Russian Main Intelligence Directorate (GRU) uses as a front for intelligence operations. The GRU has given awards to Russian national Bulat Akhatovich Yanborisov (Bulat), the head of Silk Way, for his work. Bulat appears to use his properties in Europe as transit points for GRU officers. Bulat, who is Silk Way’s CEO and general director, alongside his son Amir Bulatovich Yanborisov (Amir), use Silk Way’s logistical infrastructure to procure anti-UAV and radioelectronic warfare equipment for use on the battlefield in Ukraine.
Silk Way, Bulat, and Amir were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the defense and related materiel sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Nikolai Levin Network
U.S.-designated OOO Mayak (Mayak) assists Russian companies in circumventing sanctions through Mayak’s trading houses and consolidated warehouses in Europe, delivering parallel imports from Europe, Türkiye, and the UAE. Russian national Nikolai Aleksandrovich Levin (Levin) is the General Director and owner of Mayak and has used a network of companies to facilitate the import of U.S. and foreign electronics, industrial materials, and other goods into Russia. Levin is the Director and owner of Serbia-based Bassire Group DOO Beograd (Bassire Group) and is the sole executive of Thailand-based NAL Solutions Company Limited (NAL Solutions). Türkiye-based Expert Machinery Kimyasal Urunler Ticaret Limited Sirketi (Expert Machinery) is co-owned by Levin and has sent over $500,000 worth of high priority HS code goods to Mayak and Russia-based OOO TAV (TAV), including machines for the reception, conversion, and transmission of data and integrated electronic circuits. TAV buys and delivers imported goods and offers all types of cargo transportation all over Russia and is owned by Russian national Aleksandr Vasilyevich Tanchev (Tanchev). Tanchev is the Director of Hong Kong-based Tavit Hong Kong Co Limited (Tavit), which has sent over $2 million worth of U.S.-made goods to Mayak.
Levin, Expert Machinery, and Tavit were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy. TAV and Tanchev were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the transportation sector of the Russian Federation economy. Bassire Group and NAL Solutions were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for being owned or controlled by, or having acted or purported to act for or on behalf of, directly or indirectly, Levin.
Sudakov Gold Laundering Network
Russian national Andrey Dmitriyevich Sudakov (Sudakov), an employee of U.S.-designated Russian state-owned gold producer Public Joint Stock Company Polyus (Polyus), and his Hong Kong-based associate Mu Xiaolu (Mu), engaged in a complex, multi-layered laundering scheme whereby payments from the sale of Russian-origin gold were converted into fiat currency and cryptocurrencies through numerous UAE and Hong Kong-based front companies. The scheme used numerous Hong Kong-based trading companies, including Holden International Trading Limited (Holden) and Taube Precious HK Limited (Taube) to route payments related to gold sales through foreign financial institutions back into the Russian financial system. The scheme also used UAE-based front company Red Coast Metals Trading DMCC (Red Coast) to obfuscate payments from the sale of Russian-origin gold. Additionally, the scheme involved Hong Kong-based VPower Finance Security Hong Kong Limited (VPower) to transport the Russian-origin gold.
Sudakov, Mu, Holden, Red Coast, Taube, Red Coast, and VPower were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the metals and mining sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Chichenev Microelectronics Procurement Network
Alexey Chichenev (Chichenev) is a Russian national who manages a large-scale microelectronics procurement network based in Hong Kong. Chichenev has used his network of Hong-Kong based import-export companies, including Superchip Limited (Superchip) and Kvantek Limited (Kvantek), to ship millions of dollars’ worth of electronic integrated circuits and other high-priority technology items to Russia. Chichenev is the director and 100 percent owner of Superchip. Chichenev is also the director of Olax Finance Limited, Saril Overseas Limited, and Bargawine (Hong Kong) Limited.
Superchip and Kvantek were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy. Chichenev was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for being or having been a leader, official, senior executive officer, or member of the board of directors of Superchip. Olax Finance Limited, Saril Overseas Limited, and Bargawine (Hong Kong) Limited were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for being owned or controlled by, or having acted or purported to act for or on behalf of, directly or indirectly, Chichenev.
Elecom Network
Limited Liability Company Elecom (LLC Elecom) is a Russia-based electronic component manufacturer that has imported high-priority items, including electronic integrated circuits, from foreign companies. Pako International Trading (Pako International) is a Hong Kong-based company that has shipped high-priority items, including electronic integrated circuits and transformers, to Russian companies including LLC Elecom and U.S.-designated Limited Liability Company Promelektro Engineering (Promelektro Engineering). Valetudo Limited (Valetudo) is a Hong Kong-based company that has shipped high-priority items, including electronic integrated circuits and capacitators, to Russian companies including LLC Elecom and Promelektro Engineering. LLC Elecom, Pako International, and Valetudo were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Training the Wagner Group
Brett Warrick Mac Donald (Mac Donald) and Shaun Louw (Louw) are South African nationals who, throughout mid-2023, arranged and oversaw the execution of a training program on survival techniques for U.S.-designated Private Military Company ‘Wagner’ (the Wagner Group) personnel in the Central African Republic. Mac Donald and Louw were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for having materially assisted, sponsored, or provided financial, material, or technological support for, or goods or services to or in support of, the Wagner Group, a person whose property and interests in property are blocked pursuant to E.O. 14024.
Unmanned Systems Procurement Network
Russia-based Limited Liability Company Unmanned Systems (Unmanned Systems) is a designer and manufacturer of unmanned aircraft systems that have been used as reconnaissance drones by the Russian military. Russia’s military industrial base uses Unmanned Systems and an extensive network of Russian and foreign intermediary companies to purchase microelectronics and high-tech equipment produced abroad. Hong Kong-based Infinite Force Cargo Service HK Limited (Infinite Force) has sent camera lenses for unmanned aircraft to Unmanned Systems as well as high-priority items such as electronic integrated circuits, tantalum capacitors, and multilayer ceramic capacitors to other Russian end-users, including U.S.-designated Silkway Limited Liability Company.PRC-based Shanghai Transit International Forwarding Agency Co Ltd (Shanghai Transit)offers delivery via its own container trains to various Russian cities. Shanghai Transit has provided over $180,000 worth of high-priority items, including electronic integrated circuits, tantalum capacitors, and multilayer ceramic capacitors, to Russia-based end-users, including those supplying equipment to Unmanned Systems.
Unmanned Systems was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the defense and related materiel sector of the Russian Federation economy. Infinite Force and Shanghai Transit were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
ARP Investments
Russia-based Limited Liability Company Severnaya Zvezda (Severnaya Zvezda) is a producer and supplier of semiconductors and tantalum capacitors critical to Russia’s war effort. Severnaya Zvezda’s principal supplier is British Virgin Islands-based ARP Investments Limited (ARP), which has made hundreds of shipments of electronic components to Russia since February 2022. ARP has engaged in transactions with U.S.-designated, Serbia-based Kominvex DOO Beograd (Kominvex). Kominvex’s transactions exhibited typologies indicative of possible trade-based money laundering.
Severnaya Zvezda and ARP were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Elekkom Logistik Network
Russia-based Elekkom Logistik is an official distributor, dealer, and partner of leading foreign and domestic manufacturers of electro-technical products. Elekkom Logistik is part of a wide network of intermediaries supplying the Russian defense industry with foreign-made electronic components and materials used in the production of UAVs and has worked to procure ATXMEGA256A3-AU microchips. PRC-based Shenzhen Youxin Technology Co Ltd (Shenzhen Youxin) has provided more than half a million dollars’ worth of electronic integrated circuits, tantalum capacitors, and multilayer ceramic capacitors to Elekkom Logistik, in addition to chips found in Russian reconnaissance UAVs.
Elekkom Logistik and Shenzhen Youxin were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
UAV Proliferation
KVAND ISOOO is a Belarus-based developer of drone technology that has designed and tested loitering munition UAVs, and has jointly designed and tested surveillance UAVs with the Belarusian government. KVAND IS OOO has shipped drone technology to the Russian defense establishment. Siarhei Tytsyk is the co-owner and director of KVAND IS OOO. Additionally, Freshvale EOOD, a Bulgaria-based UAV manufacturer, marketed Russian UAVs with offensive capabilities, such as weapons systems and missiles to an African country. KVAND IS and Freshvale EOOD were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the defense and related materiel sector of the Russian Federation economy. Siarhei Tytsyk was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for being or having been a leader, official, senior executive officer, or member of the board of directors of KVAND IS OOO.
Ostec Group Sanctions Evasion Network
In May 2022, OFAC sanctioned entities comprising the Ostec Group, a Russian technology consortium and military contractor that supports Russian producers of various missile systems and aerial bombs, alongside its principal suppliers in Europe. Following those designations, new routes have emerged to attempt to enable the Ostec Group to acquire much-needed technology and equipment.
Russia-based Fabcenter LLC (Fabcenter), which shares a location with the Ostec Group and whose general director and owner has worked for the Ostec Group for more than a decade, has become a major recipient of goods in Ostec Group’s stead. Fabcenter is a construction company that specializes in the design and construction of production facilities and cleanrooms for the electronics industry.
The Ostec Group’s suppliers have shifted to sending goods—primarily semiconductor production machines, soldering and welding machines, and other technology and equipment—to Fabcenter after previously shipping to Ostec Group entities like U.S.-designated Ostec-Arttool Ltd, Ostec SMT Ltd, and Ostec-Integra Ltd.
Kazakhstan-based KBR Tekhnologii TOO (KBR Tekhnologii) has made hundreds of shipments to Fabcenter, Ostec-Arttool Ltd, Ostec-SMT Ltd, and Ostec-Integra Ltd. The co-founder of KBR Technologies is a longtime employee of U.S.-designated Evgueni Kostiouk, the owner of one the Ostec Group’s previous top suppliers, U.S.-designated Inter-Trans Spolka z Ograniczona Odpowiedzialnoscia.
Türkiye-based Alptech Makina Sanayi Limited Sirketi (Alptech) and Hong Kong-based New Horizons Trading Limited (New Horizons) have made hundreds of shipments to Fabcenter and dozens of shipments to Ostec-Arttool Ltd. KBR Technologies, Alptech, and New Horizons were all established between May and August 2022.
Other Russia-based companies that have received shipments from KBR Technologies, Alptech, and New Horizons include Kseoprom, which manufactures materials and equipment related to the production of electronics; manufacturing equipment wholesaler Niceberg Limited Liability Company (Niceberg), established in June 2023; and manufacturing equipment wholesaler Powertech Limited Liability Company (Powertech), established in July 2023.
Fabcenter was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the construction sector of the Russian Federation economy. KBR Tekhnologii was designated for having materially assisted, sponsored, or provided financial, material, or technological support for, or goods or services to or in support of, Fabcenter, Ostec-Arttool Ltd, Ostec-SMT Ltd, and Ostec-Integra Ltd. Alptech and New Horizons were designated for having materially assisted, sponsored, or provided financial, material, or technological support for, or goods or services to or in support of, Fabcenter and Ostec-Arttool Ltd. Kseoprom, Niceberg, and Powertech were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the manufacturing sector of the Russian Federation economy.
DP Microchip Network
Russia-based Design Partner Microchip LLC (DP Microchip) imports electronic components, including high-priority Harmonized System (HS) code goods. DP Microchip collaborated with multiple U.S.-designated entities in Russia to procure electronic components from outside of Russia. Türkiye-based Platform Endustriyel Gida Insaat Elektronik Ve Madencilik Dis Ticaret Limited Sirketi (Platform Endustriyel) and Onyad Bilgisayar Ticaret Limited Sirketi (Onyad Bilgisayar) and PRC-based Yiwu Xinglu Import and Export Co Ltd (Yiwu Xinglu) have together made dozens of shipments of integrated circuits and other electronics to DP Microchip.
DP Microchip, Platform Endustriyel, Onyad Bilgisayar, and Yiwu Xinglu were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
AK Microtech’s PRC Intermediaries
On July 20, 2023, OFAC designated Russia-based Limited Liability Company AK Microtech (AKM), which specializes in transferring foreign semiconductor technology to Russian microelectronics production companies, including entities that provide microelectronics to the Russian defense industry. On September 14, 2023, OFAC designated AKM’s owner and director, Andrei Rostislavovich Khokhlun (Khokhlun), and another Russia-based company owned by Khokhlun, Limited Liability Company Keko R (Keko R).
PRC-based Hangzhou Keming Intelligent Technology Co Ltd (HKIT) has made dozens of shipments to AKM as well as shipments to Keko R. The shipments have included technology such as film used in the production of electronic components.
PRC-based Shenzhen C S Im Export Ltd (Shenzhen CSI) is a prolific supplier of technology to AKM, including high-priority items such as machines and apparatus for the manufacture of boules or wafers and electrical transformers, static convertors, and inductors. Shenzhen CSI has helped AKM divert technology to Russia.
PRC national Ting Chen (Chen) is the managing director and owner of Shenzhen CSI. Chen was also involved in a sanctions evasion scheme in which AKM sought to acquire technology via Shenzhen CSI. Chen also owns Hong Kong-based Way Good Technology Limited (Way Good).
Hong Kong-based Kekotech Equipment Limited (Kekotech) has also been used to provide goods to AKM. In addition to Shenzhen CSI, Chen is also affiliated with Kekotech.
PRC national Lap Shun Lee (Lee) has represented Shenzhen CSI in many of its dealings with AKM, including schemes in which AKM sought to evade sanctions against Russia.
HKIT, Shenzhen CSI, Chen, and Lee were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy. Way Good was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for being owned or controlled by, or having acted for or purported to act for or on behalf of, directly or indirectly, Chen. Kekotech was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for having materially assisted, sponsored, or provided financial, material, or technological support for, or goods or services to or in support of, AKM, a person whose property and interests in property are blocked pursuant to E.O. 14024.
Maksim Ermakov
Maksim Yuryevich Ermakov (Ermakov), previously designated pursuant to E.O. 14024, ran a procurement network to obtain microchips for Russian state-owned enterprises, including a state-owned technology company that makes electronic warfare systems for the Russian military. Ermakov was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy. Ermakov has also been sanctioned by the UK.
Chimmed Group Network
Chimmed Group is the leading group of Russian companies that supplies Russian customers with a wide range of chemicals and lab equipment. Chimmed Group maintains an extensive network of members and affiliates to procure U.S.- and Western-origin equipment and consumables for Russian entities connected to the country’s biological and chemical weapons programs, including the Federal State Budgetary Establishment 33 Central Scientific Research Test (33rd TSNII), Federal State Budgetary Establishment 27 Scientific Center (27th Scientific Center), and Federal State Budgetary Institution 48 Central Scientific and Research Institute (48th TSNII). Chimmed Group also supplies materials—including raw materials that can be used for the production of chemical and biological weapons—to special laboratories that are a part of the Federal Security Service (FSB) that were implicated in the poisoning of Alexey Navalny.
Russia-based Obshchestvo S Ogranichennoi Otvetstvennostyu Torgovy Dom Khimmed (TD Khimmed) and Obshchestvo S Ogranichennoi Otvetstvennostyu Analiticheskaya Manufaktura (Analiticheskaya Manufaktura) are affiliates of the Chimmed Group. Analiticheskaya Manufaktura attempted to provide equipment to the 48th TSNII. Russia-based companies Obshchestvo S Ogranichennoi Otvetstvennostyu Rusmedtorg (Rusmedtorg) and Obshchestvo S Ogranichennoi Otvetstvennostyu Medstandart (Medstandart) have been closely associated with the Chimmed Group and share a delivery address. Individuals associated with the Chimmed Group purchased biological goods via Medstandart and chemicals via Rusmedtorg. Medstandart has supplied U.S. origin reagents to the Chimmed Group and attempted to provide laboratory goods to the 33rd TSNII.
Russia-based Obshchestvo S Ogranichennoi Otvetstvennostyu Elyuentlaboratoriz (Elyuentlaboratoriz) procured U.S.- and Western-origin equipment and consumables for the 27th Scientific Center and 48th TSNII.
Türkiye-based Biopharmist Medikal Urunler Dis Ticaret LTD STI (Biopharmist) exported laboratory items to affiliates of the Chimmed Group, including Elyuentlaboratoriz, Rusmedtorg, and Medstandart.
Chimmed Group, TD Khimmed, Analiticheskaya Manufaktura, Rusmedtorg, Medstandart, Elyuentlaboratoriz, and Biopharmist were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the defense and related materiel sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Intermediaries Supplying Laser Companies
Russia-based Leningrad Laser Systems (LLS) is involved in the supply, integration, and development of innovative solutions in the fields of lasers and fiber optics in Russia. LLS and U.S.-designated Russia-based laser product manufacturer Lassard are contractors for the U.S.-designated All-Russian Scientific Research Institute Of Experimental Physics’ (VNIIEF’s) Institute of Laser Physics Research. VNIIEF performs experimental testing of Russia’s nuclear weapons. Lassard is an industrial enterprise offering full-cycle manufacturing of laser technology and optical equipment with potential for military and weapons applications. Russia-based Cryotrade Engineering is a supplier of cryogenic equipment, cryogenic instruments, and analytical equipment from leading manufacturers. LLS and Cryotrade Engineering have previously been contracted by U.S.-designated L.D. Landau Institute for Theoretical Physics of Russian Academy of Sciences, a quantum computing research center. China-based Gker Laser Technology Co Ltd (Gker Laser) has sent hundreds of thousands of dollars’ worth of goods, including laser diodes, optical fiber, and lasers, to Lassard. China-based Jinan Kewei Optics Co Ltd (Jinan Kewei) has sent hundreds of high priority HS code goods to LLS and U.S.-designated electronics company Staut Company Limited, including electronic integrated circuits, tantalum capacitors, and multilayer ceramic capacitors.
LLS, Gker Laser, and Jinan Kewei were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy. Cryotrade Engineering was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in themanufacturing sector of the Russian Federation economy.
PRC-based Suppliers to Russian Military-Industrial Base
Analog Technology Limited (Analog Technology) is a Hong Kong-based electronic component distributor with locations in the PRC and India that has shipped high-priority items, including electronic integrated circuits, to Russian companies including U.S.-designated LLC Spetselservis and Limited Liability Company Spetsvoltazh. Analog Technology was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Shandong Oree Laser Technology Co., Ltd. (Shandong Oree) and Zhejiang Zhenhuan CNC Machine Tool Co., Ltd. (Zhejiang Zhenhuan CNC) are PRC-based machine tool companies that have shipped metalworking machines and other related equipment to Russia. Shandong Oree and Zhejiang Zhenhuan CNC were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the manufacturing sector of the Russian Federation economy.
PRC-based Chongqing Xianuofugeluode International Trade Co Ltd (CXI Trade) has made dozens of shipments of technology, including integrated circuits, to Russia since February 2022. CXI Trade has also acquired technology for Russian military-industrial base entities. CXI Trade was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Enka Trading Limited is a Hong Kong-based wholesaler with expertise in electronic devices and components that has facilitated the procurement of electronic components, including integrated circuits, for Russian end-use. Enka Trading Limited was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
PRC-based Shandong Ki Forest New Advanced Co Ltd (Shandong Ki Forest) has made thousands of shipments of high-priority technology to Russia, including semiconductor devices, electronic integrated circuits, tantalum capacitors, transformers, converters, and inductors. Shandong Ki Forest’s primary customers in Russia are Reomaks Limited Liability Company (Reomaks), a supplier of industrial and specialized electronic components, and Solard, an importer of electronic components. Shandong Ki Forest, Reomaks, and Solard were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Hong Kong-based HK Nicest Electric Technology Co Limited (HK Nicest) has sent over 100 shipments of high-priority items to Russia-based end-users, including electronic integrated circuits, tantalum capacitors, and multilayer ceramic capacitors. HK Nicest has supplied equipment to Russia-based end-users supplying the Russian defense industry with electronics to produce aviation equipment. One of HK Nicest’s Russian buyers has been U.S.-designated Russian electronics company Streloi Ekommerts. HK Nicest was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
PRC-based Daytek Chongqing International Trade Co Ltd (Daytek) has acquired advanced technological equipment for Russian military-industrial base end-users. PRC national Yi Xuan Wu (Wu) is the director of Daytek. Wu has helped Russian counterparts evade sanctions and acquire technology for the Russian military-industrial base. Daytek and Wu were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Türkiye-Based Suppliers to Russian Military-Industrial Base
Türkiye-based SSGCTM CNC Takim Tezgahlari Makine Sanayi Ve Ticaret Limited Sirketi (SSGCTM CNC) has provided over $6 million worth of goods to U.S.-designated Russian manufacturing company Limited Liability Company I Machine Technology (I Machine), including computer numerical controlled (CNC) machine tools. Türkiye-based Minyon Kesici Takimlar Makine Sanayi Ve Ticaret Limited Sirketi (Minyon Kesici) has sent over 600 shipments to Russia-based end-users, with shipments including tools used for metal processing and CNC machine tools, including over $800,000 worth of CNC machine tools to I Machine.
Türkiye-based Gepa Uluslararasi Ticaret Limited Sirketi (Gepa) has provided over $4 million worth of goods to U.S.-designated Russian manufacturing company Alfa Machinery Group, including various machine tools and related equipment.
Türkiye-basedKamilhan Lojistik Dis Ticaret Limited Sirketi (Kamilhan Lojistik) has sent over $3 million worth of high priority HS code goods, including electronic integrated circuits and machines for the reception, conversion, and transmission of data, to U.S.-designated Russian electronics company Limited Liability Company Trade House Kyutek.
Türkiye-based CPS Proses Kontrol Urunleri Sanayi Ve Ticaret Anonim Sirketi (CPS Proses) has shipped German and U.S.-manufactured machine and welding equipment to U.S.-designated Russian technology company and defense contractor Ostec EC Ltd.
Türkiye-based RMB Yapi Insaat Taahhut Sana Yi Ve Ti Caret Limited Sirketi (RMB Yapi) has sent hundreds of thousands of dollars’ worth of remote-controlled unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) as well as programmable controllers for UAVs and lithium-ion batteries to Russian end-users.
Türkiye-based Taksan Makina Sanayi Ve Ticaret Anonim Sirketi (Taksan Makina) has sent over $700,000 worth of goods, including metal-working centers and machine tools, to U.S.-designated Russian manufacturing company Limited Liability Company Pumori Northwest
(Pumori Northwest), a major provider of metalworking equipment and machine tools to the
Russian defense industry. Türkiye-based Dener Ithalat Ihracat Ve Dis Ticaret Anonim Sirketi (Dener Ithalat) has sent over $300,000 worth of goods to Pumori Northwest, including metalworking centers and a metalworking machine tool.
SSGCTM CNC, Minyon Kesici, Gepa, Taksan Makina, and Dener Ithalat were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the manufacturing sector of the Russian Federation economy. Kamilhan Lojistik, CPS Proses, and RMB Yapi were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy.
ANNEX 2: RUSSIA’S DOMESTIC WAR ECONOMY
The following Russia-based persons were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the defense and related materiel sector of the Russian Federation economy:
- Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo Kazanskoe Opytnoe Konstruktorskoe Byuro Soyuz manufactures weapons and ammunition.
- Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo Nauchno Proizvodstvennoe Obyedinenie Poisk manufactures fuses for projectiles, artillery, and missiles.
- Birtrans transports Russian military equipment, including armed personnel carriers and tanks.
- East West Conversion develops and sells armaments and military equipment.
- Federal Research and Production Center Nizhny Novgorod Research Institute of Radio Engineering Joint Stock Company produces radar equipment used by the Russian Army.
- Joint Stock Company Federal Scientific and Production Center Scientific Research Institute of Applied Chemistry develops and manufactures pyrotechnic systems used for the protection of armored vehicles, aviation, and marine objects.
- Joint Stock Company KB Luch (KB Luch) designed the Korsar, also known as the Corsair UAV system, which is used by the Russian Ministry of Defense for surveillance, aerial reconnaissance, patrol and observation, and target acquisition. The KB Luch-designed Korsar has been used by Russian forces in Ukraine.
- Joint Stock Company Murom Machine Building Plant Production Association manufactures weapons and ammunition.
- Joint Stock Company Scientific and Production Association Impuls produces automated controls systems used by the Russian Armed Forces and Strategic Missile Forces.
- Joint Stock Company Solikamsk Plant Ural manufactures gunpowder and explosives.
- Joint Stock Company Voronezh Central Design Bureau Polus develops and produces radio monitoring equipment used by the Russian Army and Navy.
- Limited Liability Company Geoscan manufactures UAVs used in Russia’s war against Ukraine.
- Limited Liability Company Kingisepsky Machine Building Plant develops unmanned explosive-carrying boats.
- Limited Liability Company Military Transportation transports Russian military equipment, military vehicles, and air defense systems.
- Limited Liability Company Roboavia Unmanned Systems manufactures an attack UAV used by the Russian military.
- Limited Liability Company Russian Eagle manufactures and sells weapons, ammunition, and ordnance.
- Moran Security Group Ltd (Moran) offers armed security services and has operated under contract to Russian state-owned enterprises. Russian national Alexey Badikov is Moran’s Chief Executive Officer.
- OOO Sepo Zem produces electronic control systems for military aircraft engines.
- PAO Radiofizika develops, tests, produces, installs, maintains, repairs, and sells armaments and military equipment.
- Research and Production Association Named After AS Popov manufactures and develops advanced military communication equipment used by the Russian Ministry of Defense.
- Research and Production Enterprise Kaluga Based Instrument Making Plant Typhoon Joint Stock Company manufactures radio systems and weapons systems used by the Russian Armed Forces.
- Samarskii Zavod Kommunar manufactures weapons, ammunition, small arms, ordnance, and explosives.
- Scientific Production Center of Anti-Terrorist and Forensic Equipment Spektr AT LLC develops, produces, and supplies thermal imaging systems and surveillance and inspection equipment used by the Russian Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) and U.S.-designated Federal Security Service (FSB).
- Ship Repair Yard of the Black Sea Fleet of the Ministry of Defense of the Russian Federation services minesweepers, corvettes, frigates, and other warships.
- Special Materials Corporation develops and produces personal armor protection products used by the Russian Ministry of Defense and the FSB.
- VM Trans Group of Companies LLC transports Russian military equipment.
- Taiber OOO developed drone technology for “kamikaze” drones.
Additionally, Joint Stock Company Shipbuilding Plant Named after B Ye Butoma (Butoma), located in illegally Russian-occupied Crimea, Ukraine, builds warships for Russia’s Black Sea Fleet. Butoma was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the defense and related materiel sector of the Russian Federation economy.
The following Russia-based entities were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the manufacturing sector of the Russian Federation economy:
- Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo Malmyzhskii Zavod Po Remontu Dizelnykh Dvigatelei overhauls engines for U.S.-designated Kamaz, a supplier of armored vehicles to Russia’s military, and is involved in machining and the repair of machinery and equipment.
- Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo Moven NN manufactures and supplies ventilation, climate, and refrigeration equipment for shipbuilding facilities and markets its goods to Russian military customers.
- Scientific and Production Association of Automatics Named after Academician Na Semikhatov develops and manufactures control systems and radio-electronic equipment and markets its goods to Russian military customers.
- Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo NPTS Spetselektronsistemy manufactures 3D structures and micromodules, including semiconductors, and is located at Technopolis Moscow, a special economic zone managed by U.S.-designated Joint Stock Company Special Economic Zone Technopolis Moscow.
- Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo Sinara Transportnye Mashiny sells machinery, repairs and maintains vehicles, including tracked machines, and works with the Government of the Russian Federation.
- JSC The Special Boiler Design Bureau designs, manufactures, and repairs boiler equipment for naval use.
- Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo Strela manufactures electrical equipment and holds a license from the Russian Ministry of Defense.
- Alyans Riteil manufactures metal structures, metal barrels, fabricated metal, and fasteners. Alyans Riteil markets fittings used in special military equipment.
- AOProton Impuls manufactures semiconductors, diodes, transistors, and special purpose machinery. AO Proton Impuls also manufactures circuit boards, a critical component in Russian UAVs.
- AO Proton PM manufactures jet engines and liquid missile engines.
- Armorgrupp manufactures armored vehicles.
- Astrosib repairs electronic, precision, and optical equipment and produces optical instruments.
- Avtonomnoe Uchrezdenie Tekhnopark Mordoviya facilitates the production and assembly of UAVs and operates an industrial park that hosts producers of electronic warfare equipment.
- Belogorodskaya Shipyard Limited Liability Company manufactures berthing complexes and crane vessels and markets its goods to Russian military customers.
- DD Imeks builds, repairs, and maintains ships and conducts machining activities.
- Elektroradioavtomatika JSC manufactures fastening products for cable runs and electrical equipment, electrical connectors and electrical distribution devices, and markets its goods to Russian military customers.
- Gruppa Kompanii Astrokupol develops automated shelters for special-purpose optical equipment.
- Gruppa Promavto manufactures special-purpose vehicles, including vehicles for Russia’s Ministry of Internal Affairs.
- Joint Stock Company Alekseev Central Hidrofoil Design Bureau manufactures high-speed vessels, hydrofoils, hovercrafts, and amphibious platforms, and markets its goods to Russian military customers.
- Joint Stock Company Factory Crizo manufactures electrical equipment for the Russian Navy, including products installed on surface vessels and submarines.
- Joint Stock Company Novaya Era manufactures electric power systems for ships and vessels of the Russian Navy.
- Joint Stock Company NPO Stekloplastic manufactures multifunctional fiber-based materials and state-of-the-art composites with military applications.
- Joint Stock Company OboronAuto manufactures armored vehicles marketed to Russian military customers.
- Joint Stock Company Omskiy Nauchno Issledovatelskiy Institut Priborostroeniya produces electronic warfare systems and specialized communication systems.
- Joint Stock Company Polema manufactures crude iron, steel, tubes, pipes, and steel bars and holds a license for explosive and chemically hazardous production.
- Joint Stock Company Research and Implementation Enterprise Protek manufactures radar equipment.
- Joint Stock Company Research and Production Center Vigstar manufactures electronic components and markets its products to Russian military customers.
- Joint Stock Company Soedinitel manufactures hermetic and corrosion-resistant connectors and cable fittings, and markets its goods to Russian military customers.
- Joint Stock Company SR Space manufactures engines and develops UAVs and UAV detection and suppression systems.
- Joint Stock Company the Central Research Institute Kurs designs shipboard electronic weaponry and onboard equipment for ship-based aircraft and missile weapons.
- Joint Stock Company Tizol manufactures non-combustible insulation materials and structural fire protection systems for shipbuilding, including for military projects.
- Joint Stock Corporation Shipbuilding and Ship Repair Technology Center is a shipbuilding company that provides support for combat ship design and construction and manufactures valves and fittings for all types of ships and vessels.
- JSC Research and Production Company Magneton manufactures magnets and industrial magnetic systems used by the Russian Ministry of Defense.
- JSC Resurs manufactures fixed resistors, resistor sets, microwave resistors, and absorbers, which it markets to Russian military customers.
- Lifors designs and manufactures electric accumulators and batteries and sells voltage regulators, which are critical components in Russian UAVs.
- Limited Liability Company Carbontex manufactures composites from 3D weaved volumetrically reinforced all-woven preforms, which it markets to Russian military customers.
- Limited Liability Company Merkator Holding manufactures machinery and equipment, including snow removal machines used by the Russian Ministry of Defense.
- Limited Liability Company Neva Tool Factory manufactures nodes, parts, rotary-plunger hydraulic motors, and tools, which it markets to Russian military customers.
- Limited Liability Company Plastik Stroymarket manufactures anticorrosive materials, integrated waterproof mixtures, adhesives, and sealants, which it markets to Russian military customers.
- Limited Liability Company Production Plant Named After Shaumyan manufactures lubrication oils and greases approved for use in weapons and military equipment by the Russian Ministry of Defense.
- Limited Liability Company Rosizolit produces components for UAVs and supplies composite materials to the Russian military-industrial base.
- Limited Liability Company Scientific and Production Association of Structural Materials Prometey manufactures ship fittings, deck equipment, as well as various marine equipment, including pneumatic tankers, spires, hatch closures, and steering machines, and markets its goods to Russian military customers.
- Limited Liability Company Scientific Production Company Advent produces rotary support devices and ship structures for clients including Russian government agencies.
- Limited Liability Company Volgograd Ship Engineering Plant produces ship portholes, hatches, viaducts, fittings for ventilation, and air conditioning systems used for equipping Russian military surface vessels and ships.
- LKKA Company Limited produces springs and wires and markets its products to the Russian Armed Forces.
- Lyskovskii Elektrotekhnicheskii Zavod manufactures printed circuit boards and power tools and produces generators for Russia’s military industry.
- Limited Trade Development Chimtech-R manufactures sealant materials supplied to the Russian military-industrial base.
- Marine Equipment Engineering Corporation JSC manufactures integrated combat information and control systems, radar and sonar equipment, and navigation and communication systems.
- Microem manufactures connectors and cable assemblies for all types of applications and components for computer and server equipment. Microem imports components used in Russian UAV navigation modules.
- Nauchno Proizvodstvennaya Firma Trekol manufactures all-terrain vehicles and markets its vehicles to Russian military customers.
- Nauchno Proizvodstvennoe Obyedinenie Gorizont develops and manufactures optical electronic modules, industrial computers, and anti-drone systems.
- OOO Gazprommash manufactures machinery and holds licenses for the operation of explosive production facilities.
- OOO Soyuz Podshipnik manufactures bearings, including for U.S.-designated Russian military armored vehicle supplier Kamaz.
- OOOValcom develops and manufactures high-precision intelligent sensors and integrated automation systems for specialized vessels, including icebreakers and naval vessels.
- Otkrytoe Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo Vladimirskii Zavod Elektropribor manufactures metal structures and electronic printed circuits and is a partner of U.S.-designated JSC Aerospace Defense Concern Almaz-Antey, a Russian state-owned enterprise that designs, develops, and manufactures anti-aircraft, anti-missile, and non-strategic missile defense systems.
- PJSC Rostov Optical and Mechanical Plant manufactures night vision devices for fire control systems in armored military equipment.
- PKP Segment Energo produces cables meant to operate in extreme conditions that are marketed to Russian military customers.
- Public Joint Stock Company Priboy produces automated submarine radios.
- Regional Center of Laser Technologies CJSC is involved in 3D laser cutting, laser welding, and processing of titanium and markets its products to Russian military customers.
- Research And Production Company Micran Joint Stock Company manufactures electronic devices, radar systems, test and measurement equipment, and mobile and complex communication solutions.
- Rezonit manufactures printed circuit boards, which are critical components used in Russian UAVs.
- Rotor works with aircraft and electrical equipment and is involved in the production of electrotechnics and electronics.
- Shiprepairing And Shipbuilding Corporation JSC manufactures, repairs, and maintains vessels and related equipment for the Russian Navy.
- Sitem manufactures metal structures, fabricated metal products, and machinery. Sitem supplies, designs, and installs surveillance systems, perimeter protection systems, and supplies thermal imaging equipment.
- Technology Research Centre Ank LTD develops and manufactures sealed accumulators and battery products, including lithium-ion storage batteries for unmanned and manned underwater vehicles.
- TPK Vostok Resurs manufactures specialized materials and works with specialized machines. TPK Vostok Resurs has received items from U.S.-designated Yantai Iray Technology Co Ltd, a supplier of telescopic and thermal sights to Russia.
- Troitsk Crane Plant Limited Liability Company produces specialized equipment for shipbuilding and ship repair and markets its products to Russian military customers.
- Ural Metal Processing Company LTD manufactures packaging tapes, pipes, and steel profiles used to package military-industrial complex loads.
The following Russia-based persons were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the technology sector of the Russian Federation economy:
- Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo Kontsern Radiostroeniya Vega is a Russian government enterprise that develops, produces, and repairs radio electronic systems and equipment, as well as special-purpose systems and components.
- Federal State Autonomous Scientific Institution Central Research and Experimental and Design Institute of Robotics and Technical Cybernetics is a Russian government institution that conducts work in robotics, photonics, and optoelectronic systems.
- Institute of High Current Electronics Siberian Branch Russian Academy of Sciences develops devices and technologies for electronics, plasma physics, quantum electronics, and photonics, and has participated in a conference hosted by a U.S.-designated Russian weapons laboratory.
- Joint Institute for High Temperatures of the Russian Academy of Sciences researches energy efficient technologies and combustion, detonation, and explosions, and has participated in a conference hosted by a U.S.-designated Russian weapons laboratory.
- Joint Stock Company Institute for Networking Technology develops software and markets its secure multiservice networks and communication infrastructure to the Russian Armed Forces.
- Joint Stock Company Sitronics KT develops ship control systems and geographic information systems marketed to Russian military customers.
- Limited Liability Company Farad supplies electronic components, including transistors, which are a component in Russian UAVs.
- Limited Liability Company GK Triz Robotics develops software for robotics and offers simulators to provide experience in the field of robotics and computer numerical control (CNC) for milling and tuning.
- Limited Liability Company Prime Radar Technology develops UAV detection and suppression technology and portable jammers.
- Limited Liability Company RevolEMC (RevolEMC) provides information security services for information systems and information facilities and produces and supplies anechoic chambers and shielded telecommunication cabinets.
- Limited Liability Company Yuzhpolymetal Holding produces mobile technology for chemical analysis used by the Russian Ministries of Internal Affairs and Defense and the FSB.
- LLC Applied Mechanics specializes in engineering and radio-electronics, and produces radio-electronics, high-precision mechanisms including hexapods, and motion simulators, which it markets to Russian military customers.
- Ostec Smart Technologies Limited Liability Company specializes in the implementation of technological solutions for electronics assembly and installation, and imports semiconductor production machines.
- Paritet sells electronics and computers and is involved in data processing and information technology.
- Research and Manufacturing Association Development of Innovative Technologies develops aircraft computing equipment and software that it markets to Russian military customers.
- Special Design Bureau of Electric Instrument Engineering LLC produces instruments used for electrotechnical equipment diagnostics and electric modules that it markets to Russian military customers.
- Timkom imports field-programmable gate arrays from the PRC.
- Zakrytoe Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo Zolotoi Shar is one of the largest Russian suppliers of imported electronic components.
Russia-based Limited Liability Company Bank Tochka (Bank Tochka), founded in 2023, provides financial services to an organization that supports Russian combat troops and to an entity that provides ammunition to Russian military personnel. Bank Tochka was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the financial services sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Russia-based Ekodor is involved in transportation activities, including cargo handling, transport forwarding, and rail transport. Ekodor was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the transportation sector of the Russian Federation economy.
ANNEX 3: LIMITING RUSSIA’S FUTURE REVENUE FROM LIQUEFIED NATURAL GAS
The following Russia-based persons were designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the construction sector of the Russian Federation economy:
- Aktsionernoe Obshchestvo RusGazDobycha is implementing the construction of a natural gas processing and liquefaction facility in Russia.
- Arktik SPG 1 manages and supervises construction projects and is developing a gas production site.
- Limited Liability Company Obsky Gas Chemical Complex is implementing the construction of a gas production and processing site in Russia.
- OOO Gazprom Invest designs and constructs gas industry facilities.
Russia-based Arktik SPG 3 is involved in geological exploration, including prospecting and evaluation of mineral deposits. Arktik SPG 3 also mines clay, sand, kaolin, gravel, and other minerals. Artktik SPG 3 was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the metals and mining sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Russia-based Limited Liability Company International Innovation Center for Marine Structures and Ship Repair (International Innovation Center) manufactures enclosed sections of vessels for U.S.-designated shipbuilder Limited Liability Company Shipbuilding Complex Zvezda (Zvezda), which is involved in the construction of specialized liquefied natural gas (LNG) tankers. International Innovation Center was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the manufacturing sector of the Russian Federation economy.
Russia-based Regent Baltica Company Limited (Regent Baltica) manufactures cryogenic isothermal panels for LNG storage. Regent Baltica was designated pursuant to E.O. 14024 for operating or having operated in the manufacturing sector of the Russian Federation economy.
U.S.-designated Joint Stock Company Sovcomflot (Sovcomflot) is the operator of four LNG tankers that are currently under construction. The following four vessels were identified pursuant to E.O. 14024 as property in which Sovcomflot, a person whose property and interest in property are blocked pursuant to E.O. 14024, has an interest:
- Sergei Witte (IMO: 9904687)
- Alexey Kosygin (IMO: 9904546)
- Pyotr Stolypin (IMO: 9904675)
- Zvezda 044 (IMO: 9904699)
U.S.-designated Zvezda is building an additional three LNG tankers at its shipyard. The following vessels were identified pursuant to E.O. 14024 as property in which Zvezda, a person whose property and interest in property are blocked pursuant to E.O. 14024, has an interest:
- Zvezda 047 (IMO: 9918781)
- Zvezda 046 (IMO: 9918779)
- Zvezda 045 (IMO: 9904704)
SANCTIONS IMPLICATIONS
As a result of today’s action, all property and interests in property of the persons above that are in the United States or in the possession or control of U.S. persons are blocked and must be reported to OFAC. In addition, any entities that are owned, directly or indirectly, 50 percent or more by one or more blocked persons are also blocked. All transactions by U.S. persons or within (or transiting) the United States that involve any property or interests in property of designated or blocked persons are prohibited unless authorized by a general or specific license issued by OFAC, or exempt. These prohibitions include the making of any contribution or provision of funds, goods, or services by, to, or for the benefit of any blocked person and the receipt of any contribution or provision of funds, goods, or services from any such person.
In addition, foreign financial institutions that conduct or facilitate significant transactions or provide any service involving Russia’s military-industrial base run the risk of being sanctioned by OFAC. For additional guidance, please see the updated OFAC advisory, “Updated Guidance for Foreign Financial Institutions on OFAC Sanctions Authorities Targeting Support to Russia’s Military-Industrial Base,” as well as OFAC Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) 1146-1157.
The power and integrity of OFAC sanctions derive not only from OFAC’s ability to designate and add persons to the SDN List, but also from its willingness to remove persons from the SDN List consistent with the law. The ultimate goal of sanctions is not to punish, but to bring about a positive change in behavior. For information concerning the process for seeking removal from an OFAC list, including the SDN List, please refer to OFAC’s FAQ 897 here. For detailed information on the process to submit a request for removal from an OFAC sanctions list, please click here.
Any persons included on the SDN List pursuant to E.O. 14024 may be subject to additional export restrictions administered by the Department of Commerce, Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS).
For identifying information on the individuals and entities sanctioned today, click here.
US unveils sweeping sanctions targeting Russia over Ukraine war
The United States announced a raft of new sanctions Wednesday aimed at constraining Moscow's war in Ukraine while raising the stakes for foreign banks that still deal with Russia, ahead of G7 talks.
The Treasury Department and State Department's sanctions hit more than 300 targets, including entities in Russia and in countries like China, Turkey and the United Arab Emirates.
Those designated include the Moscow Exchange and several subsidiaries, a move set to complicate billions of dollars in transactions, as well as entities involved in liquefied natural gas (LNG) projects.
"Today's actions strike at their remaining avenues for international materials and equipment, including their reliance on critical supplies from third countries," said Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen.
"We are increasing the risk for financial institutions dealing with Russia's war economy and eliminating paths for evasion, and diminishing Russia's ability to benefit from access to foreign technology, equipment, software, and IT services," she added.
Secretary of State Antony Blinken said separately that the United States "remains concerned by the scale and breadth of exports" from China supplying Moscow's military industry.
Russia vowed to respond to the "aggressive" the latest sanctions, according to the state-run TASS news agency, while Moscow Exchange said it would halt foreign exchange trading in dollars and euros.
Besides fresh sanctions, the Treasury is broadening its definition of Russia's "military-industrial base."
Until now, foreign banks could be sanctioned for supporting Russia's defense industry. The latest step expands the reach of so-called secondary sanctions to all Russian individuals and entities that have already been impacted by US sanctions.
This means foreign financial institutions could be hit for conducting transactions involving any blocked person or designated Russian banks like VTB or Sberbank -- with the list of exposed targets growing from over 1,000 to about 4,500.
Washington is also restricting the supply of IT services and software support to people in Russia.
- Global networks -
The latest sanctions impact transnational networks, hitting more than 90 people and entities in China, South Africa, Turkey and the UAE.
The United States charges that goods and services from these foreign networks helped Russia to sustain its war and avoid sanctions.
A senior US official told reporters Wednesday that efforts to restrict Russia's ability to sustain the war in Ukraine have had a "significant impact."
"Global exports to Russia have fallen by almost $90 billion, and US exports to Russia have essentially halted for everything but certain medical items like vaccines," the official added on condition of anonymity.
The Treasury also expanded its list of information for five sanctioned Russian financial institutions to include addresses and aliases of their foreign locations.
In a separate statement, the Commerce Department said it was adding eight Hong Kong addresses to a blacklist, in a move targeting shell companies.
The addresses listed will impact almost $100 million in high-priority items including semiconductors, the US official said, adding that much of the circumvention appears to be going through entities in China.
Washington's actions come ahead of this week's G7 summit in Italy.
The White House earlier said that steps to aid Ukraine using frozen Russian assets would be announced during the gathering.
G7 leaders hope to reach a deal on using the profits from the interest on 300 billion euros ($325 billion) of immobilized Russian central bank assets to help Kyiv. The idea is to use the profits as collateral for a loan of up to $50 billion.
US widens sanctions on Russia to discourage countries such as China from doing business with Moscow
Posted:
Updated:
The United States widened its sanctions against Russia Wednesday as G7 leaders prepared to gather in Italy for a summit where the top priorities will be boosting support for Ukraine and grinding down Russia’s war machine.
Wednesday’s package targeted Chinese companies which help Russia pursue its war in Ukraine and raised the stakes for foreign financial institutions which work with sanctioned Russian entities.
It also targeted Russia’s financial infrastructure, in an attempt to limit the amount of money flowing in and out of Russia. Shortly after the sanctions were made public, the Moscow Exchange announced it would suspend transactions in dollars and euros.
The U.S. has sanctioned more than 4,000 Russian businesses and individuals since the war began, in an effort to choke off the flow of money and armaments to Moscow, whose superior firepower has given it an advantage on the battlefield in recent months. Nonetheless, new companies continually pop up as Russia attempts to rework supply chains.
“We have to be very honest with ourselves that Putin is a very capable adversary who is willing to adapt and find those willing collaborators,” Aaron Forsberg, the State Department’s Director for Economic Sanctions Policy and Implementation, told The Associated Press.
Sanctions against Russia, he said, are therefore a “dynamic affair.”
That includes listing addresses for the first time in a bid to crack down on companies reopening at the same address under a different name.
While sanctions have not stopped the flow of illicit goods, the aim is to make it harder for Russia to source crucial technology as well as drive up the markup on the goods. Wednesday’s package targets more than $100 million in trade between Russia and suppliers for its war.
More than 300 new sanctions are largely aimed at deterring individuals and companies in countries including China, the United Arab Emirates and Turkey from helping Moscow circumvent Western blocks on obtaining key technology. They also threaten foreign financial institutions with sanctions if they do business with almost any sanctioned Russian entity, underscoring the U.S. view that the Kremlin has pivoted the Russian economy to a war footing.
Russia’s military is “desperate for access to the outside world,” said Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen.
The announcement came shortly before President Joe Biden arrived in Italy where he and other G7 leaders are urgently looking at aiding Ukraine, including turning frozen Russian assets into billions of dollars of support for Kyiv.
Seven Chinese and Hong-Kong-based companies were targeted Wednesday for shipping millions of dollars of material to Russia, including items which could be used in Russian weapons systems.
U.S. officials say China is the leading supplier of critical components to Russia, supplying both Chinese and Western technology.
On Wednesday the U.S. sanctioned a Chinese state-owned defense company which officials said had shipped military equipment for use in the Russian defense sector.
The move sends the message that the U.S. is “willing to wade into more treacherous territory” by increasing the pressure on the Chinese government, said Benjamin Hilgenstock, senior economist at the Kyiv School of Economics.
“We will address (China’s) support for the Russian defense industrial base. And we will confront China’s non-market policies that are leading to harmful global spillovers,” White House national security spokesman John Kirby told reporters Tuesday.
China did not sanction Russia after President Vladimir Putin invaded Ukraine, and Putin ended a visit to China in May by emphasizing the two countries’ burgeoning strategic ties.
“The Chinese leadership is not interested in making these sanctions a success,” said Janis Kluge, a Russia sanctions specialist at the German Institute for International and Security Affairs in Berlin (SWP.)
Beijing, Kluge said, is reluctant to stop a valuable trade that is worth large amounts of money and it does not want to “add to the pressure on Putin in this war.”
Imports from China are vital to Russia because Beijing is a major producer of critical components, including for Western companies. Chinese companies also act as intermediaries for the sale and shipment of Western components to Russia.
But while Chinese technology has been found on the battlefield in Ukraine, most of the components still come from Western nations including those which are “overwhelmingly” found in high-tech drones and ballistic missiles, said Hilgenstock.
As well as China, the U.S. targeted businesses in Turkey and the United Arab Emirates which officials said sent high-priority items to companies in Russia, including to businesses which were already sanctioned.
In December, the White House said foreign financial institutions could be sanctioned if they worked with entities in Russia’s defense sector. Wednesday’s expansion of sanctions now means that those institutions could face such measures if they work with almost any sanctioned Russian entity.
U.S. President Joe Biden’s top foreign policy adviser, Jake Sullivan, told reporters on the way to the G7 that the message to China and other countries was that they are “at serious risk of running afoul of the Treasury Department and falling under a sanctions regime.”
The fear of triggering secondary sanctions is an effective threat, analysts said.
While President Xi Jinping may not want to facilitate Western sanctions on Russia, “Chinese banks have always been very careful not to become a target of secondary sanctions because it would be very costly,” Kluge said, pointing to cases where Chinese banks have ended relationships with Russian customers.
The package also aims to hobble the development of Russia’s energy sector and future sources of cash, including Arctic liquified natural gas projects which have been shipped critical LNG technology by a Chinese company.
In addition, the package targeted people involved in the forced transfer and deportation of Ukrainian children to Russia. Five people in Russia and Russian-occupied Ukraine were sanctioned after participating in the forced militarization and reeducation of the children and providing them with Russian passports.
—-
AP White House Reporter Colleen Long aboard Air Force One contributed to this report

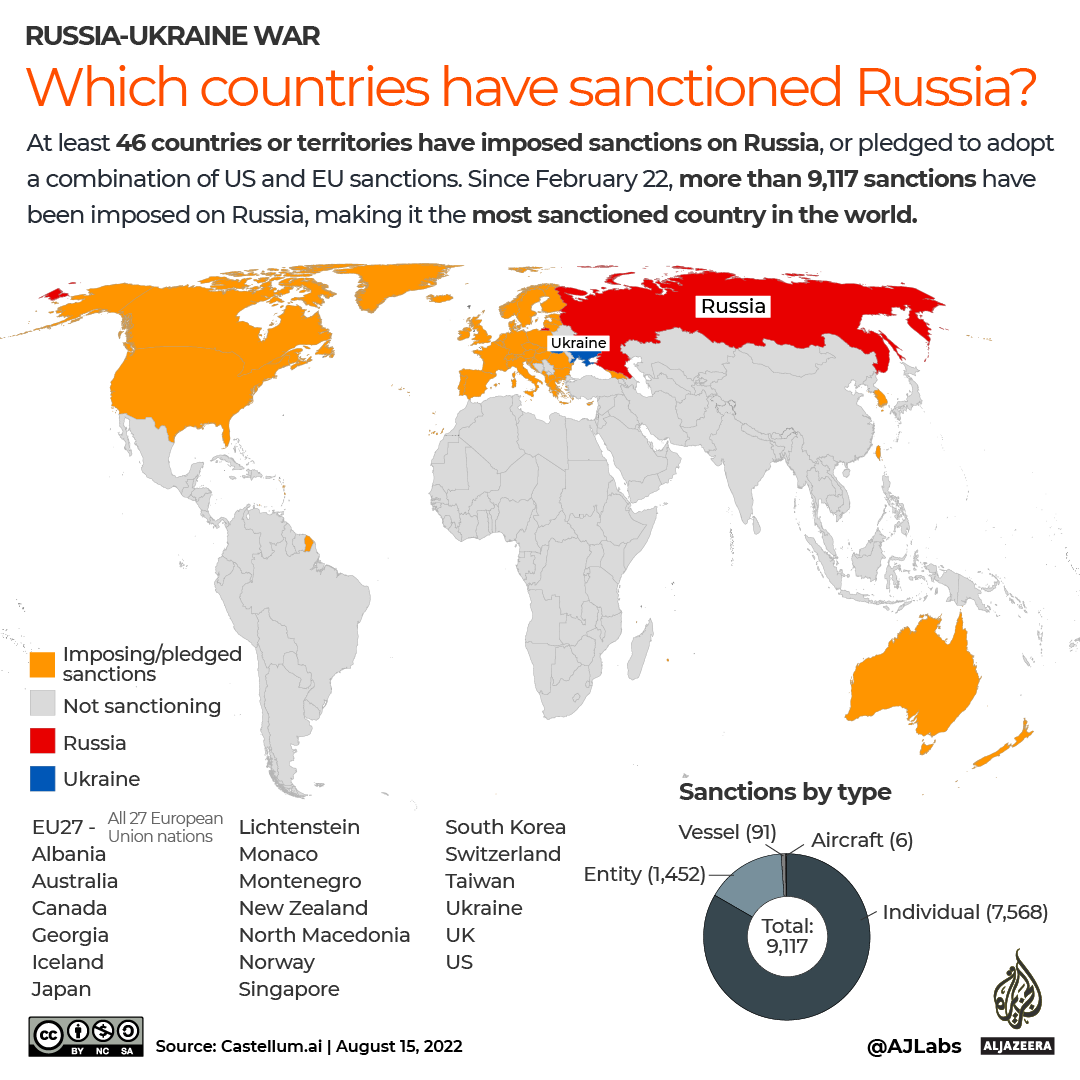



















No comments:
Post a Comment