- INTERNET
Wednesday, 10 Jul 2024
TECHNOLOGY
Wired World: 35 Years of Submarine Cables in One Map
Published 5 years agoon December 2, 2019
By Nick Routley
Long gone are the days when images would load pixel row by pixel row. Now, even high-quality video is instantly accessible from almost everywhere. How did the internet get so fast? Because it’s moving at the speed of light.
The Information Superhighway
The miracle of modern fiber optics can be traced to a single man, Narinder Singh Kapany. The young physicist was skeptical when his professors asserted that light ‘always travels in a straight line’. His explorations into the behavior of light eventually led to the creation of fiber optics—essentially, beaming light through a thin glass tube.
The next step to using fiber optics as a means of communication was lowering the cable’s attenuation rate. Throughout the 1960-70s, companies made gains in manufacturing, reducing the number of impurities and allowing light to cross great distances without a dramatic decrease in signal intensity.
By the mid-1980s, long distance fiber optic cables had finally reached the feasibility stage.
Crossing the Pond
The first intercontinental fiber optic cable was strung across the floor of the Atlantic Ocean in 1988. The cable—known as TAT-8*—was spearheaded by three companies; AT&T, France Télécom, and British Telecom. The cable was able to carry the equivalent of 40,000 telephone channels, a ten-fold increase over its galvanic predecessor, TAT-7.
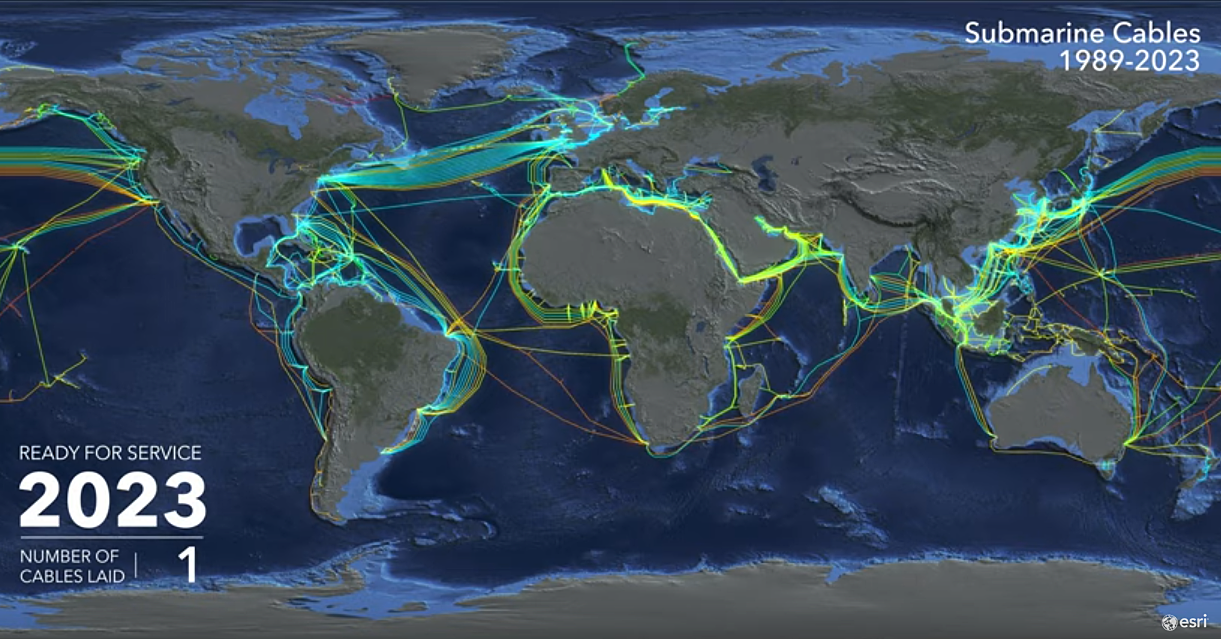
Once the kinks of the new cable were worked out, the floodgates were open. During the course of the 1990s, many more cables hit the ocean floor. By the dawn of the new millennium, every populated continent on Earth was connected by fiber optic cables. The physical network of the internet was beginning to take shape.
As today’s video from ESRI shows, the early 2000s saw a boom in undersea cable development, reflecting the uptick in internet usage around globe. In 2001 alone, eight new cables connected North America and Europe.
From 2016-2020, over 100 new cables were laid with an estimated value of $14 billion. Now, even the most remote Polynesian islands have access to high-speed internet thanks to undersea cables.
*TAT-8 does not appear in the video above as it was retired in 2002.
The Shifting Nature of Cable Construction
Even though nearly every corner of the globe is now physically connected, the rate of cable construction is not slowing down.
This is due to the increasing capacity of new cables and our appetite for high-quality video content. New cables are so efficient that the majority of potential capacity along major cable routes will come from cables that are less than five years old.
Traditionally, a consortium of telecom companies or governments would fund cable construction, but tech companies are increasingly funding their own submarine cable networks.
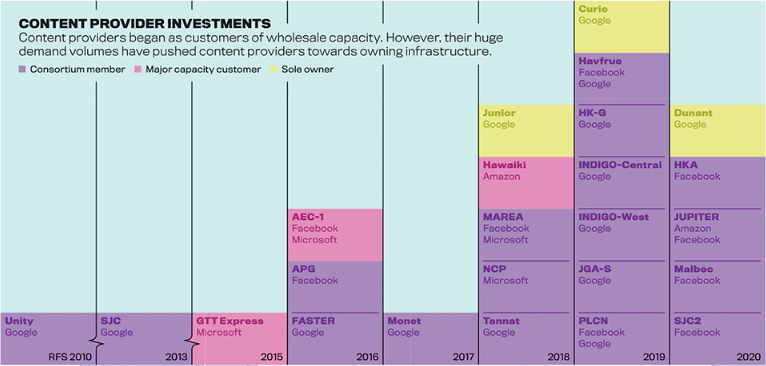
Amazon, Microsoft and Google own close to 65% market share in cloud data storage, so it’s understandable that they’d want to control the physical means of transporting that data as well.
These three companies now own 63,605 miles of submarine cable. While laying cable is a costly endeavor, it’s necessary to meet surging demand—content providers’ share of data transmission skyrocketed from around 8% to nearly 40% over the past decade.
A Bright Future for Dark Fiber
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
INTERNET UNDERSEA CABLES NEWS MONITORING
- Published on Jul 9, 2024

NATO funds project to reroute internet via satellites if undersea cables are cut
In brief: Fears that a rogue nation could attack undersea cables as a way of impacting internet connectivity and digital communications have risen in recent times. To prepare for the worst, NATO is helping to finance a project that will investigate a way …
Source: TechSpot - NEUTRAL - Published on Jul 9, 2024

NATO Supports to Reroute Internet from Undersea Cables to Space
A NATO banner seen outside the Washington convention center where the NATO summit will be taking place in Washington, DC, from July 9th to the 11th. (Photo : MANDEL NGAN/AFP via Getty Images) On the eve of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization's ( …
Source: Venture Capital Post - UNCATEGORIZED - Published on Jul 9, 2024

NATO plans to send internet to space if subsea cables are cut
According to a new Bloomberg report, NATO is backing a project aimed at ensuring continuous internet connectivity should undersea cables, crucial for digital communications, come under attack. Researchers from the US, Iceland, Sweden and Switzerland are …
Source: TechRadar Pro - LABEL PENDING - Published on Jul 9, 2024

Tonga struggles with internet outages, considers Starlink amid cable repair delay
Internet users in Tonga’s Vava’u and Ha’apai islands are still facing connectivity issues, since last week’s abrupt disconnection, as a cable repair ship is nine days away. Reports of difficulties with telephone calls and intermittent ATM and EFTPOS …
Source: Talanoa 'O Tonga - LABEL PENDING - Published on Jul 8, 2024
NATO Backs Effort to Save Internet by Rerouting to Space in Event of Subsea Attacks
(Bloomberg) -- NATO is helping finance a project aimed at finding ways to keep the internet running should subsea cables shuttling civilian and military communications across European waters come under attack. Researchers, who include academics from the …
Source: BNN Bloomberg - NEUTRAL - Published on Jul 8, 2024

Nato backs effort to save internet by rerouting to space in event of subsea attacks
Eyup Kuntay Turmus, adviser and programme manager at the Nato programme, confirmed the project was recently approved and said by email that implementation will start “very soon”. The initiative, which has not yet been publicly announced, comes amid …
Source: South China Morning Post - UNCATEGORIZED - Published on Jul 9, 2024

Safaricom scrambles to shore up Gen Z market in wake of protests
Safaricom CEO Peter Ndegwa during The launch of Spark Accelerator - a program to support start- ups at Micheal Joseph Centre, Safaricom House in Nairobi on January 12, 2024 [Boniface Okendo, Standard] Last week, Safaricom sent out an invite for a media …
Source: The Standard - UNCATEGORIZED - Published on Jul 9, 2024

Senate NDAA 2025 Boosts Military Cyber and AI Initiatives
AI-Based Attacks , Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning , Fraud Management & Cybercrime Military Omnibus Bill Includes Focus on Cybersecurity, Countering Drone Technology Chris Riotta (@chrisriotta) • July 9, 2024 The nearly $1 trillion …
Source: Bank Information Security - New Jersey - NEUTRAL - Published on Jul 1, 2024

Why Taiwan Needs to Secure Its Undersea Cables By Jordan McGillis and Pieter van Wingerden In the context of an ...
With each passing month, Taiwan’s global economic profile rises. The latest flurry of enthusiasm was set off by the return of the island’s long-departed native son, Nvidia founder Jensen Huang, who visited for the Computex tech confab in June. More than …
Source: The Diplomat - NEUTRAL - Published on Jul 1, 2024
Iraq Enhances Internet Connectivity with New Undersea Cable Agreement
By John Lee. The Iraqi Ministry of Communications, under the direct supervision of Minister Dr. Hayam Al-Yasiri, announced the signing of a contract for the deployment of the 2Africa Pearls undersea cable. The agreement, signed with Gulf Submarine Cables …
Source: Iraq Business News - NEUTRAL - Published on Jul 1, 2024
New Undersea Cable Routes Underpin Vietnam’s Digital Ambitions
Vietnam has unveiled an ambitious plan to significantly enhance its digital infrastructure by constructing at least 10 new undersea cable routes by 2030, increasing the total to 15 routes with a minimum capacity of 350 Tbps. This strategic development, …
Source: OpenGov Asia - NEUTRAL - Published on Jun 30, 2024

Undersea Cables at Risk of Vulnerable Key Communication Links amid Geopolitical Tensions
Last March, a significant communication cable cutting incident occurred in the Indian Ocean, reportedly interrupting about 25% of data flow between Asia and Europe. Yemeni Houthi rebels were suspected of deliberately cutting the undersea cable, …
Source: Business Korea - NEUTRAL

.jfif)



No comments:
Post a Comment