Reports about the installation of GBU-39 on Ukrainian aircraft — according to analysts — may explain some of the recent attacks on Russian positions, including an occupied hospital in Vovchansk. . .
GBU-39 bombs under a Ukrainian aircraft
It is also significant that the GBU-39 bombs are most likely resistant to interference generated by Russian electronic warfare systems. Detecting and intercepting this American ammunition is also difficult due to the missile's small size.
- The precision of hitting targets with the GBU-39 bomb is also significant. The hit accuracy is estimated at 5–8 meters, which minimizes the risk of hitting a random civilian object.
- Accuracy is guaranteed not only by the GPS but also by the wings of the bomb, which unfold during the dive phase.
- Thanks to them, an extensive strike range can also be achieved. It can reach up to 109 kilometres when the ammunition is dropped from a high altitude.
GBU-39 can cause significant devastation on the front, primarily due to its difficulty in detection and potent destructive power. Equipped with a tungsten tip construction (fuselage), it can penetrate concrete shelters made of thick walls, while the detonation system allows for a delayed explosion after impact.
As a result, GBU-39 can penetrate heavily fortified structures and detonate inside them — without the risk that concrete walls will protect the infrastructure from the strike. This is a characteristic that Ukrainians can use, for example, to attack objects occupied by Russians, as well as shelters (e.g., aircraft shelters) where valuable tools (like aeroplanes) are hidden.
Boeing awarded GBU-39 bombs contract for Bulgarian, Ukrainian F-16s
The U.S. Air Force recently awarded a contract to Boeing Co., based in St. Louis, Missouri, with a ceiling value of $6.9 billion. This contract is designated for the production of GBU-39 Small Diameter Bombs Increment One. The final recipients of this ammunition will be Japan, Bulgaria, and Ukraine. Covering lots 20-29, the work on this contract is anticipated to be completed by the end of 2035.

- HVGP hypersonic missile system captured on Japanese highway
- Dassault Aviation pushes Indonesia to acquire 100 Rafale jets
- Dramatic moment: Russian Su-35 passes inches from USAF F-16
Details regarding other contract parameters have not been disclosed by the U.S. Air Force. Japan utilizes two types of American aircraft – the F-15J and the F-35A.
In contrast, Bulgaria and Ukraine both operate F-16s. Notably, Ukraine has begun flying the initially delivered F-16 AM/BM Block 20, whereas Bulgaria is set to receive the first of its 16 Block 70/72 F-16 fighters in 2025.
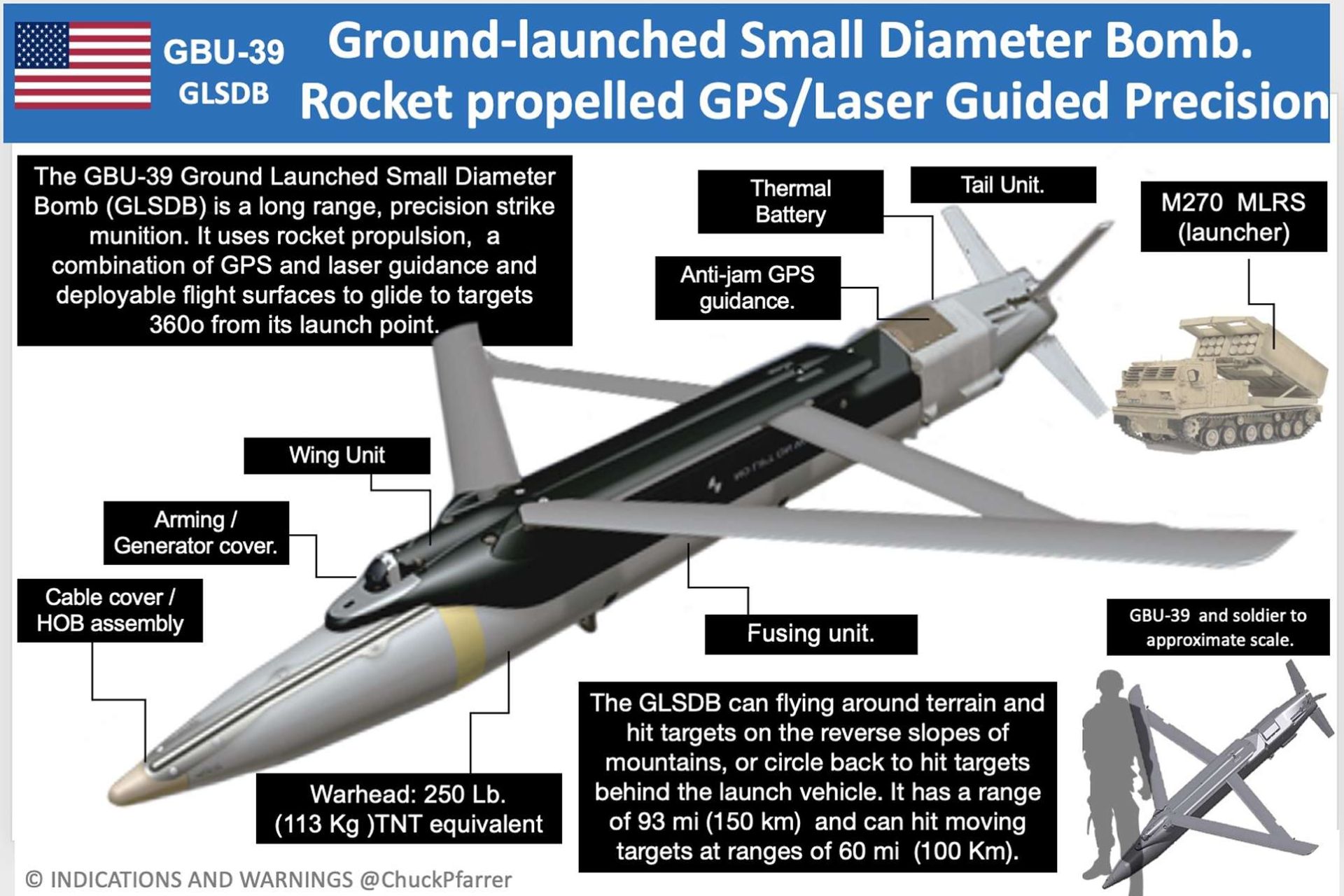
The GBU-39 Small Diameter Bomb [SDB] is a precision-guided small-diameter weapon designed to destroy targets with minimal collateral damage.
- It weighs about 113 kg and has a length of 1.8 meters, and it can be mounted on various combat aircraft.
- It is equipped with a GPS/INS guidance system, which provides it with high precision when hitting targets in different weather conditions.
- The bomb has a small radius of defeat and is effective against fortified targets due to its penetrating warhead.

The GBU-39 has a range of up to 110 km when launched from high altitude, allowing the carrier aircraft to engage targets from a safe distance. In addition, its small size allows aircraft to carry several such bombs on one pylon, increasing the platform’s firepower. The bomb is suitable for both conventional and stealth operations thanks to its minimal radar footprint.
The GBU-39 entered operational use in 2006 and quickly proved its effectiveness in combat. The weapon was first used by the US Air Force during military operations in Iraq and Afghanistan, where its high accuracy and minimal collateral damage were especially valued when striking densely populated areas. Thanks to its small size and precision targeting, the SDB allows pilots to engage fortified targets with minimal risk to civilians and infrastructure.
In subsequent years, the GBU-39 has been used in several international conflicts, including Syria and Libya, where allied forces continue to rely on its accuracy and effectiveness. The bomb is integrated into a variety of combat aircraft, including the F-15, F-16, F-22, and F-35, making it an essential component of NATO and other partner nations’ air campaigns. Its widespread use demonstrates the weapon’s versatility and ability to meet a wide range of military tasks.
- Bulgaria contracted for the delivery of eight F-16 Block 70 fighter jets in 2019 as part of the modernization of its air force.
- This was the first order of fighters of this type for the country, with which Bulgaria aimed to replace the outdated Soviet MiG-29 aircraft.
The deal was worth about $1.256 billion and included, in addition to the planes, pilot, and ground crew training as well as armaments. Subsequently, in 2022, Bulgaria approved an additional order for eight more F-16s, bringing the total number of aircraft to 16.
- The Netherlands and Denmark are among the first countries to pledge to provide aircraft to the Ukrainian Air Force.
- In August 2023, the Netherlands announced its intention to deliver up to 42 F-16 aircraft to Ukraine, depending on the progress of pilot and technical personnel training.
- Denmark has also committed to providing 19 fighter jets, with the first to be delivered later that year.

In August 2024, Ukraine officially received the first F-16s from Denmark. At the same time, the process of training Ukrainian personnel continues in various countries, including the USA. The F-16 fighters are part of efforts to increase the combat capabilities of the Ukrainian Air Force in the face of the ongoing conflict with Russia.
- Sending GBU-39s to Japan, Bulgaria, and Ukraine is not just a transaction; it is an expression of US strategic interests in various regions.
- In Japan, the expansion of defense capabilities is key in the context of China’s growing military presence in the Pacific region.
- The Japanese Air Force, which operates the F-15J and F-35A, is seeking to strengthen its precision strike capability, particularly in the context of territorial disputes and the growing threat of missiles.
Regarding Bulgaria, the country is looking to renew and modernize its air force, pursuing strategic partnerships with NATO. The delivery of the GBU-39 is a strategic signal to strengthen cooperation between the US and Bulgaria, which is of particular importance in light of the volatile situation in the region, especially Russia.

In the case of Ukraine, the delivery of the GBU-39 is critical to increasing the country’s defense capabilities in the context of the conflict with Russia. The precise and effective strikes that SDB offers can prove decisive in battles affecting key infrastructure targets and enemy military equipment.
The strategic procurement of the GBU-39 not only strengthens the defense capabilities of these nations but also solidifies US influence in the global defense architecture. It is important to emphasize that through this type of treaty, the US not only strengthens its allies but also controls the spread of high-tech weapons, which is a strategically important aspect of international politics.







No comments:
Post a Comment