Monday, January 05, 2026
CONSTELLATION PAYLOAD DEPLOYMENT: SpaceX COSMO-Skymed satellite in amazing view from space
Tonight's liftoff was the first of 2026 not just for SpaceX but for the global launch community.
It's no surprise that SpaceX is breaking in the year. Elon Musk's company launched a whopping 165 orbital missions in 2025 — far more than any other entity, either commercial or governmental. That was also a record for SpaceX, which the company may aim to break again this year.
Editor's note: This story was updated at 9:25 p.m. ET on Jan. 2 with news of successful launch, rocket landing and satellite deployment.
A Falcon 9 rocket lifted off from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California tonight at 9:09 p.m. EST (6:09 p.m. local California time; 0209 GMT on Jan. 3), carrying an Italian Earth-observing satellite to orbit.
The rocket's first stage landed back at Vandenberg as planned about 8.5 minutes after liftoff. It was the 21st flight for this particular booster, according to SpaceX.
About 4.5 minutes later, the Falcon 9's second stage deployed the payload — a COSMO-SkyMed Second Generation satellite — into low Earth orbit for the Italian Space Agency and the Italian Ministry of Defense.
COSMO-SkyMed Second Generation is a
small network designed to "monitor the Earth for the sake of emergency
prevention, strategy, scientific and commercial purposes, providing data
on a global scale to support a variety of applications," -------according to a European Space Agency explainer.
Among
those applications are
- "risk management,
- cartography,
- forest & environment protection,
- natural resources exploration,
- land management,
- defense and security,
- maritime surveillance,
- food & agriculture management," ___________________the explainer adds.
OBSESSED: The Daily Beast
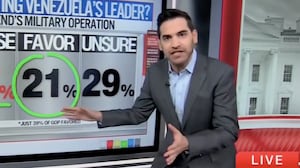
Squealing Stephen Miller Loses It on CNN in Venezuela Debate
HYSTERIA HOUR
“You love doing that smarmy thing, Jake, and I was hoping you’d be better than that this time,” Miller said.



Top Trump Target Quits After Being Hit by Vile Murder Slur
OVER AND OUT
The former VP candidate has faced growing scrutiny over allegations of widespread fraud in his state.
Mohamed El-Erian Warns of Dangerous GDP-Employment Gap
Edit & Opinions
Global economy must adapt to avoid tumult this year
The
American and global economies recorded strong growth, and stock markets
soared in 2025. But the new year will pose numerous problems that won’t
be so easily overcome
The global economy faced many hurdles in 2025. The US government upended longstanding economic wisdom in a manner many economists feared would harm both the American economy and those of other countries. International institutions were sidelined, tariffs levied, the independence of the Federal Reserve questioned — all while debt continued to rise.
- Add that to geopolitical crises throughout the world and the nonchalant manner with which capital markets financed artificial intelligence, and there were many opportunities for market failures and recession. Yet the American and global economies recorded strong growth, and stock markets soared.
Even though the Trump administration boycotted the Group of 20 summit, blanketed the globe in tariffs and dismantled the Washington consensus on liberalization and free markets that US governments had repeatedly advocated to others, the American economy managed to accelerate real GDP growth to 4.3 per cent in the third quarter and avoid major trade retaliation from most countries.
The global economy grew at a respectable 3 per cent; the Chinese economy demonstrated remarkable agility against America’s protectionist measures, making up its roughly 30 per cent drop in exports to the United States by shipping more to Europe and Southeast Asia. China’s trade surplus, for the first time, exceeded $1 trillion — a staggering feat.
Then there were AI leaders and the capital markets that enabled them. Valuations soared, driving a 21 per cent gain in the Nasdaq and 17 per cent in the S&P 500 stock market indexes. Nvidia became the world’s first $5 trillion company. OpenAI announced a $1 billion deal with Disney. It often seemed that financing had no limits for AI companies — even those with less-than-robust revenue and business models and, even worse, those that simply plastered an AI label on existing activities. We also saw the resurgence of self-financing, including when Nvidia essentially gave OpenAI money to buy Nvidia’s products.
The same capital markets continued to fund enormous debts and deficits in the advanced world. Yet the much-anticipated general increase in borrowing costs did not materialize. In fact, interest rates ended the year lower. And while there were jitters over some fiscally weaker countries like France and Britain, these were limited and ultimately did little harm as both governments acted to calm markets, at least in the short term.
These achievements were all impressive. But they are essentially first-round wins.
Then there were AI leaders and the capital markets that enabled them. Valuations soared, driving a 21 per cent gain in the Nasdaq and 17 per cent in the S&P 500 stock market indexes. Nvidia became the world’s first $5 trillion company. OpenAI announced a $1 billion deal with Disney. It often seemed that financing had no limits for AI companies — even those with less-than-robust revenue and business models and, even worse, those that simply plastered an AI label on existing activities. We also saw the resurgence of self-financing, including when Nvidia essentially gave OpenAI money to buy Nvidia’s products.
The same capital markets continued to fund enormous debts and deficits in the advanced world. Yet the much-anticipated general increase in borrowing costs did not materialize. In fact, interest rates ended the year lower. And while there were jitters over some fiscally weaker countries like France and Britain, these were limited and ultimately did little harm as both governments acted to calm markets, at least in the short term.
These achievements were all impressive. But they are essentially first-round wins.
The new year will most likely bring risks to economic and financial well-being. There is no coasting on past successes, especially as the warning signs for stability are already mounting.
Lower-income consumer resilience can’t be counted on. Trade retaliation might increase. Fiscal and monetary policies are loosening. The labour market is cooling, widening the decoupling of employment from economic growth. China’s redirection of trade could cause reprisals from other countries. Add to that a growing divergence in performance among economies, and a picture emerges of a fragile global order. Meanwhile, some of the very narrowly focused AI companies will probably struggle to significantly raise revenues, failing to keep pace with the huge investments made in them.
To come through 2026 in a strong position, governments need to enact sustainable productivity improvements, rather than stimulate the economy via spending and lower interest rates. We need coherent AI adoption policies — ones that attempt to maximise output gains while limiting labour market shocks — designed and carried out in collaboration with leading companies. And investors must make fewer reckless choices if we want to avoid market instability. Pouring money indiscriminately into AI should give way to backing a smaller group of winners in a more disciplined manner.
American foreign trade and investment policies must become more strategic. The United States needs to work with partners to avoid a fragmentation of the global order that threatens the dollar and risks a spiral in which zero-sum thinking causes countries to act against each other, ultimately making everyone worse off. China, on its side, needs to accelerate its economic restructuring that unleashes domestic consumption rather than redirecting exports around the world; otherwise, it risks becoming a catalyst for protectionism not just from America, but also European and other Asian countries.
Political and social pressures around affordability are likely to mount in a US election year. Policymakers must address the so-called K-shaped economy, in which the wealthy see their incomes and assets grow while the less fortunate are hit hard by high prices, heavy debt burdens and decreasing buying power.
Lower-income consumer resilience can’t be counted on. Trade retaliation might increase. Fiscal and monetary policies are loosening. The labour market is cooling, widening the decoupling of employment from economic growth. China’s redirection of trade could cause reprisals from other countries. Add to that a growing divergence in performance among economies, and a picture emerges of a fragile global order. Meanwhile, some of the very narrowly focused AI companies will probably struggle to significantly raise revenues, failing to keep pace with the huge investments made in them.
To come through 2026 in a strong position, governments need to enact sustainable productivity improvements, rather than stimulate the economy via spending and lower interest rates. We need coherent AI adoption policies — ones that attempt to maximise output gains while limiting labour market shocks — designed and carried out in collaboration with leading companies. And investors must make fewer reckless choices if we want to avoid market instability. Pouring money indiscriminately into AI should give way to backing a smaller group of winners in a more disciplined manner.
American foreign trade and investment policies must become more strategic. The United States needs to work with partners to avoid a fragmentation of the global order that threatens the dollar and risks a spiral in which zero-sum thinking causes countries to act against each other, ultimately making everyone worse off. China, on its side, needs to accelerate its economic restructuring that unleashes domestic consumption rather than redirecting exports around the world; otherwise, it risks becoming a catalyst for protectionism not just from America, but also European and other Asian countries.
Political and social pressures around affordability are likely to mount in a US election year. Policymakers must address the so-called K-shaped economy, in which the wealthy see their incomes and assets grow while the less fortunate are hit hard by high prices, heavy debt burdens and decreasing buying power.
History is littered with those who celebrated too early — in sports, in war, and in economics and finance. In 2025, the American and global economy, led by AI and capital markets, skated through a series of obstacles. But the next round is just beginning. No number of successes in the last round will guarantee success in the next.
(Mohamed A. El-Erian, the chairman of Gramercy Funds Management, is the former president of Queens’ College at Cambridge University and the former chief executive of PIMCO, an investment management firm)
No comment
Dimon’s $770 Million Windfall Shows How Banking Is Great Again
Regulations are lifting, and deal-making is heating up. For Jamie Dimon, being JPMorgan Chase’s chief executive was more lucrative in 2025 than ever.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
-
Flash News: Ukraine Intercepts Russian Kh-59 Cruise Missile Using US VAMPIRE Air Defense System Mounted on Boat. Ukrainian forces have made ...