February 22, 2022
Ukraine Invasion Updates
This page collects the Critical Threats Project (CTP) and the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) updates on the invasion of Ukraine. In late February 2022, CTP and ISW began publishing daily synthetic products covering key events related to renewed Russian aggression against Ukraine. These Ukraine Conflict Updates replaced the “Indicators and Thresholds for Russian Military Operations in Ukraine and/or Belarus,” which we maintained from November 12, 2021, through February 17, 2022.
This list also includes prominent warning alerts that CTP and ISW launched outside the crisis update structure. These products addressed critical inflection points as they occurred.
Follow the Critical Threats Project on Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook.
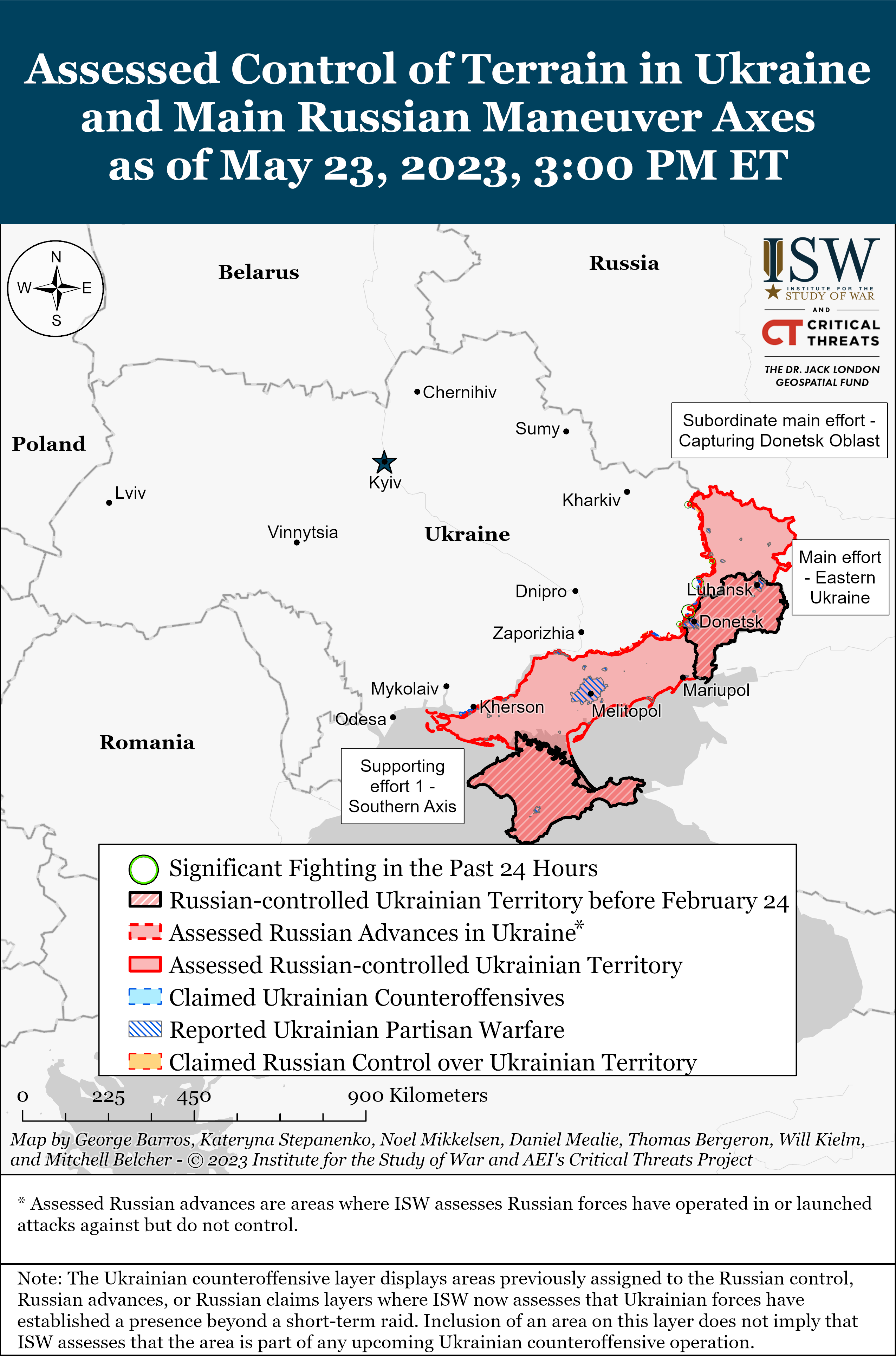
- Maps on Assessed Control of Terrain in Ukraine and Main Russian Maneuver Axes
- Recent Updates
- February 2022 - April 2023 Updates
- Related Reads
Maps on Assessed Control of Terrain in Ukraine and Main Russian Maneuver Axes
This interactive map complements the static daily control-of-terrain maps that CTP and ISW produce with high-fidelity and, where possible, street level assessments of the war in Ukraine.
The Critical Threats Project and the Institute for the Study of War are publishing a summary of the methodology of our map for those whowould like to learn more about the tradecraft for mapping conventional military operations from the open source.
Previous versions of these static maps are available in our past publications.
Recent Updates
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 23, 2023
Note: The data cutoff for this product was 4pm ET on May 23. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the May 24 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
Russian authorities ended the “counterterrorism” operation in Belgorod Oblast and claimed to have defeated the all-Russian pro-Ukrainian Russian Volunteer Corps (RDK) and the Freedom of Russia Legion (LSR) in the region on May 23. The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) claimed that Western Military District (WMD) Border Guards units defeated the raid and expelled all “saboteurs” from Belgorod Oblast.[i] Belgorod Oblast Governor Vyacheslav Gladkov announced that the “counterterrorism” operation had ended but called on civilians who evacuated to wait before returning to the border settlements.[ii] Russian authorities later announced on May 23 that authorities evacuated 100 civilians from nine border settlements in Belgorod Oblast on May 22 after Gladkov originally denied conducting formal evacuations.[iii] Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov stated that Russian President Vladimir Putin will not hold an emergency meeting of the Russian Security Council to discuss the Belgorod raid but will instead discuss the situation during the Security Council’s planned May 26 meeting, likely in an effort to project confidence about Russian handling of the situation.[iv]
Russian forces likely pushed the RDK and LSR forces at least to the Kozinka border settlement and possibly out of Russian territory as of May 23. Kozinka is located approximately 76km southeast of Sumy City. Russian sources amplified footage of Russian forces firing on RDK and LSR vehicle positions near the Kozinka border checkpoint overnight and claimed that Russian forces recaptured Kozinka and its border checkpoint in the morning.[v] Geolocated footage from Russian state media shows damaged and destroyed vehicles at the checkpoint.[vi] Some Russian sources claimed that RDK and LSR forces entrenched themselves in the Kozinka church but that preliminary reports suggest Russian forces may have ousted the Ukrainian forces by the evening.[vii] Russian sources claimed that Russian forces began clearing operations in Kozinka and Glotovo (immediately east of Kozinka) on May 23.[viii] Geolocated footage posted on May 23 shows the aftermath of shelling Gora Podol (about 6km northwest of Kozinka) and Russian infantry conducting patrols between Grayvoron (about 7km northwest of Kozinka) and Gora Podol, suggesting that RDK and LSR personnel no longer hold or never held positions in the settlement.[ix] It is unclear whether the RDK and LSR captured any villages on May 22 or May 23, however. The LSR claimed that LSR and RDK personnel continued to operate in Belgorod Oblast on May 23, however.[x]
Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces conducted raids across the Kharkiv-Belgorod border on May 23, but ISW has observed no confirmation that these raids occurred. Some Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian and Ukraine-affiliated formations – including Azov Regiment, Kraken Regiment, Territorial Defense, and regular Ukrainian forces – and RDK personnel attempted additional raids near Gorkovsky, Bogun-Gorodok, and Tsapovka, and managed to cross the border south of Shchetinovka.[xi] Other Russian sources denied claims that sabotage groups crossed the Kharkiv-Belgorod border.[xii]Russian sources also claimed that Ukrainian forces accumulated reserves less than 10 kilometers from the Kharkiv-Belgorod border and expressed fear about the threat of further raids.[xiii] One milblogger claimed that the Azov Regiment, Kraken Regiment, Territorial Defense, and regular Ukrainian forces all took part in a raid in Bryansk Oblast on May 22, but ISW has still not observed confirmation of this claimed raid.[xiv]
The Russian information space largely hyperfixated on speculated goals for the raids and on the conduct of the Russian response. Some Russian milbloggers amplified claims that a drone struck the Russian Federal Security Service (FSB) building in Belgorod City and speculated that Ukrainian forces aimed to attack the FSB and Ministry of Internal Affairs (MVD) in the raid.[xv] Russian sources also amplified a photograph of Colonel General Alexander Lapin posing with a captured vehicle and claimed that Lapin led the counterterrorism operation alongside elements of the 3rd Motorized Rifle Division (20th Guards Combined Arms Army, Western Military District).[xvi] Many Russian sources praised Lapin for organizing Russian forces to conduct coherent counterterrorism operations after the Russian Border Service failed to repel the raids.[xvii] Some sources criticized the decision to give Lapin command and noted Lapin’s prior military failures such as the disastrous Siverskyi Donets river crossing near Bilohorivka, Luhansk Oblast in May 2022.[xviii] Lapin has notably returned to commanding Russian operations in eastern Ukraine after suffering intense criticism for commanding the operations to take Severodonetsk and Lysychansk, and Lapin has not received much praise in the information space since the campaign to undermine him led to Lapin’s dismissal in November 2022.[xix] The openness of Russian milbloggers to praise Lapin for commanding the defense against an extremely small and limited border incursion suggests that at least some milblogger factions are amenable to Russian President Vladimir Putin’s tendency to rotate old and disgraced commanders.[xx] The Russian reaction to the raid in the information space and in the reported military activities appears to be a highly disproportionate response to a very small and localized undertaking. Russian forces should not have required significant reinforcements—or the involvement of a colonel general—to repulse a raid conducted by reportedly 13 armored vehicles.[xxi]
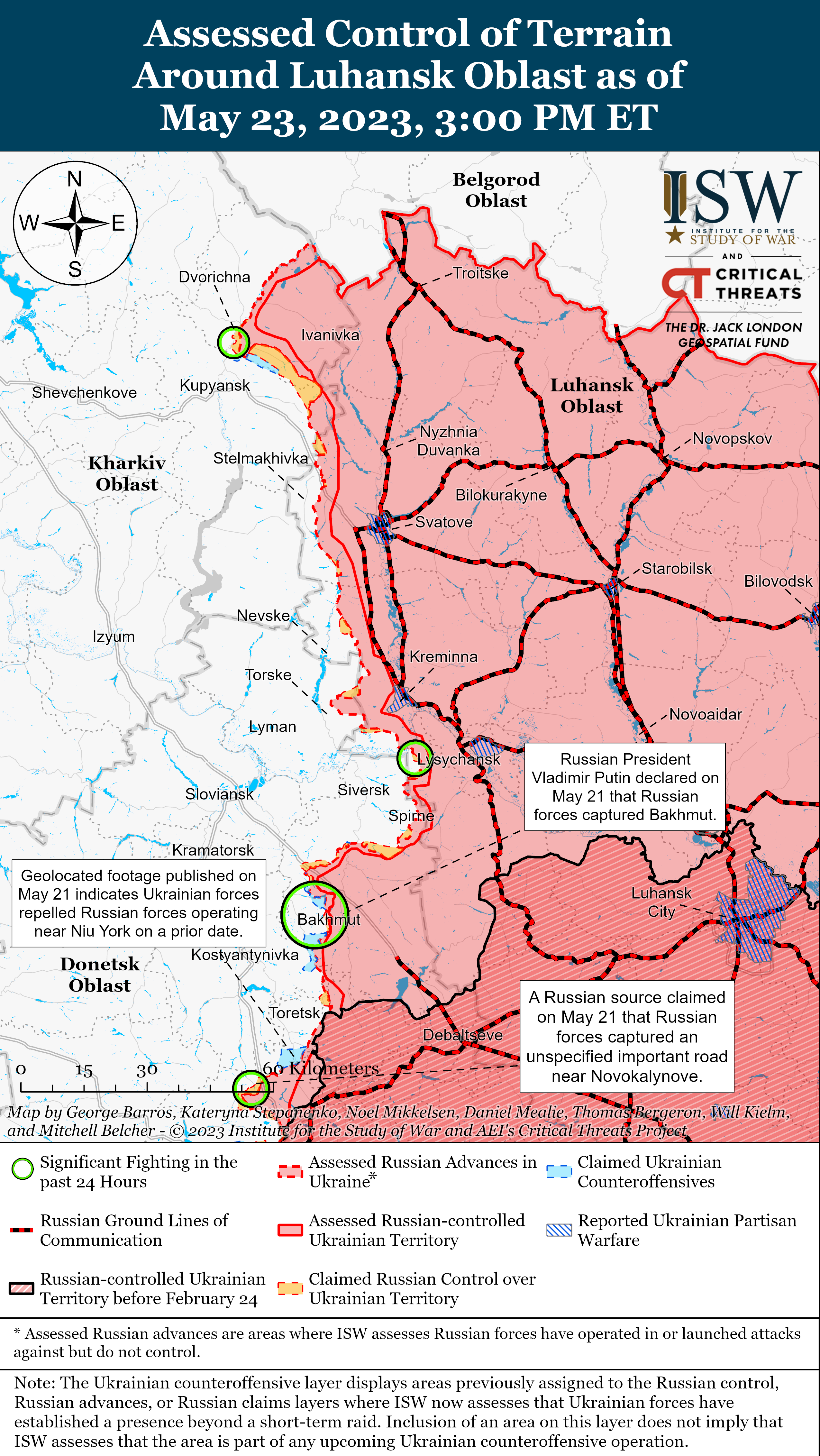
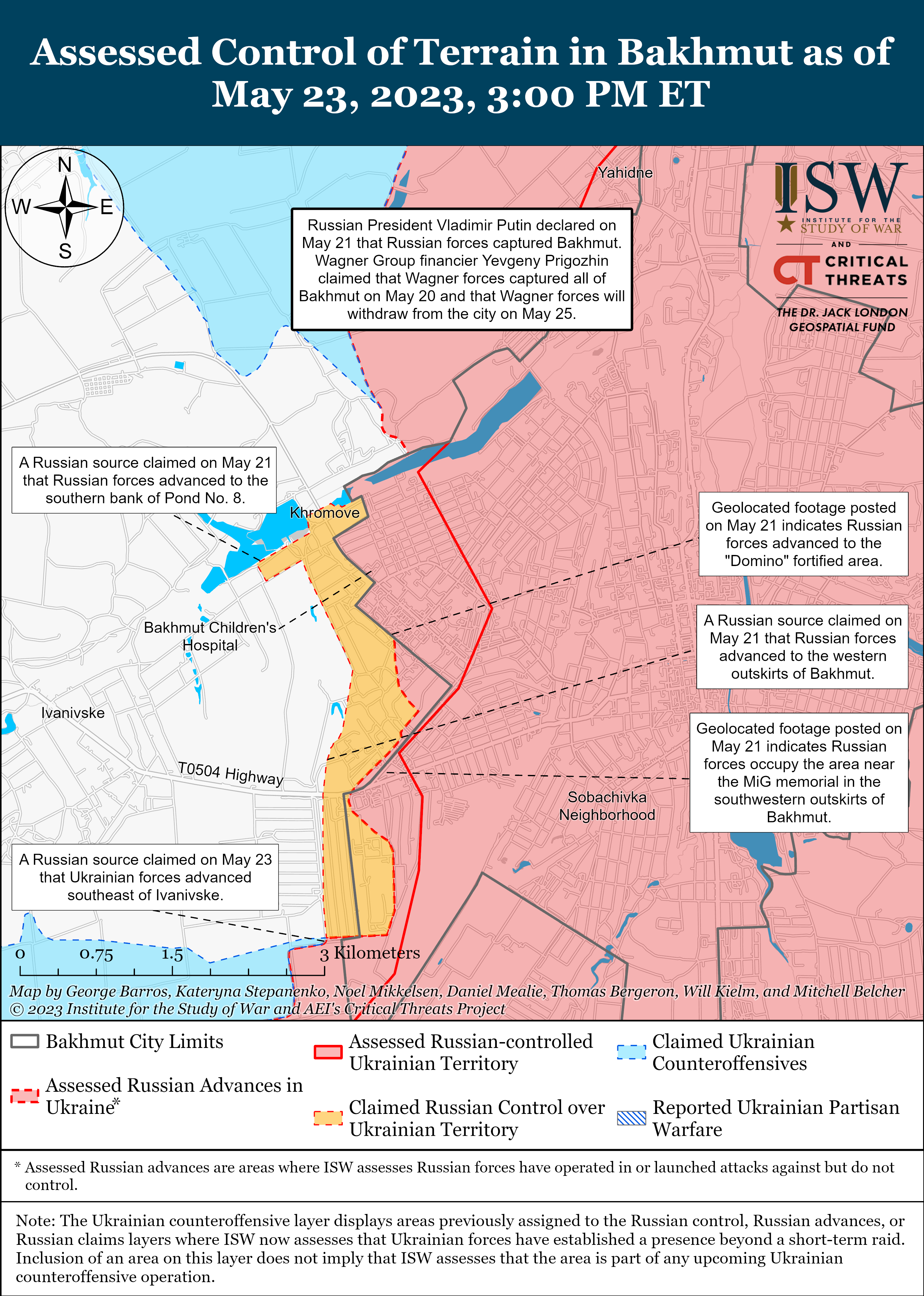
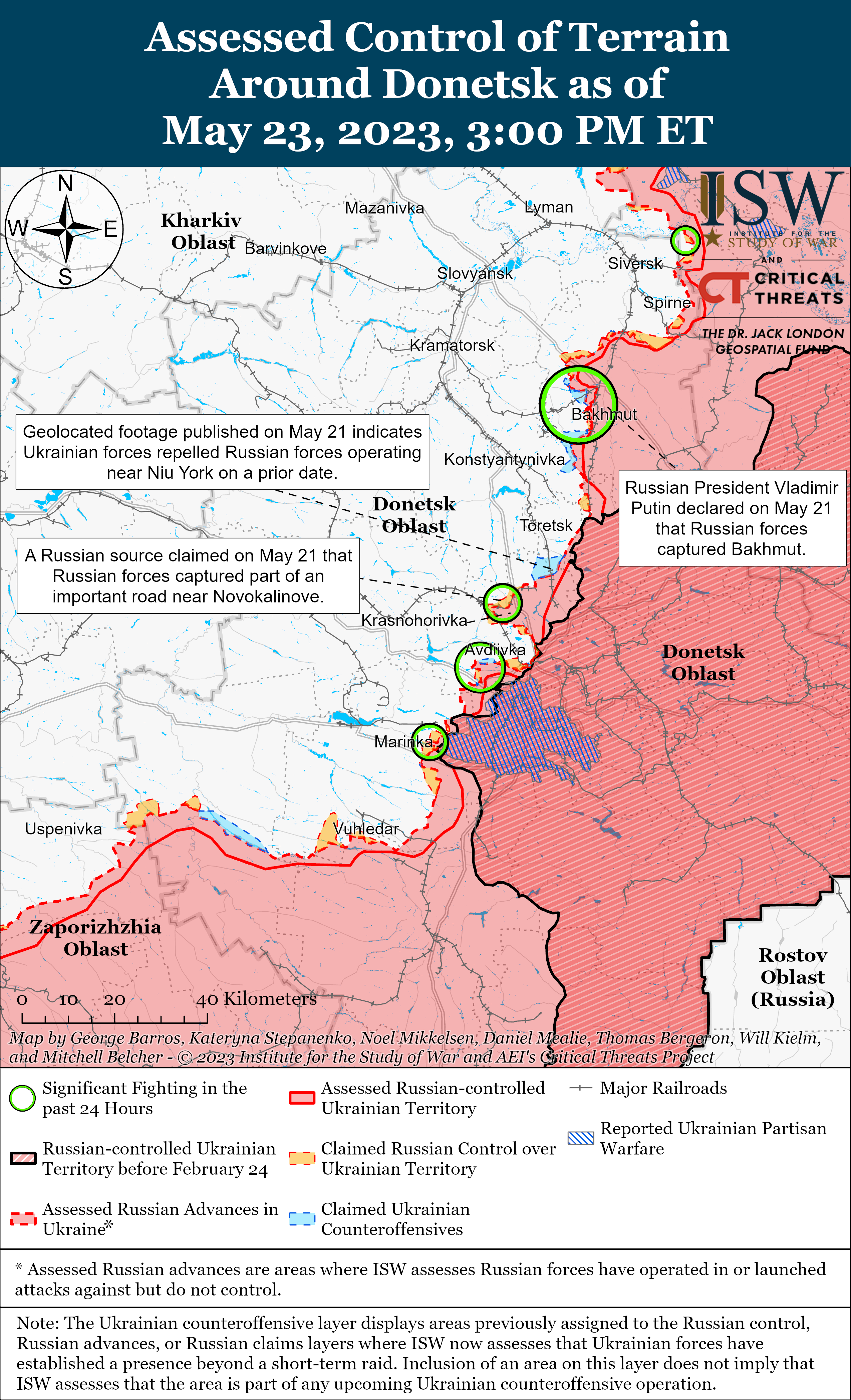
Ukrainian officials stated that the pace of fighting in the Bakhmut direction has decreased amid continued limited Ukrainian counterattacks on Bakhmut’s flanks on May 23. The Ukrainian General Staff did not report fighting in Bakhmut City in its 1800 situational report for the first time since December 2022, suggesting that Wagner Group forces may have made further advances within the city. The General Staff also reported that Russian forces conducted unsuccessful offensive actions near Khromove (immediately west of Bakhmut).[xxii] Ukrainian Deputy Defense Minister Hanna Malyar stated that combat operations have decreased in and around Bakhmut and reiterated that Ukrainian forces maintain positions in a fortified area near the MiG-17 monument in western Bakhmut.[xxiii] A milblogger amplified video footage purportedly showing Wagner forces near the MiG-17 monument and claimed that there are no Ukrainian forces in the area, however.[xxiv] Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Spokesperson Colonel Serhiy Cherevaty stated that Ukrainian forces advanced 200 to 400 meters along the flanks of Bakhmut and still control a number of buildings and fortifications in southwestern Bakhmut.[xxv] A Russian milblogger claimed that Ukrainian forces advanced near Yahidne (1km northwest of Bakhmut) and that Russian forces unsuccessfully attacked near Hryhorivka (8km northwest of Bakhmut) and Ivanivske (immediately west of Bakhmut).[xxvi] Another milblogger denied reports that Ukrainian forces made gains during counterattacks northwest and southwest of Bakhmut and assessed that a Russian offensive from Bakhmut toward Ivanivske or Bohdanivka remains unlikely.[xxvii]
Key Takeaways
- Russian authorities ended the “counterterrorism” operation in Belgorod Oblast and claimed to have defeated the all-Russian pro-Ukrainian Russian Volunteer Corps (RDK) and the Freedom of Russia Legion (LSR) in the region on May 23.
- Russian forces likely pushed the RDK and LSR forces at least to the Kozinka border settlement and possibly out of Russian territory as of May 23.
- Russian sources claimed that Ukrainian forces conducted raids across the Kharkiv-Belgorod border on May 23, but ISW has observed no confirmation that these raids occurred.
- Ukrainian officials stated that the pace of fighting in the Bakhmut direction has decreased amid continued limited Ukrainian counterattacks on Bakhmut’s flanks on May 23.
- Russian forces conducted limited ground attacks northeast of Kupyansk and along the Svatove-Kreminna line.
- Russian forces continued offensive operations on the Avdiivka-Donetsk City line.
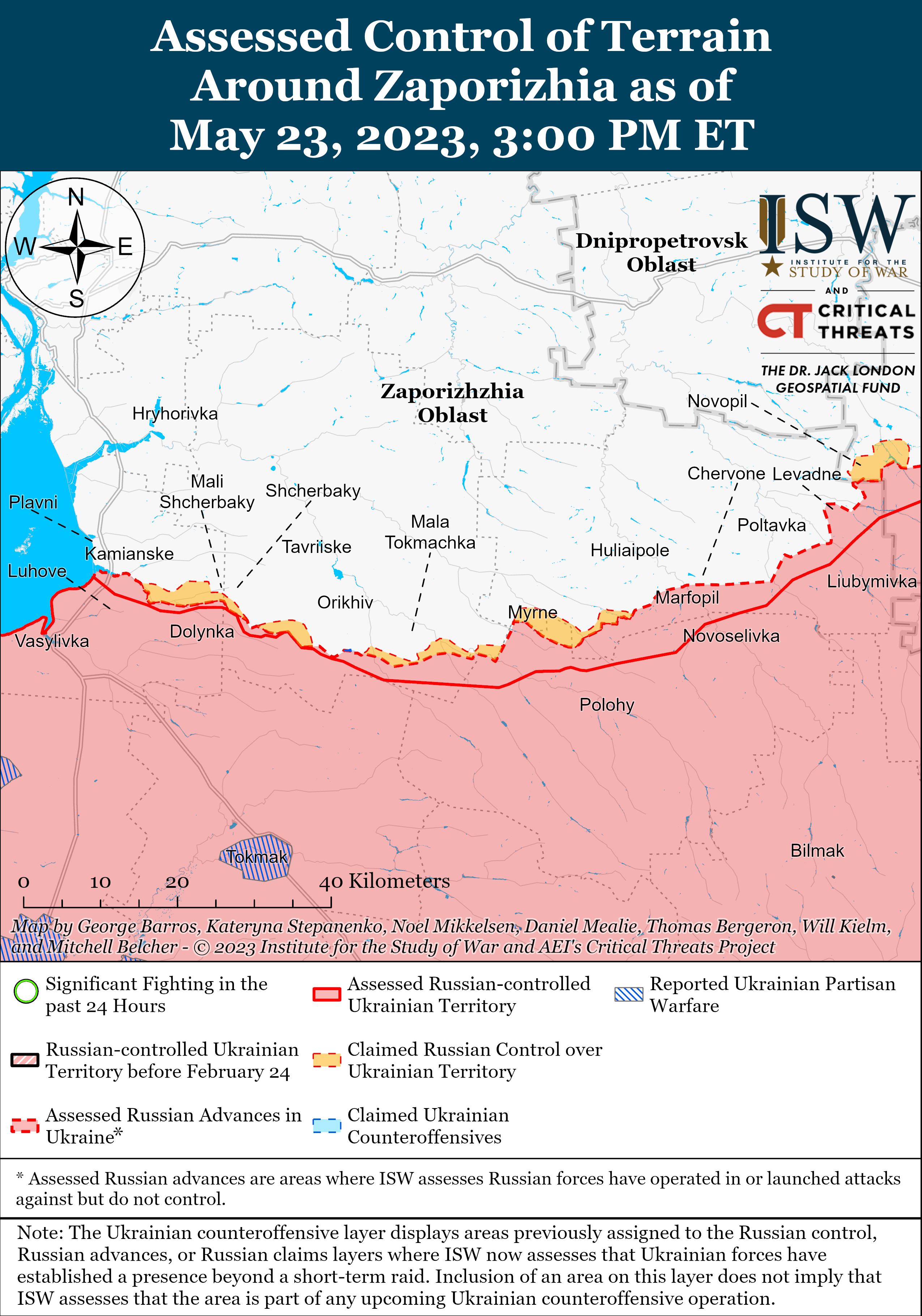
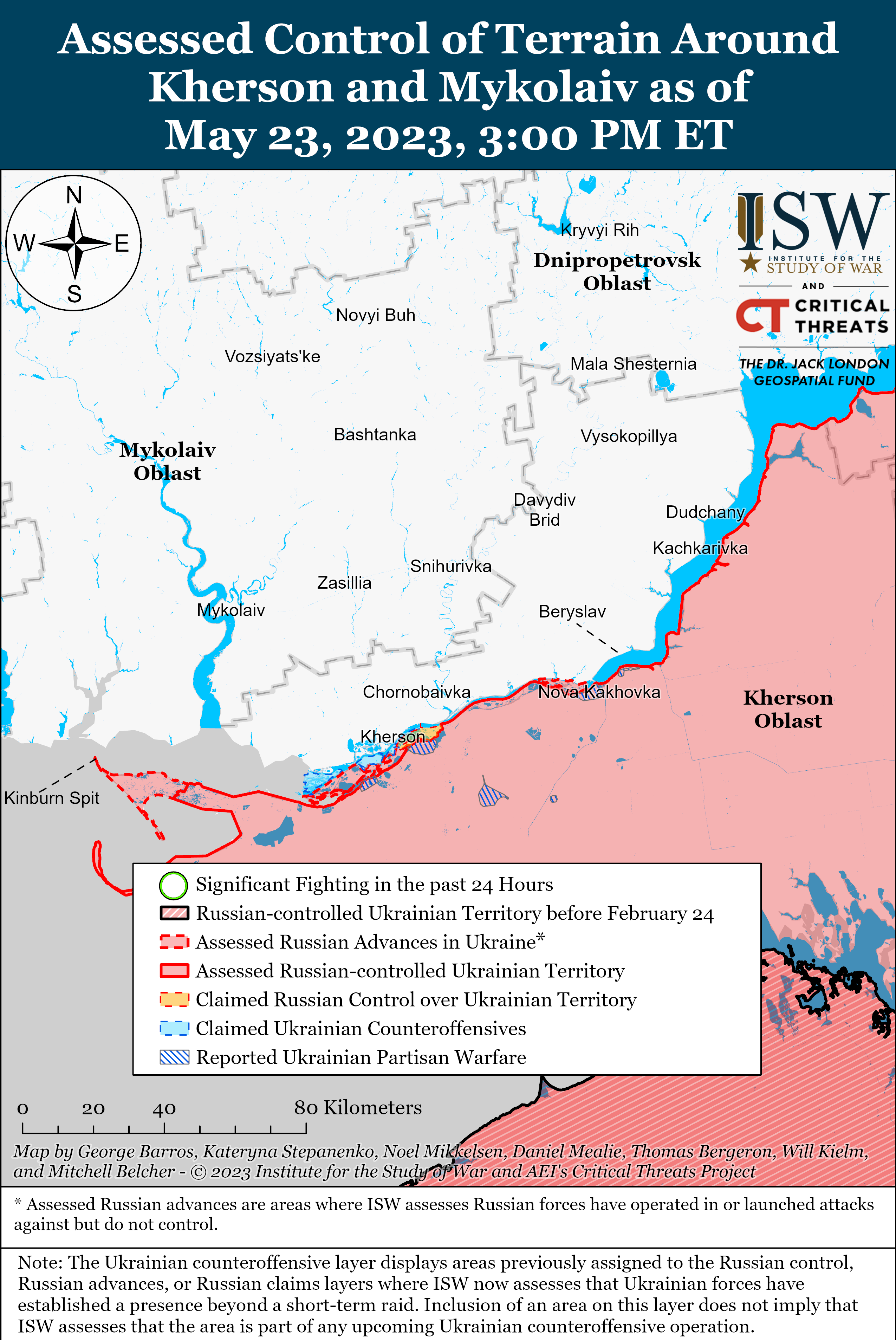
- Russian forces continued defensive operations in southern Ukraine ahead of the planned Ukrainian counteroffensive.
- Pardoned Wagner Group convicts continue to commit crimes in Russia after finishing their military contracts with Wagner.
- Zaporizhia Oblast occupation officials announced the start of preliminary voting for the ruling United Russia party.


No comments:
Post a Comment