The United States has announced a new $1.2bn military aid package for Ukraine that will include air defence systems, conventional artillery and counter-drone ammunition, satellite imagery services and funding for military training.
Read also: US training 2,000 Ukrainian troops in Germany – Pentagon
According to Blinken, at every step of support to Kyiv, “we’ve worked with now more than 50 countries to adjust, to adapt, depending on the nature of the fight, where it was, what was needed, to make sure that, again, they had what they needed.”
“And it’s a process and we’re working literally every single day with the Ukrainians and with this coalition of countries to make sure they have support,” he added.
“If there are gaps, if there are shortages, they’ll tell us and we will make every effort to make good on them.”
Read also: US reportedly removing ‘sensitive’ equipment from Abrams tanks earmarked for Ukraine
The U.S. official added that different countries will do different things depending on their own capacities, depending on their own technology, depending on what makes the most sense.
“So we’ve provided some things uniquely to Ukraine through this process,” he said.
“Other countries may do things different than what we’re doing. The question is: Does the whole thing add up to what Ukraine needs? And we’re determined that it – that it do so.”
The U.S. Department of Defense announced a $300 million military aid package for Ukraine on May 3. The package includes howitzers, artillery rounds, and HIMARS ammunition, among other things.
On May 9, the U.S. Department of Defense announced a $1.2 billion military aid package for Ukraine, which includes additional air defense systems and munitions, artillery rounds, etc.
Read also: Blinken: Zelenskyy should consider the will of Ukrainians in Crimea’s de-occupation
In total, the United States has provided almost $37 billion in military aid to Ukraine since Russia’s full-scale invasion in February 2022.
We’re bringing the voice of Ukraine to the world. Support us with a one-time donation, or become a Patron!
Read the original article on The New Voice of Ukraine
US announces $1.2bn in additional military aid for Ukraine
New assistance package for Ukraine includes air defence systems and conventional and counter-drone ammunition.
U.S. Provides Ukraine $1.2 Billion for Air Defense, Artillery
WASHINGTON (AP) — The U.S. will provide $1.2 billion more in long-term military aid to Ukraine to further bolster its air defenses as Russia continues to pound Ukraine with drones, rockets and surface-to-air missiles, the Pentagon said Tuesday.
The aid package will be provided under the Ukraine Security Assistance Initiative. Unlike U.S. equipment, weapons and ammunition sent from Pentagon stocks that can be delivered to Ukraine quickly, this money is to be spent over the coming months or even years to ensure Ukraine’s future security needs.
The Pentagon said it will fund air-defense munitions and drones for air defense, and provide equipment to help modify Western air-defense launchers, missiles and radars so they can be used with Ukraine’s systems. It will also buy artillery rounds, howitzer ammunition, satellite imagery assistance and funding for ongoing maintenance and spare parts for a variety of systems. U.S. officials said the weapons include HAWK air-defense systems. They spoke on condition of anonymity because that has not yet been formally announced.
The Pentagon said the aid will build the capacity of Ukraine’s military “to defend its territory and deter Russian aggression over the long term.”
Including this package, the U.S. has provided Ukraine nearly $37 billion in military aid since Russia invaded in February 2022.
The latest aid comes as Ukraine prepares to launch a spring offensive against Russian forces, with air defense a persistent issue.
Ukraine’s air defenses shot down 35 Iranian-made drones over Kyiv in Russia’s latest nighttime assault, officials said Monday. Wreckage from a drone struck a two-story apartment building in Kyiv’s western Svyatoshynskyi district, while other debris struck a car parked nearby, setting it on fire, Kyiv Mayor Vitali Klitschko said in a Telegram post.
Russian shelling of 127 targets across northern, southern and eastern parts of Ukraine killed three civilians, the Ukrainian defense ministry said.
Facing economic sanctions and limits on its supply chains due to its invasion of Ukraine, Russia has routinely turned to Iran’s Shahed drones to bolster its firepower. And U.S. aid packages — including more immediate military weapons and support — have included systems to shoot down and otherwise defeat the drones.
___ Associated Press writer Tara Copp contributed to this report.
Ukraine Invasion Updates
This page collects the Critical Threats Project (CTP) and the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) updates on the invasion of Ukraine. In late February 2022, CTP and ISW began publishing daily synthetic products covering key events related to renewed Russian aggression against Ukraine. These Ukraine Conflict Updates replaced the “Indicators and Thresholds for Russian Military Operations in Ukraine and/or Belarus,” which we maintained from November 12, 2021, through February 17, 2022.
This list also includes prominent warning alerts that CTP and ISW launched outside the crisis update structure. These products addressed critical inflection points as they occurred.
Follow the Critical Threats Project on Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook.
- Maps on Assessed Control of Terrain in Ukraine and Main Russian Maneuver Axes
- Recent Updates
- February 2022 - April 2023 Updates
- Related Reads
Maps on Assessed Control of Terrain in Ukraine and Main Russian Maneuver Axes
This interactive map complements the static daily control-of-terrain maps that CTP and ISW produce with high-fidelity and, where possible, street level assessments of the war in Ukraine.
The Critical Threats Project and the Institute for the Study of War are publishing a summary of the methodology of our map for those who would like to learn more about the tradecraft for mapping conventional military operations from the open source.
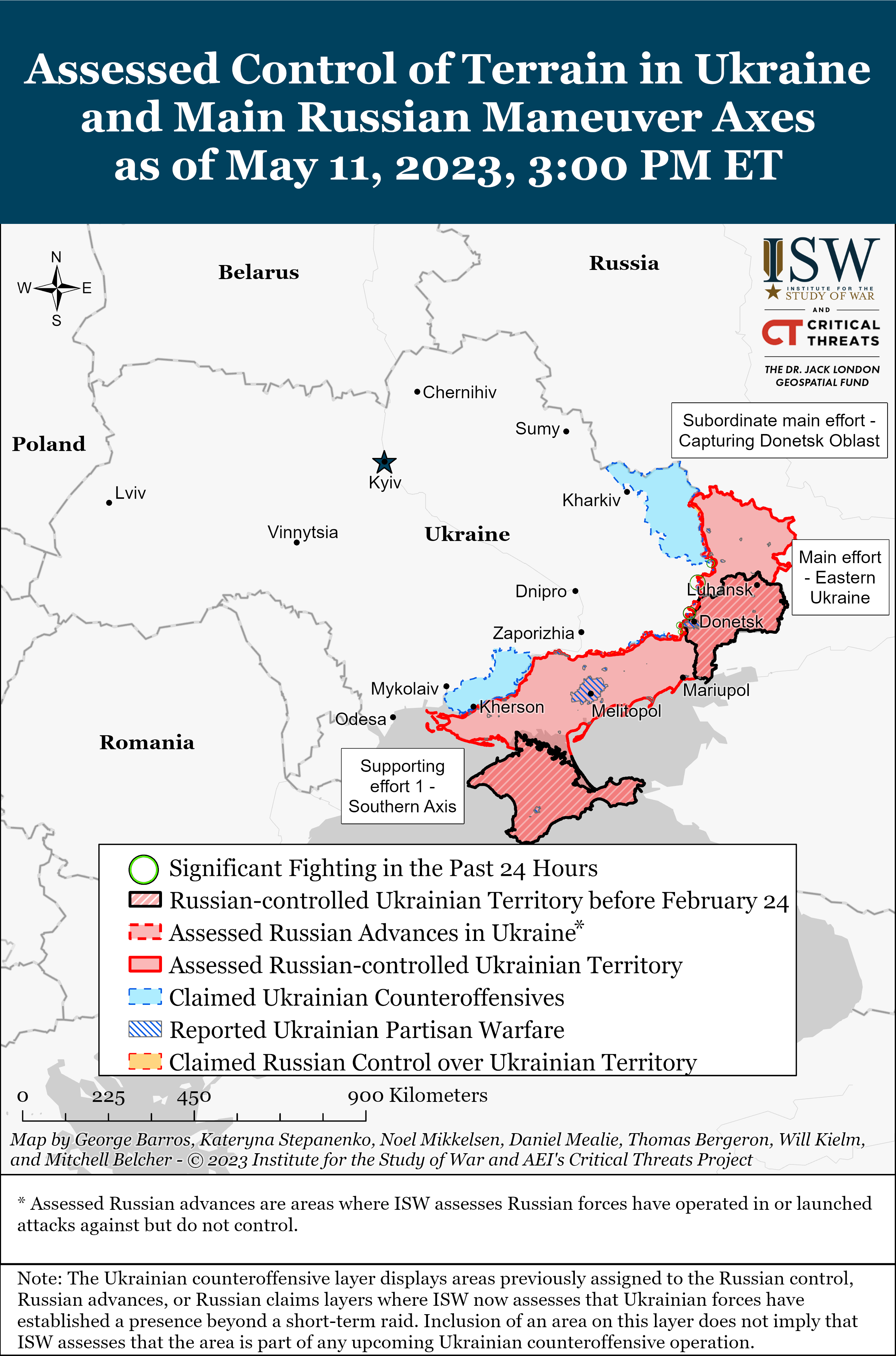
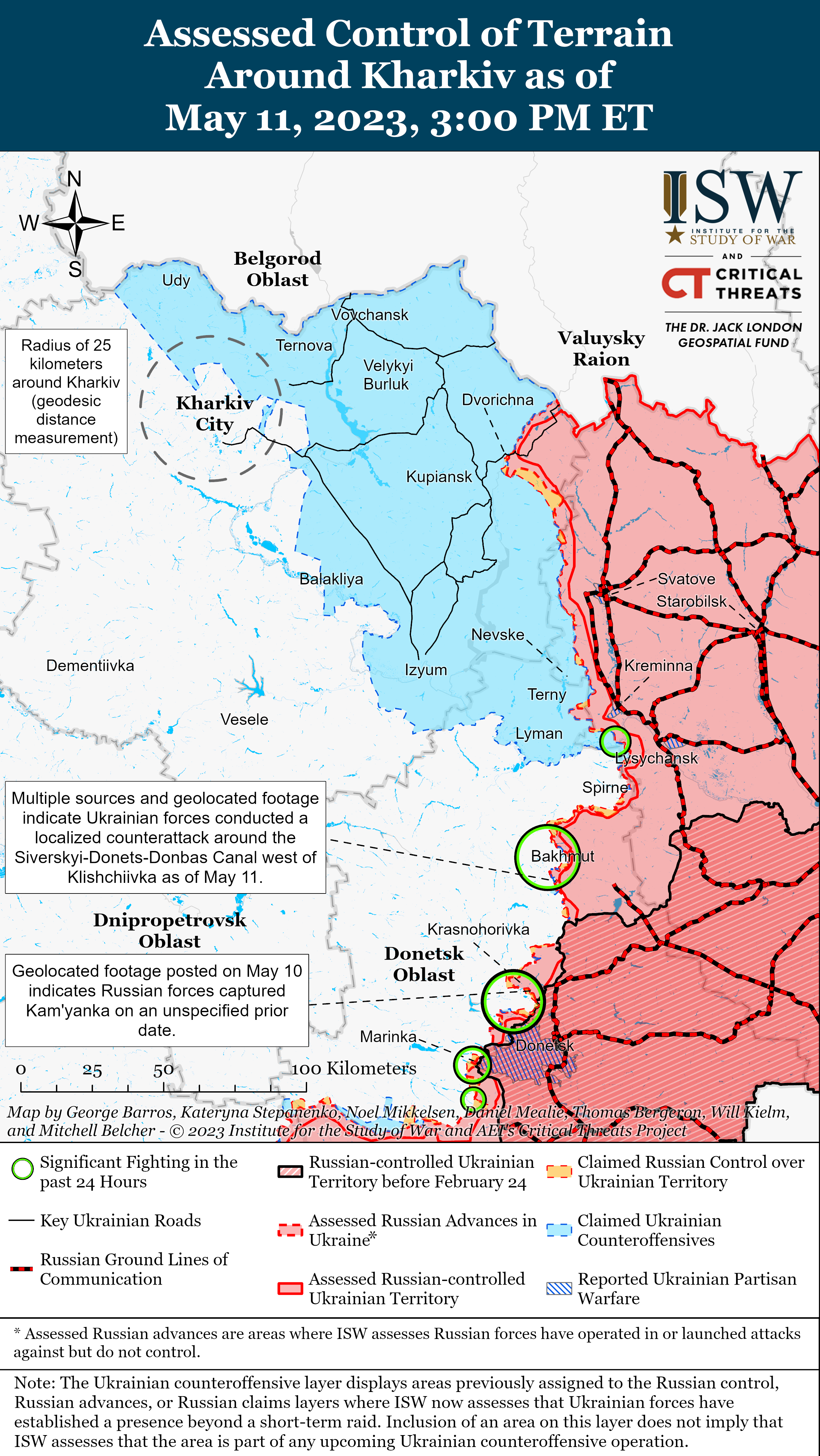

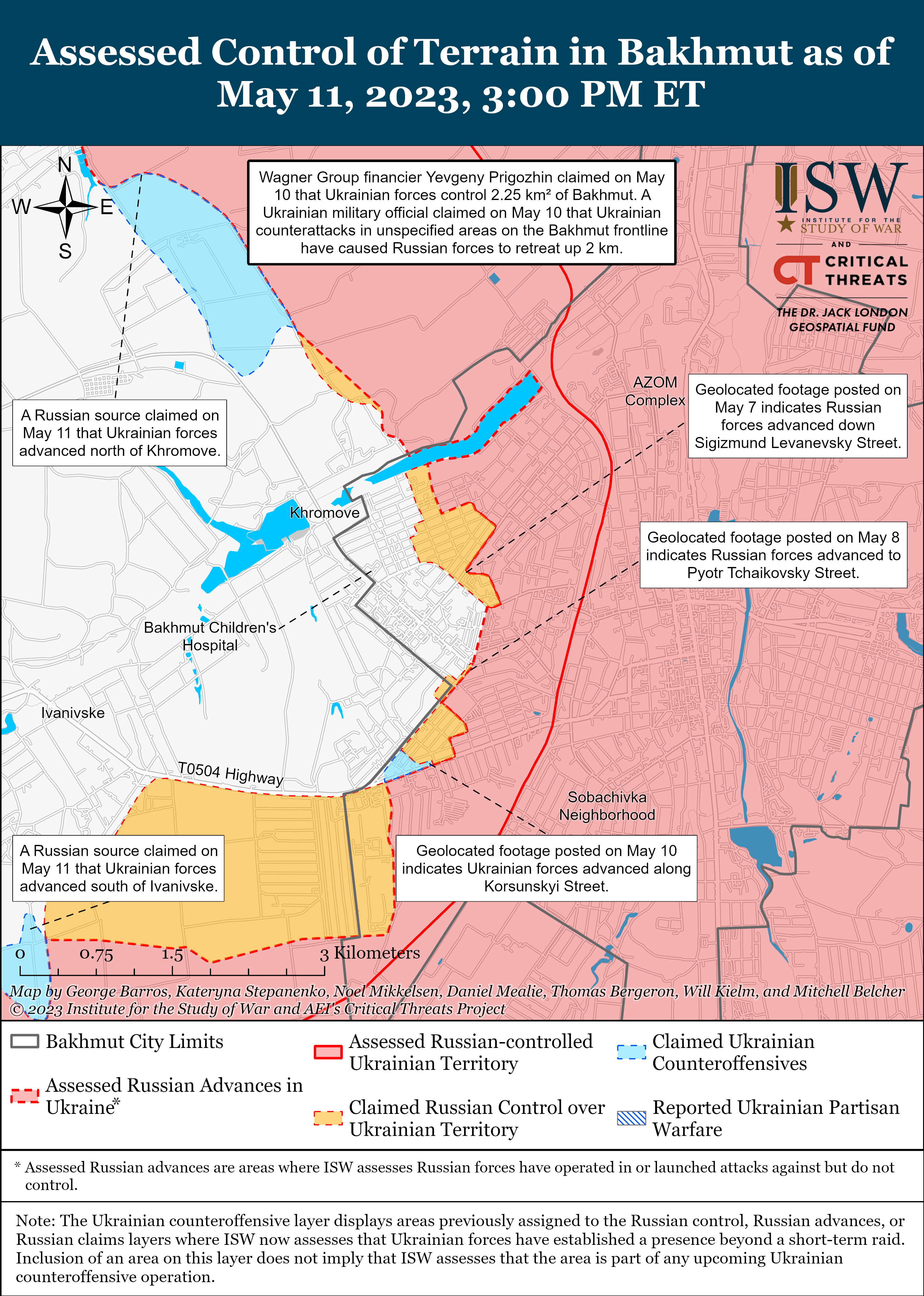
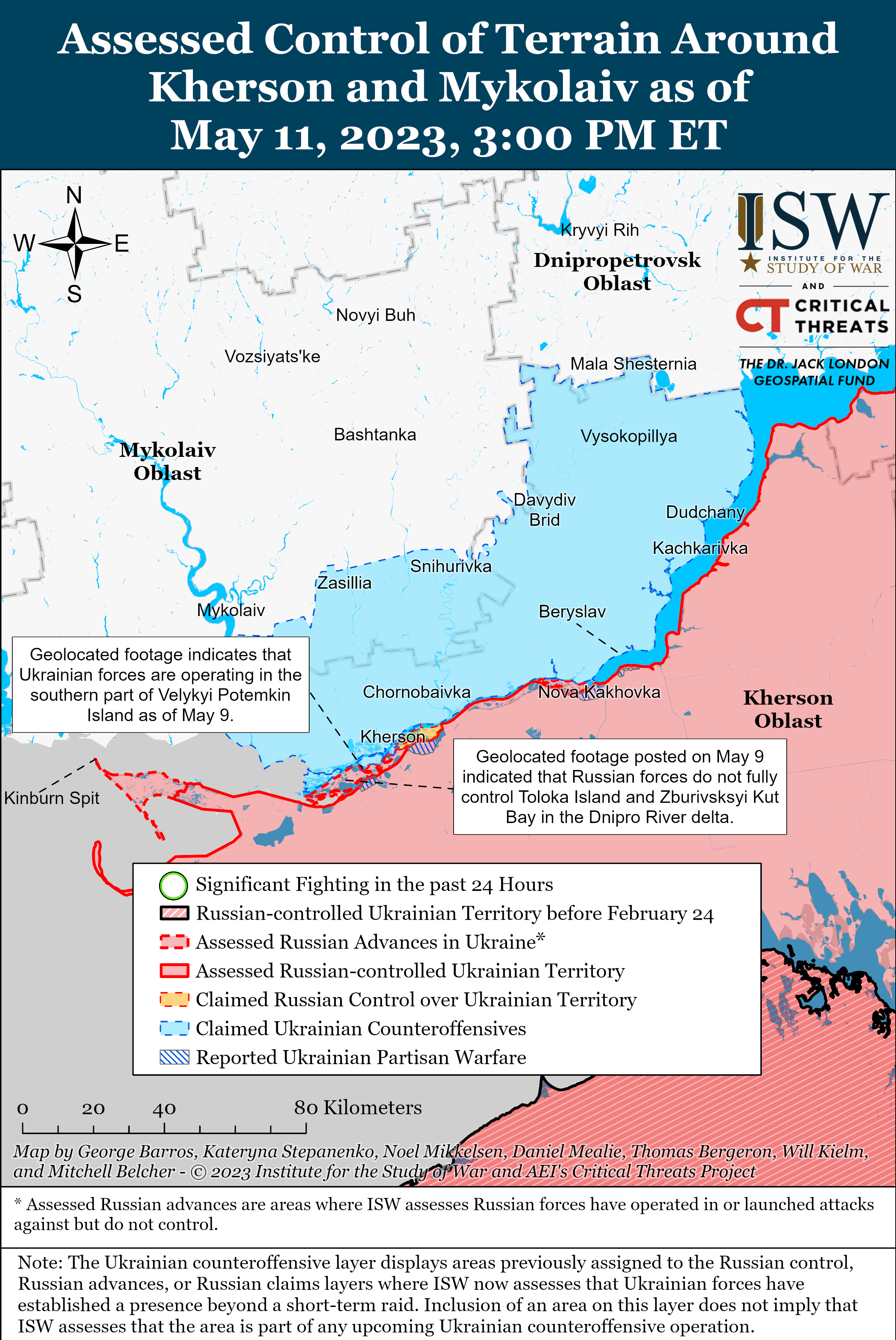
Previous versions of these static maps are available in our past publications.
Recent Updates
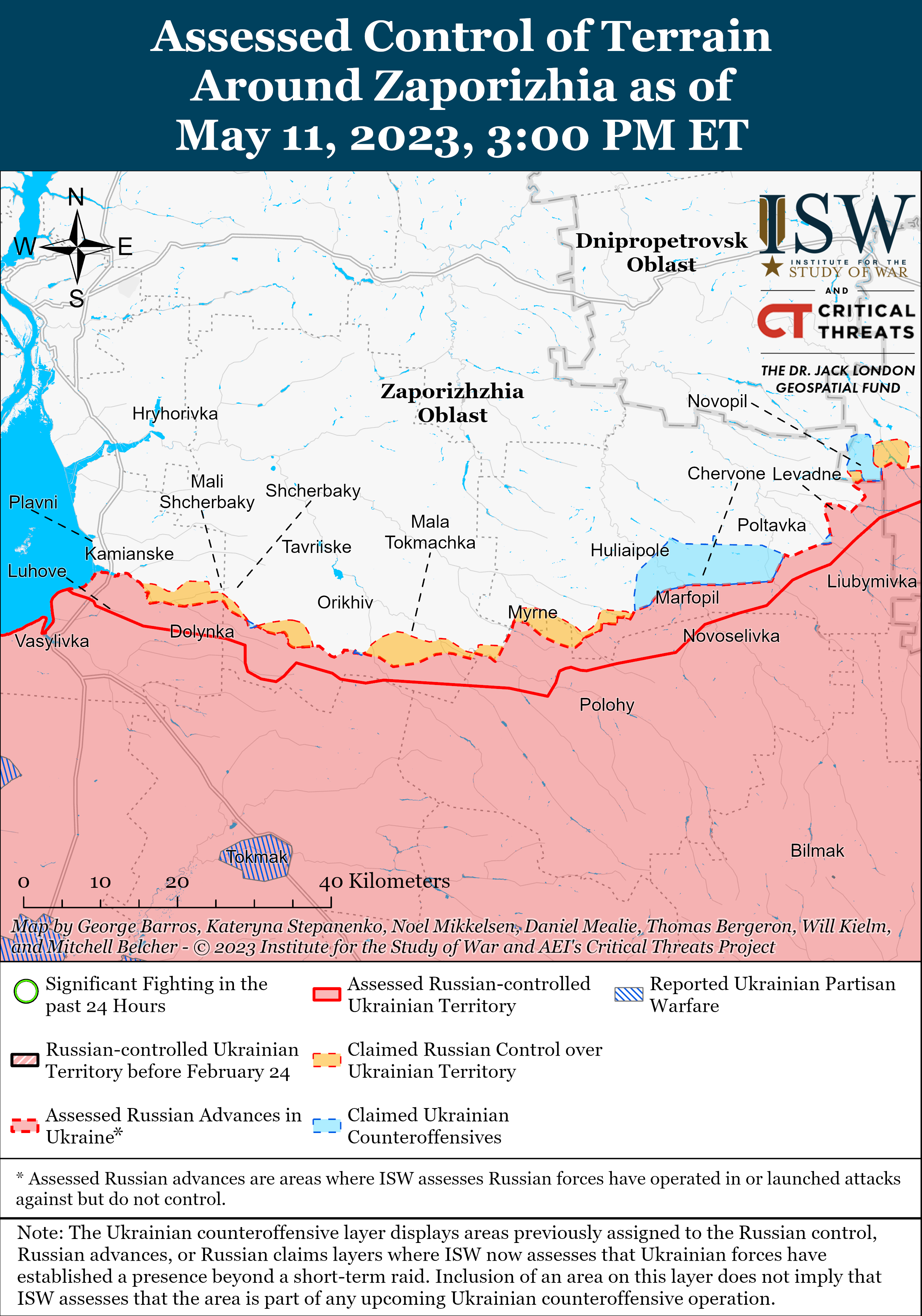
Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, May 11, 2023
Note: The data cutoff for this product was 2:00 pm ET on May 11. ISW will cover subsequent reports in the May 12 Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment.
Ukrainian forces likely broke through some Russian lines in localized counterattacks near Bakhmut, prompting responses from Wagner Group financier Yevgeny Prigozhin and the Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD). Ukrainian Eastern Group of Forces Commander Colonel General Oleksandr Syrskyi stated that Russian forces retreated up to two kilometers behind Russian lines in unspecified sectors of the Bakhmut front.[1] Syrskyi’s confirmation of Ukrainian gains prompted a response from Prigozhin, who claimed that Ukrainian forces have started the counteroffensive and recaptured three kilometers of ground in and around Bakhmut.[2] The Russian MoD acknowledged the Ukrainian counterattacks uncharacteristically quickly, claiming that Russian forces repelled eight ground attacks and three reconnaissance-in-force efforts in the Donetsk direction but denied reports that Ukrainian forces broke through the Russian defensive lines.[3] Prigozhin’s and the MoD’s responses are reflective of increased panic in the Russian information space over speculations about planned Ukrainian counteroffensives and indicate increased concern among Wagner and Russian MoD leadership as well as reflecting Kremlin guidance to avoid downplaying Ukrainian successes.[4]
The deployment of low-quality Russian forces on the flanks around Bakhmut suggests that the Russian MoD has largely abandoned the aim of encircling a significant number of Ukrainian forces there. The Russian MoD likely began a broader deprioritization of the Bakhmut effort by January 2023 when the MoD cut off Wagner Group penal recruitment efforts, which likely prompted Prigozhin to ramp up the Soledar-Bakhmut effort in January and publicly complain about the lack of MoD support for his efforts starting in February 2023.[5] The Russian MoD briefly allocated more resources to the Bakhmut front line in March and April by sending T-90 tanks and Russian Airborne (VDV) forces to the Bakhmut area and assigning mobilized reservists to Wagner, however.[6] Prigozhin claimed on April 24 that the Russian MoD only deployed irregular and degraded units to hold Bakhmut’s flanks, and the inability of these units to fulfill even this limited mission indicates that Russian flanks in Bakhmut and other similarly-manned areas of the front are likely vulnerable to Ukrainian counterattacks.[7] The MoD’s allocation of forces combined with changes in the geometry of the battlespace also suggests that the danger of a Russian encirclement of significant Ukrainian forces in Bakhmut may have passed. Wagner forces will likely continue conducting frontal assaults in Bakhmut, which would allow Ukrainian forces to conduct organized withdrawals from threatened areas in a shallower partial envelopment rather than facing encirclement on a large scale.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky stated that Ukraine needs more time to launch a counteroffensive because it is waiting for the delivery of promised military aid. Zelensky told the BBC that some of the expected military equipment has not arrived in Ukraine and that, although Ukrainian forces are ready for the counteroffensive, Ukraine would suffer too many casualties.[8] Zelensky also stated that the Ukrainian counteroffensive is important to prevent Russia from freezing the war.
Kremlin Spokesperson Dmitry Peskov contradicted the pre-war Kremlin justifications for the war by asserting that the Russian “special military operation” began as “a conflict between Russia and Ukraine.” He said that Russia has “partially” achieved the goals of “protecting” people in Donbas,[9] but added that Russia is still far from fully achieving these goals. He said that it was ”hard to believe” at the beginning of the war that NATO, the United States, and European countries would ”intervene in this conflict.” ISW previously reported that the Kremlin has begun to shift its domestic narratives to claim that Russia is fighting only against NATO in an effort to set informational conditions for potential Russian military failures during the planned Ukrainian counteroffensive.[10] Peskov’s statement is consistent with the new Russian narrative but contradicts Russian President Vladimir Putin’s statements prior to the February 24, 2022 invasion. Putin stated on February 21, 2022, that Russia is ”not fighting the Ukrainian people” and claimed that Ukraine had become a hostage of its ”Western masters.”[11] The Russian pre-war justification for the invasion relied heavily on portraying a NATO threat to Russia supposedly emanating from Ukraine.[12]
Unnamed Kremlin sources claimed that Wagner Group Yevgeny Prigozhin’s recent rhetoric is “seriously disturbing the top leadership” of Russia. Two Kremlin sources told Russian opposition outlet Meduza that the Kremlin saw Prigozhin’s attempts to blackmail the Russian MoD on May 5 as a “serious threat” and that Prigozhin is not acting in the Kremlin’s interests.[13] One interlocutor stated that Prigozhin is committed to claiming Bakhmut as a personal victory in order to have influence over the Russian MoD. The Kremlin reportedly expressed further concerns over Prigozhin’s May 9 mockery of the “happy grandfather” figure who is responsible for future Russian generations.[14] ISW assessed on May 9 that Prigozhin was likely referring to Putin, and a Kremlin source claims that Prigozhin’s statement was a direct allusion to Putin. The second interlocutor claimed that Prigozhin’s rhetoric cannot be interpreted as a “direct attack” on Putin, however. Prigozhin attempted on May 10 to downplay his original statements, claiming that the “happy grandfather” did not refer to Putin.[15] The sources noted that Prigozhin’s escalating behavior is likely a result of his inability to meet an unspecified deadline for the capture of Bakhmut. One source claimed that Prigozhin is blaming conventional units in order to avoid accepting responsibility for failing to follow through on his “personal promise” to capture Bakhmut.
The interlocutors noted that Prigozhin may have crossed the Kremlin’s “red lines” and may alienate his supporters within the Russian inner circle. Prigozhin reportedly is losing contact with one of his patrons, Russian billionaire and Putin’s “personal banker” Yuriy Kovalchuk. Kovalchuk was reportedly one of the leading voices supporting the full-scale invasion of Ukraine after developing a strong relationship with Putin during the Covid-19 pandemic.[16] The sources noted that Russian propagandists received a directive to discredit Prigozhin as a traitor if he continues to critique the Kremlin – an effort that has previously failed.[17] The sources assessed that Prigozhin is not at risk while Wagner is still on the frontline, which allows Prigozhin to have contact with Putin.
The Russian Ministry of Defense (MoD) denied official Ukrainian and US reports that a Patriot missile defense system shot down a Kinzhal missile on the night of May 4.[18] Kremlin newswire TASS reported on May 11 that a “high-ranking source in the Russian MoD” denied reports that Ukraine intercepted a Kinzhal missile. Ukrainian Air Force Commander Mykola Oleshchuk had reported that Ukrainian forces used the Patriot system to shoot down a Kinzhal missile in the air over Kyiv Oblast at night on May 4.[19] The Russian MoD denied this report only after the US Department of Defense confirmed on May 9 that a Patriot air defense system had shot down a Russian Kinzhal missile.[20]
Russian occupation authorities seized the cathedral of the Orthodox Church of Ukraine in Simferopol as oppression of the Ukrainian Orthodox Church continues in Russian-occupied Crimea. The Commissioner of the Crimean Eparchy of the Orthodox Church of Ukraine, Metropolitan Kliment of Simferopol, and Crimean journalist Andriy Shchekun reported on May 11 that representatives of the Russian State Property Fund of the Republic of Crimea and other occupation authorities broke down the doors of the church and began stealing the property of the cathedral.[21] ISW has previously reported on Russia’s religious repression throughout occupied Ukraine.[22]
Key Takeaways. . .
Read more https://www.criticalthreats.org/analysis/ukraine-invasion-updates-ctp





No comments:
Post a Comment