Shondiin Silversmith is an award-winning Native journalist based on the Navajo Nation. Silversmith has covered Indigenous communities for more than 10 years, and covers Arizona's 22 federally recognized sovereign tribal nations, as well as national and international Indigenous issues.
A TO Z
Tucson approves move to return ancestral land to the Tohono O’odham Nation

A mural in Tucson created in 2017 by Victor Ving and Lisa Beggs. Local muralist Rock Martinez contributed by adding his artwork to the letter C. Photo by Carol M. Highsmith | Carol M. Highsmith Archive, Library of Congress, Prints and Photographs Division
"The Tucson City Council is moving forward with the effort to return the ancestral homelands near the base Sentinel Peak to the Tohono O’odham Nation for its continued preservation and reverence.
The city council unanimously approved the motion to transfer land ownership during a study session before their regular council meeting on April 18. The move comes after decades of conversations the City of Tucson has had surrounding what to do with the land.
> Tucson Mayor Regina Romero said the piece of land near Sentinel Peak has more than 4,500 years of history and archeology that proves it is an ancestral Hohokam Village.
“This is where our city was born,” Romero said
GET THE MORNING HEADLINES DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX
The initiative to return the land to the Tohono O’odham “without any strings attached” has been led by Romero and Tucson Council Member Lane Santa Cruz.
Santa Cruz said over the years, many different efforts and ideas have been introduced to the city on what to do with that land. But, in the end, returning the land was the best and most respectful option.
Santa Cruz said when they started having conversations with the tribe about returning the land, they were skeptical.
“Rightly so,” she added, “they’ve never had a good relationship with the city.”
Santa Cruz said it always seemed as if the city treated the tribe separately, as if they are over there and we are over here, even though many Indigenous people live in the city.
She said it took that ongoing conversation and meeting with tribal members, listening to their stories about the land and what it meant to them. She recalls how tribal members talked about how even if the city chose to acknowledge or not that the land rightfully belongs to the Tohono O’odham, they already know it is theirs.
“We know it is. You don’t need to tell us,” Santa Cruz said, and she agreed.
When the motion was introduced during the April 18 study session, Santa Cruz said she was shocked they could get it to this point.
Santa Cruz said she’s always felt the City of Tucson didn’t honor or revere the area’s Indigenous peoples. She noted that Indigenous peoples made the city possible and continue to care for the land, which the city needs to pay attention to and listen to.
“I believe that there is a reverence that is owed to this land,” she said. “A reconciliatory acknowledgment of the desecration, destruction, and erasure that was perpetrated on our Tohono O’odham relatives.”
Santa Cruz said that returning the land to the Tohono O’odham Nation honors Tucson’s Indigenous legacy by showing that they are still here and these lands are sacred.
Romero said during the session that the City of Tucson has an excellent opportunity to become a city that would dare take this step and do the right thing of putting this land into the hands of the Tohono O’odham people, who are the rightful heirs.
The motion passed 6-0, and the city attorney and staff will draft a resolution for the mayor and City Council consideration and approval at an upcoming meeting. . ."
HERE IN MESA AND THE SALT RIVER VALLEY - A different story
The watery secret of ancient North America
Crisscrossing Phoenix, Arizona, are 180 miles of canals – more than twice as many as Venice and Amsterdam combined. As a native Phoenician, I've spent many hours bicycling their banks alongside joggers and fishermen casting for carp. I've joined wildlife watchers strolling the main Arizona Canal on a summer evening to watch Mexican free-tailed bats make a mass fluttering exodus from their roost. And I've chatted with long-time residents who fondly recall fashioning water skis from plywood, tying a tow rope to a pickup truck and jetting through their neighbourhoods in a spray of water and dust.
The canals deliver irrigation and drinking water throughout the metro area, allowing millions of people to live in this sun-baked desert. They are a major reason Phoenix exists, and the city's name hints at their mysterious origins.
In 1867, the city's founding father, Jack Swilling – a prospector who had fought on both sides of the Civil War – stood above the Salt River Valley and saw the remnants of irrigation channels squiggling across the landscape like stretchmarks. He realised that, centuries before, some society had farmed this desert. Soon after, Swilling began scouring out the debris-clogged ditches to bring agriculture back to the region.
Three years later, Swilling and other Anglo pioneers met to consider names for their settlement. The top contenders were Pumpkinville and Stonewall. Luckily, eccentric English adventurer "Lord" Darrell Duppa proposed a name inspired by the resurrection of the canals. "A great race once dwelt here, and another great race will dwell here in the future," he mused. "I prophesy that a new city will spring, phoenix-like, from the ruins and ashes of the old."
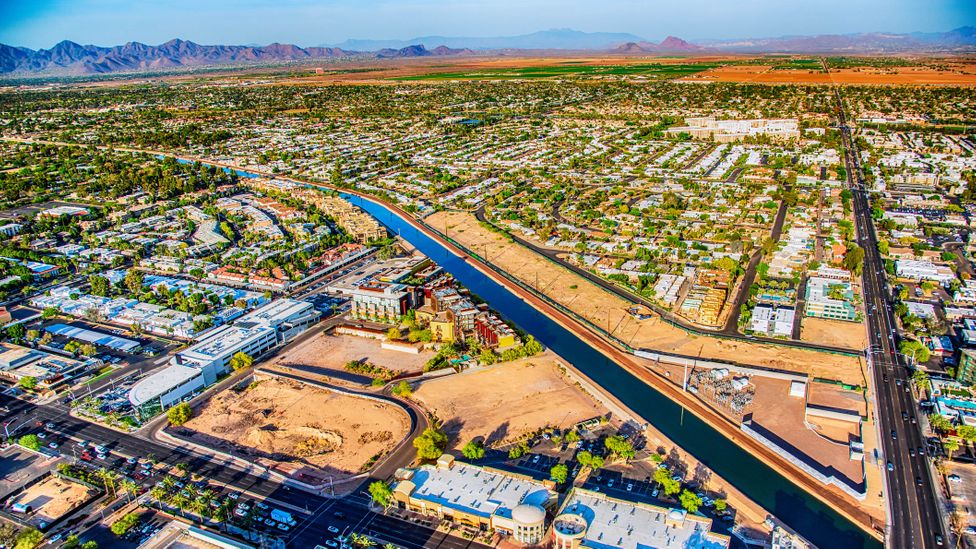

That great society was the Hohokam. Between 100 and 1450 CE, they constructed 1,000 miles of canals – the largest system of waterways in the Americas north of Peru. This sophisticated irrigation system harnessed river water and a meagre seven inches of annual rainfall and funnelled it to more than 100,000 acres of farmland. And they dug it all by hand with stones and sticks.
"The engineering is phenomenal," said Kathy Henderson, principal investigator at Desert Archaeology, an Arizona-based cultural resources management and research company. "We don't see a sequence where they start small. The canals are being built to scale as early as 500 or 600 [CE]. They must have been very attuned to how to transport water a long distance."
For Gary Huckleberry, a geologist and adjunct researcher at the University of Arizona, the water-wise Hohokam and their ancestors are still relevant today. "In the Southwest, we have some serious issues to deal with in terms of water," he said. "The Colorado River is the main source of water for the Southwest, and it's over allocated. You've got population growth and climate change. How are we going to deal with that? I think there's something to be learned by looking at past societies who managed water for thousands of years."
. . .By the 13th Century, as many as 50,000 Hohokam people lived in villages that were regularly spaced along the canal system. This suggests to archaeologists that water and irrigation land was distributed fairly equitably amongst the community.
Over the centuries, the canal system was reorganised numerous times, but its essential structure remained the same. However, after 1300, the society and the canals began to diminish, and by 1450 the population had plunged.
No one knows why. Climate may have played a role, but there's no evidence of especially intense climatic events at the time. And though some irrigation-based cultures have faced salinisation of their soils, evidence indicates the Hohokam managed salt build-up well. While archaeologists once believed the Hohokam population collapsed following a catastrophe, improved techniques now point to a very gradual decline resulting from a complicated combination of community coalescence, flooding, siltation, reduced wild food resources and conflict.
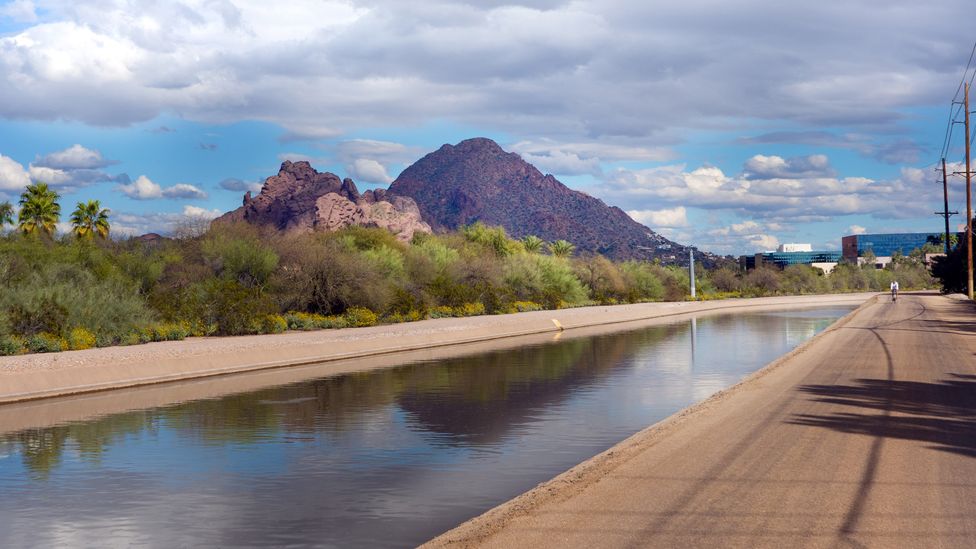

The Grand Canal is getting spruced up as part of a project to connect Phoenix's east and west suburbs in a continuous multi-use trail (Credit: BCFC/Getty Images)
Still, Huckleberry says, there's much to learn from the Hohokam and their ancestors, who utilised canal irrigation for 3,000 years. "That, to me, is the definition of sustainable," he said. "They learned how to sustainably farm, to manage water, to not destroy their soils in a way that is commendable and might give us insight into how we might deal with the current plight. I think one of the key lessons is that you don't put all your eggs in one basket; you plan for the worst, and you diversify your strategies."
The Hohokam may have stopped managing their canal system, but they did not disappear. Their story continues with their descendants, the Akimel O'odham ("River People") and Tohono O'odham ("Desert People"), who live in central and southern Arizona today.
Their legacy also lives on in the city's modern canals, many of which were constructed by retracing the Hohokam's handiwork. The Grand Canal is now getting spruced up as part of a project to connect Phoenix's east and west suburbs in a continuous multi-use trail. "Today we are integrating the canals into our communities to improve neighbourhood access, add new public art spaces and contribute to a healthier Phoenix by introducing them as a recreational amenity," announced Phoenix Mayor Kate Gallego in 2020.
The Hohokam's heritage is also preserved in one of their villages, Pueblo Grande, a museum and archaeological park where visitors can see ballcourts, a platform mound (ceremonial house) and re-created adobe houses. Hikers can search for Hohokam petroglyphs of coyotes, mountain sheep and spirals along the trails of South Mountain Preserve and Deer Valley Petroglyph Preserve. And travellers can use the A Deeper Map app to swipe right on a modern map of Phoenix and reveal the Hohokam innovations hidden beneath their feet.
But perhaps one of the Hohokam's most important legacies is less tangible: the idea that it's possible – through cooperation, commitment and shared knowledge – to live sustainably in this sun-baked desert."
Ancient Engineering Marvels is a BBC Travel series that takes inspiration from unique architectural ideas or ingenious constructions built by past civilisations and cultures across the planet.
Archeological Evidence of History Before The Pioneers
The Indians were displaced. We now only have artifacts.
To make a long story short, way too much of "Pre-History: has been white-washed by fabricated LDS attempts to make-over history. Here in Mesa we are fortunate to have more than artifacts. We can now see evidence of earlier cultures and maps like the one shown to the right of the Rio Salado Valley and a system of canals superimposed on a gridwork that permits us to locate areas of what became land claims by Mormon settlers sent from Utah to expand their Kingdom of Deseret in The New Zion.
NOTE: The Spanish word MESA on the map in Section 22.
NOTE: The Spanish word "acequias" or irrigation ditches
NOTE ALSO: The Spanish word "Pueblo" (small village or town) that marks where people are living settled on the land
_________________________________________________________________________
vb
_________________________________________________________________________
Let's tie-in a couple of loose threads to see how far-fetched the Church of Jesus Christ of the Latter-Day Saints can go to claim some unbelievable connection with The Israelites and A TALE OF TWO NATIONS.
The LDS Temple grounds here in Mesa on Main Street was designed to look like and mimic a Jewish temple in the Holy Land of Palestine to give the impression that somehow the tribes of Israel and Mormon settlers have historic roots - even claiming to have found evidence of Israelites in The New World thousands of years ago!
The opening image is taken from the Book of Mormon Archeological News http://taleof2nations.blogspot.com/2011/05/
"Illuminating the credibility of the Book of Mormon through archaeological photographs. Book of Mormon Archaeology is real, authentic, scientifically researched, a proven fact. Claims Book of Mormon Archaeology is based upon scant evidence is deception for the masses. Ancient Israelites did come to America over 2400 years ago. Here you find the photographic, archaeological, and Biblical evidences. B.O.M.A.N. reveals hard evidences Jesus did came to another ancient people besides the Jews.
RELATED CONTENT ON THIS BLOG:
Quite fortunately, we do have maps of The Salt River Valley that clearly mark the locations and sites of earlier pueblos, plazas, canals, casas and casitas, las acequias(swamps), and reservoirs and even more temples - one of which is in an area called 'Pueblo Moroni' .
____________________________________________________________________________
1  Just like a recent image shown on this blog from a press release about a "Trees For The Dead" - "Shade-and-Shelter" campaign at the Mesa City Cemetery, this site in Nogales at Kino Springs certainly looks serene.
Just like a recent image shown on this blog from a press release about a "Trees For The Dead" - "Shade-and-Shelter" campaign at the Mesa City Cemetery, this site in Nogales at Kino Springs certainly looks serene.
Other than that, adjacent to the city cemetery here in Mesa is the Mesa Country Club where some people play golf. Both are on high ground close to ancient Hohokam canals in the Salt River Valley. Kino Springs, in the Santa Cruz River Valley, has an long documented history of early settlements.
Here in Mesa - and in Tempe and Phoenix and Scottsdale - there's documentation as well for what Frank Midvale called "The Pre-Historic Irrigation of the Salt River Valley" of earlier indigenous cultures that were established for centuries before anyone recorded their versions of that history when evidence of those who were here before was "discovered" and their settlements patterns were mapped.
< Here's a closer look from a Digital Geo Map 2003 uploaded by Richard A. Neely.
Major Hohokam Irrigation Systems in the Lower Salt River Valley
The link is below if you're interested in more details.
But let's note at this point, that it was the usual practice to bury the dead on higher ground above the irrigation canals close to settlements and housing patterns.
Finding artifacts or human remains is often the result of chance - or new construction.
Research Gate
___________________________________________________________________________
2  Hohokam Human Remains Found in Arizona
Hohokam Human Remains Found in Arizona
_________________________________________________________________________________
That's the way it happened in Kino Springs on 29 Sept 2019 -
< The remains were found at the Kino Springs Golf Course, which lies near the Santa Cruz River east of Nogales.
(Google Map from report on Nogales International)
Ancient human remains found at golf course
A maintenance crew working at the Kino Springs Golf Course this week discovered human remains that authorities say date to prehistoric times.
The Santa Cruz County Sheriff’s Office received a call shortly before 11 a.m. on Tuesday from someone who said they were working on installing water pipes and came across what they believed were human remains.
Sgt. Santiago Gonzales said Sheriff’s Office personnel proceeded to take photos of the remains, and the images were then sent to the Pima County Office of the Medical Examiner for review.
“They were able to determine that the remains were prehistoric, so at this point the case is going to be referred to the Arizona Historical Museum,” Gonzales said.
The golf course is set along the north-flowing Santa Cruz River, and according to the article “Archaeological discoveries reveal value of Santa Cruz River in prehistory,” posted to the website of the University of Arizona Water Resources Research Center, the Santa Cruz River Valley is one of North America’s longest inhabited regions, with the earliest evidence of human occupation dating back 12,000 years.
“Around 4,000 prehistoric sites have been identified in the Santa Cruz watershed and exciting new discoveries continue to be made,” the article saysSource: Nogales International
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)